
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 677-682.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2023.06.003
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Tao1( ), LI Zihua2,3,4, ZHANG Cuiying2,3,4, ZHAO Wei2,3,4,*(
), LI Zihua2,3,4, ZHANG Cuiying2,3,4, ZHAO Wei2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2023-06-27
Revised:2023-11-14
Online:2023-12-30
Published:2023-12-22
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Tao, LI Zihua, ZHANG Cuiying, ZHAO Wei. Identification and analysis of host proteins in the cyst wall and cyst fluid of Echinococcus granulosus in human infection[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(6): 677-682.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2023.06.003
Fig. 3
SDS-PAGE and Western blotting analysis in the cyst wall and fluid of Echinococcus granulosus in patients A: SDS-PAGE analysis of cyst wall samples; B: SDS-PAGE analysis of cystic fluid samples; C: Western blotting analysis of full protein in cyst wall; D: Western blotting analysis of full protein in cyst fluid; E: SDS-PAGE analysis of the whole protein of the cyst wall; F: SDS-PAGE analysis of whole protein in cyst fluid. M: Protein marker; 1-10: Samples from each group; ALB: albumin; IgG H: Immunoglobulin G heavy chain; IgG L: Immunoglobulin G light chain.
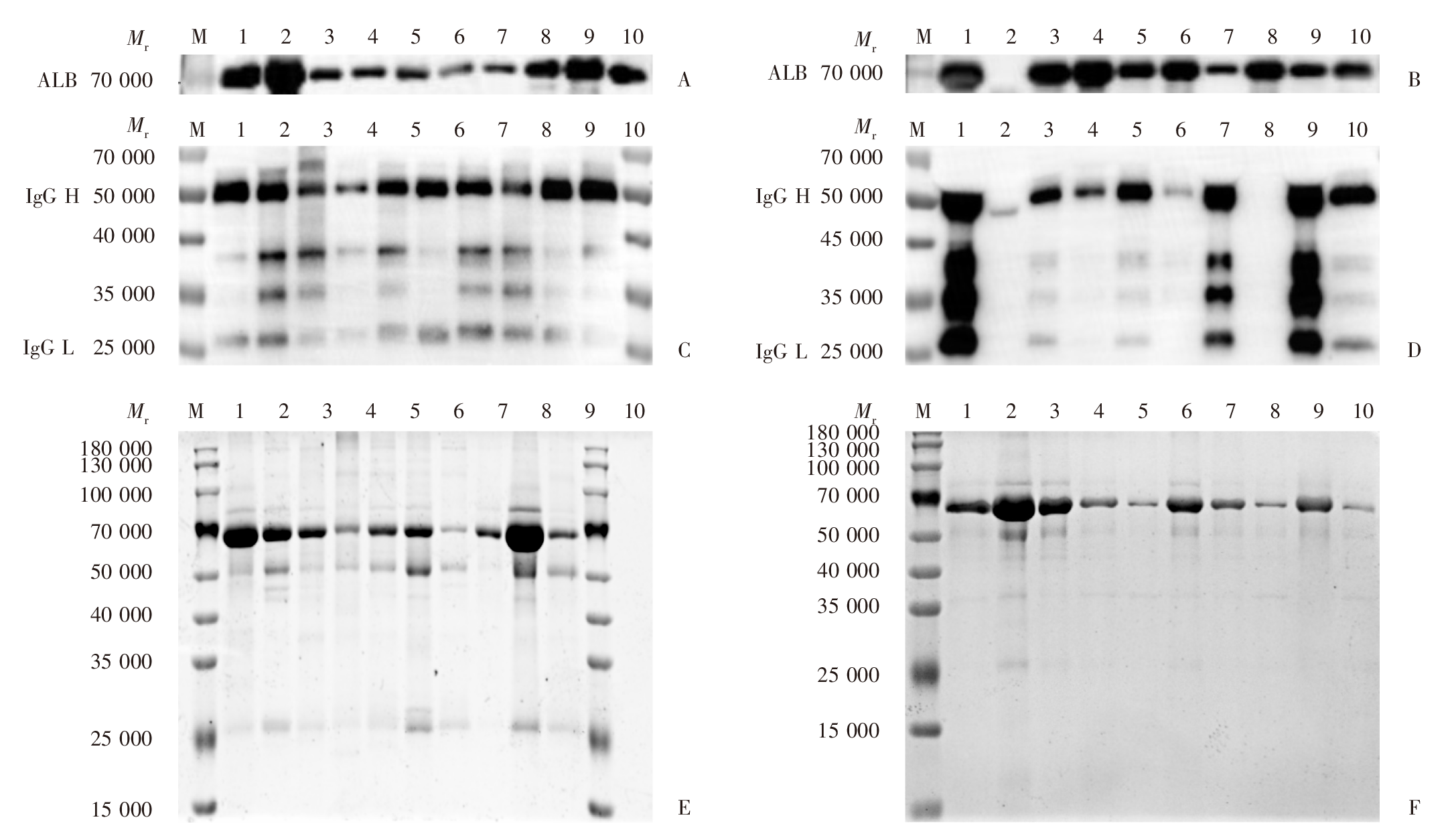
Table 1
Comparison of biochemical analysis results between patient’s serum and cyst fluid of Echinococcus granulosus
| 项目 Project | 囊液 Cyst fluid | 血清 Serum | t值 t values | P值 P values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 渗透压/mOsm Osmotic pressure/mOsm | 313.50 ± 73.33 | 301.59 ± 6.20 | 0.52 | > 0.05 |
| Na+浓度/mmol·L-1 Na+ concentration/mmol·L-1 | 143.40 ± 25.61 | 141.43 ± 2.42 | 0.24 | > 0.05 |
| K+浓度/mmol·L-1 K+ concentration/mmol·L-1 | 5.53 ± 0.86 | 3.92 ± 0.33 | 5.56 | < 0.05 |
| Cl-浓度/mmol·L-1 Cl- concentration/mmol·L-1 | 101.56 ± 12.42 | 105.35 ± 3.75 | 0.92 | > 0.05 |
| 葡萄糖浓度/mmol·L-1 Glucose concentration/mmol·L-1 | 3.07 ± 2.61 | 4.65 ± 0.26 | 1.91 | > 0.05 |
| 白蛋白浓度/g·L-1 Albumin concentration/g·L-1 | 0.57 ± 0.46 | 39.42 ± 2.77 | 43.71 | < 0.05 |
| 胆固醇浓度/mmol·L-1 Cholesterol concentration/mmol·L-1 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 3.79 ± 1.53 | 7.74 | < 0.05 |
| [1] | Wu WP, Wang H, Wang Q, et al. A nationwide sampling survey on echinococcosis in China during 2012—2016[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018, 36(1): 1-14. (in Chinese) |
| (伍卫平, 王虎, 王谦, 等. 2012—2016年中国棘球蚴病抽样调查分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018, 36(1): 1-14.) | |
| [2] | Wu WP. Prevalence and distribution of two types of echinococcosis in China[J]. China Anim Heath, 2017, 19(7): 7-9. (in Chinese) |
| (伍卫平. 我国两型包虫病的流行与分布情况[J]. 中国动物保健, 2017, 19(7): 7-9.) | |
| [3] | Kui Y, Xue CZ, Wang X, et al. Progress of echinococcosis control in China, 2021[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2023, 41(2): 142-148. (in Chinese) |
| (蒉嫣, 薛垂召, 王旭, 等. 2021年全国棘球蚴病防治进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2023, 41(2): 142-148.) | |
| [4] | Zhao R, Dong F, Zhao YQ, et al. Analysis of current status and influencing factors of echinococcosis infection among rural residents in three counties of Ningxia in 2018[J]. J Ningxia Med Univ, 2020, 42(8): 795-798. (in Chinese) |
| (赵瑞, 董飞, 赵殷奇, 等. 2018年宁夏三县区农村居民包虫病感染现况及影响因素分析[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2020, 42(8): 795-798.) | |
| [5] |
Tsai IJ, Zarowiecki M, Holroyd N, et al. The genomes of four tapeworm species reveal adaptations to parasitism[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7443): 57-63.
doi: 10.1038/nature12031 |
| [6] | Pan WQ, Tang LH. Molecular parasitology[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2004. (in Chinese) |
| (潘卫庆, 汤林华. 分子寄生虫学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2004.) | |
| [7] | Wang XY, Hu W, Zhang W. Ultrastructural study on the endogenous hair follicle of Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Qinghai Med J, 1995, 25(2): 1-2. (in Chinese) |
| (汪晓筠, 王虎, 张伟. 细粒棘球蚴内生发囊的超微结构研究[J]. 青海医药杂志, 1995, 25(2): 1-2.) | |
| [8] |
Hustead ST, Williams JF. Permeability studies on taenid metacestodes: I. Uptake of proteins by larval stages of Taenia taeniaeformis, T. crassiceps, and Echinococcus granulosus[J]. J Parasitol, 1977, 63(2): 314-321.
pmid: 67206 |
| [9] |
Machnicka B, Grzybowski J. Host serum proteins in Taenia saginata metacestode fluid[J]. Vet Parasitol, 1986, 19(1/2): 47-54.
doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(86)90031-2 |
| [10] |
Hayunga EG, Sumner MP, Letonja T. Evidence for selective incorporation of host immunoglobulin by strobilocerci of Taenia taeniaeformis[J]. J Parasitol, 1989, 75(4): 638-642.
pmid: 2760776 |
| [11] |
Aldridge JR Jr, Jennette MA, Kuhn RE. Uptake and secretion of host proteins by Taenia crassiceps metacestodes[J]. J Parasitol, 2006, 92(5): 1101-1102.
doi: 10.1645/GE-835R.1 pmid: 17152958 |
| [12] |
Zheng YD. Proteomic analysis of Taenia hydatigena cyst fluid reveals unique internal microenvironment[J]. Acta Trop, 2017, 176: 224-227.
doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.08.015 |
| [13] |
Liu CS, Cao JP, Zhang HB, et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by Echinococcus multilocularis: important players in angiogenesis promotion[J]. Microbes Infect, 2023, 25(7): 105147.
doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2023.105147 |
| [14] |
Nicolao MC, Rodrigues CR, Coccimiglio MB, et al. Characterization of protein cargo of Echinococcus granulosus extracellular vesicles in drug response and its influence on immune response[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2023, 16(1): 255.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05854-6 |
| [15] |
Ahn CS, Kim JG, Han XM, et al. Comparison of Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus granulosus hydatid fluid proteome provides molecular strategies for specialized host-parasite interactions[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(57): 97009-97024.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v8i57 |
| [16] |
Monteiro KM, de Carvalho MO, Zaha A, et al. Proteomic analysis of the Echinococcus granulosus metacestode during infection of its intermediate host[J]. Proteomics, 2010, 10(10): 1985-1999.
doi: 10.1002/pmic.200900506 pmid: 20217864 |
| [17] | The Surgical Professional Committee of Hydatid Disease of the Surgical Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of liver two types of echinococcosis(2019)[J]. Chin J Digest Surg, 2019, 18 (8): 711 -721. |
| 中国医师协会外科医师分会包虫病外科专业委员会. 肝两型包虫病诊断与治疗专家共识(2019版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2019, 18(8): 711-721.) | |
| [18] |
Liu F, Hu W, Cui SJ, et al. Insight into the host-parasite interplay by proteomic study of host proteins copurified with the human parasite, Schistosoma japonicum[J]. Proteomics, 2007, 7(3): 450-462.
doi: 10.1002/pmic.v7:3 |
| [19] |
van Hellemond JJ, Retra K, Brouwers JF, et al. Functions of the tegument of schistosomes: clues from the proteome and lipidome[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2006, 36(6): 691-699.
pmid: 16545817 |
| [20] | Tielens AGM, van Hellemond JJ. Unusual aspects of metabolism in flatworm parasites[J]. Parasit Flatworms, 2006: 387-407. |
| [21] | Brehm K, Koziol U. Echinococcus-host interactions at cellular and molecular levels[J]. Adv Parasitol, 2017, 95: 147-212. |
| [22] | Peón AN, Espinoza-Jiménez A, Terrazas LI. Immunoregulation by Taenia crassiceps and its antigens[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2013, 2013: 498583. |
| [23] |
McSorley HJ, Hewitson JP, Maizels RM. Immunomodulation by helminth parasites: defining mechanisms and mediators[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2013, 43(3/4): 301-310.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2012.11.011 |
| [24] |
Damian RT. The exploitation of host immune responses by parasites[J]. J Parasitol, 1987, 73(1): 3-13.
pmid: 3553518 |
| [25] |
Schroeder H, Skelly PJ, Zipfel PF, et al. Subversion of complement by hematophagous parasites[J]. Dev Comp Immunol, 2009, 33(1): 5-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.07.010 pmid: 18762211 |
| [26] |
Kouoh F, Gressier B, Luyckx M, et al. Antioxidant properties of albumin: effect on oxidative metabolism of human neutrophil granulocytes[J]. Farmaco, 1999, 54(10): 695-699.
pmid: 10575739 |
| [27] |
Silva-Álvarez V, Folle AM, Ramos AL, et al. Echinococcus granulosus antigen B: a hydrophobic ligand binding protein at the host-parasite interface[J]. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 2015, 93: 17-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2014.09.008 pmid: 25451555 |
| [1] | LU Junxia, XU Junying, ZHAO Bin, WANG Qianwen, LI Wenhua, GENG Yuqing, HOU Jun, WU Xiangwei, CHEN Xueling. Echinococcus granulosus infection induces macrophages to express CD73 and A2AR to suppress inflammatory response [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 559-566. |
| [2] | WU Xiaoying, HU Yuan, CAO Jianping. Preparation of Echinococcus granulosus peptide embedded in chitosan quaternary ammonium salt nanoparticles [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 300-305. |
| [3] | LI Benfu, WANG Zhengqing, XU Qian, ZI Jinrong, YAN Xinliu, PENG Jia, LI Jianxiong, CAI Xuan, WU Fangwei, YANG Yaming. Sequence analysis of mitochondrial co1 and nd1 genes in Echinococcus granulosus in Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 306-311. |
| [4] | GUO Gang, REN Yuan, JIAO Hongjie, WU Juan, GUO Baoping, QI Wenjing, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao. Effect of intraperitoneal inoculation with Echinococcus microcysts on the infection and pathogenicity of E. multilocularis in mouse liver [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 156-162. |
| [5] | JIAO Hongjie, QI Wenjing, GUO Gang, BAO Jianling, WU Chuanchuan, SONG Chuanlong, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao, YAN Mei. Polarization effect of Echinococcus granulosus antigen B on the mouse macrophage RAW264.7 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 23-28. |
| [6] | WU De-fang, FU Yong, REN Bin, ZHANG Yao-gang, XU Xiao-lei, PANG Ming-quan, FAN Hai-ning. Genetic diversity and differentiation time of human isolates of Echinococcus granulosus and E. multilocularis from Qinghai [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 610-615. |
| [7] | QIAO Shi-yuan, ZHOU Xue, LIU Cheng-hao, JIANG Hui-jiao, BU Yuan-yuan, CHEN Xue-ling, WU Xiang-wei. Effect of albendazole-loaded vesicles on the vitality of protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 324-329. |
| [8] | SUN Ye-ting, JIANG Nan, JIANG Yan-yan, LI Teng, JIANG Xiao-feng, CAO Jian-ping, SHEN Yu-juan. Study on the polarization of MDSC stimulated by Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex-derived exosomes in vitro [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 175-180. |
| [9] | ZHOU Wen-zheng, SUN Jun-gang, ZHAO Xi-bin, CAO Li. Therapeutic effect of intensity modulated radiation therapy on secondary femur infection with Echinococcus granulosus in rats [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 443-448. |
| [10] | TIAN Meng-xiao, ZANG Xiao-yan, GUO Gang, QI Wen-jing, GUO Bao-ping, REN Yuan, LI Jun, ZHANG Wen-bao. Expression and activity assay of serine protease in Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 233-239. |
| [11] | FAN Jun-jie, HAN Xiu-min, Nur Fazleen Binti Idris, LI Kai, TAN Qing-qing, CAO Wen-qiao, LI Xiang, LIAO Peng, YE Bin. Bioinformatics characteristics and immunoreactivity of protein kinase A of Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 682-687. |
| [12] | SHI Chun-li, YANG Hui, PAN Wen, ZHANG Xin, ZHU Xiao-ting, ZHAO Jia-qing. Proteomic analysis of human proteins in extracellular vesicles secreted by protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 695-701. |
| [13] | YU Xiao-dong, YALI Ya-sen, WANG Jia-ling, LI Meng, YE Jian-rong. Establishment of BALB/c mouse model of Echinococcus granulosus-induced sensitization and changes of related immune cells [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(4): 412-416. |
| [14] | LI Zhi-dan, ZHANG Wei, WANG Xiao-ling, XU Bin, HU Wei. Effects of Schistosoma japonicum infection on OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation in mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 271-278. |
| [15] | CAO Sheng-kui, ZHANG Xiao-fan, WEI Yu-huan, PAN Jia-ming, CAO Jian-ping, SHEN Yu-juan, CHEN Jia-xu. Expression and function of arginase in livers of mice infected with Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 304-309. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||