
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 156-162.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2023.02.005
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
GUO Gang1,2( ), REN Yuan1, JIAO Hongjie3, WU Juan4, GUO Baoping1, QI Wenjing1, LI Jun1, ZHANG Wenbao1,*(
), REN Yuan1, JIAO Hongjie3, WU Juan4, GUO Baoping1, QI Wenjing1, LI Jun1, ZHANG Wenbao1,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-11
Revised:2022-11-19
Online:2023-04-30
Published:2023-05-10
Contact:
ZHANG Wenbao
E-mail:guog@foxmail.com;wenbaozhang2013@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
GUO Gang, REN Yuan, JIAO Hongjie, WU Juan, GUO Baoping, QI Wenjing, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao. Effect of intraperitoneal inoculation with Echinococcus microcysts on the infection and pathogenicity of E. multilocularis in mouse liver[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 156-162.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2023.02.005
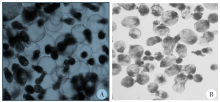
Fig. 1
Morphology of cultured protoscoleces to microcysts of E. granulosus and E. multilocularis in vitro respectively (× 40) A: E. granulosus protoscoleces cultured in vitro for 6 weeks, most of the rostellum has disappeared and PSCs developed into cysts; B: E. multilocularis cultured in vitro for 8 weeks, PSCs developed into cysts which is slightly smaller, while the rostellum has not disappeared completely.
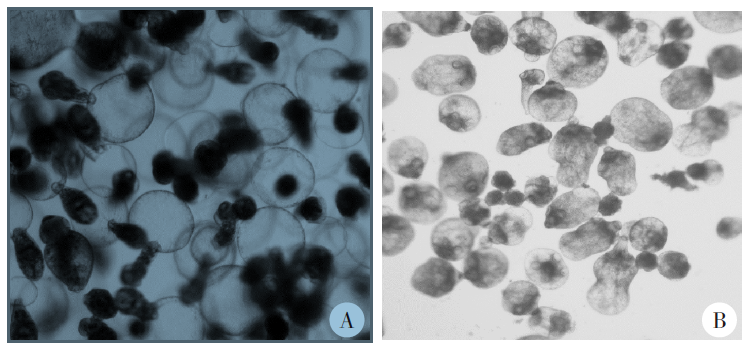
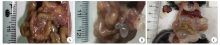
Fig. 3
Growth of cysts after intraperitoneal infection with Echinococcus granulosus microcapsules in mice of Eg/Em infected group A:After 2, 4, and 7 months of intraperitoneal infection with Echinococcus granulosus microcapsules in mice of Eg/Em infected group, the cysts continued to grow as the infection progressing.
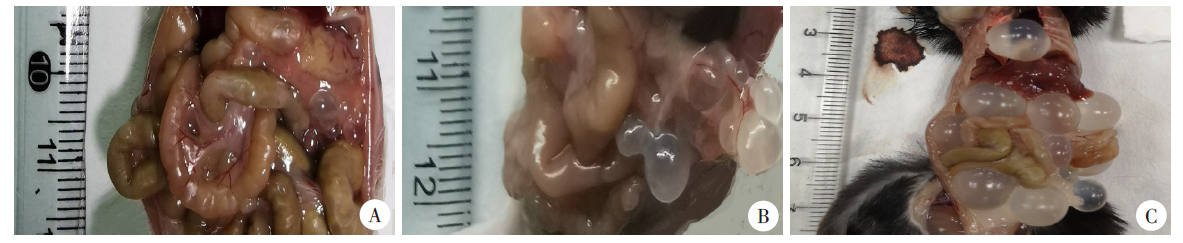
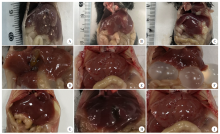
Fig. 4
Hepatic lesions of mice in each group after hepatic portal vein infection with E. multilocularis protoscolex A-C: 1, 3, and 6 months after hepatic portal vein infection with the protoscolex of E. multilocularis, the liver lesions of mice in the Em liver infection group were more serious, with dozens of vesicular lesions; D-F: 1, 3, and 6 months after hepatic portal vein infection with the protoscolex of E. multilocularis, the liver lesions of mice in the Eg/Em infection group were mild or no lesions, G-I: 1, 3, and 6 months after hepatic portal vein infection with the protoscolex of E. multilocularis, the liver in the Em/Em infection group and the sham operation group had no lesions.
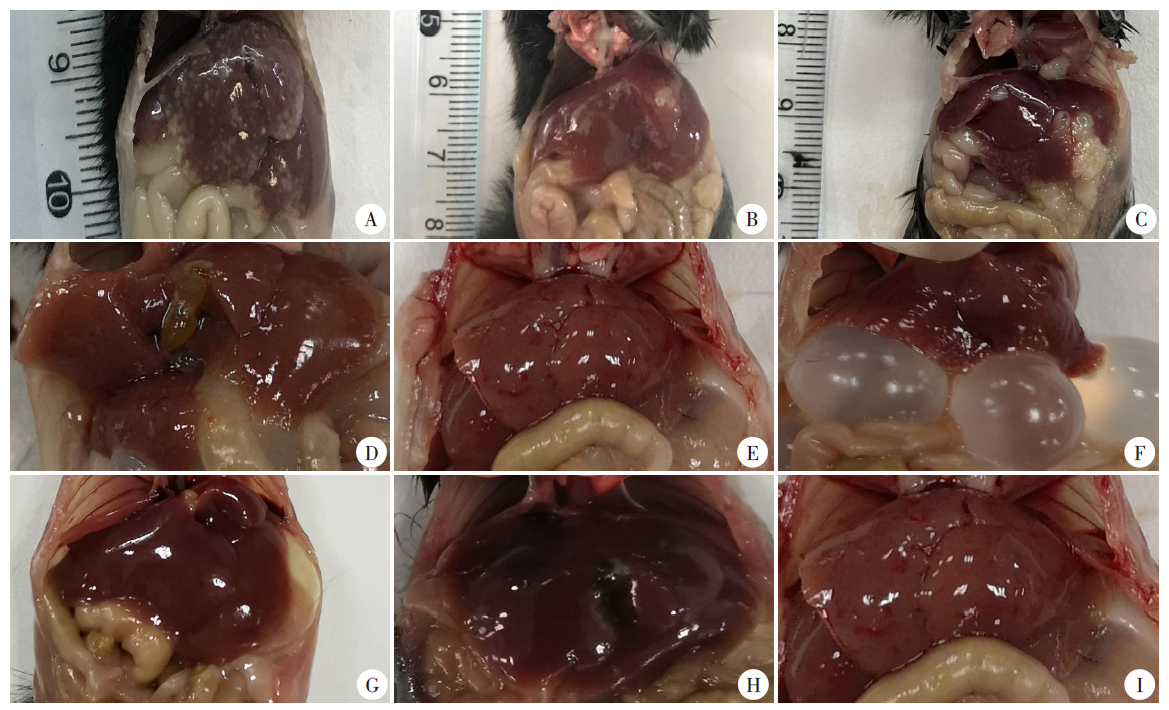
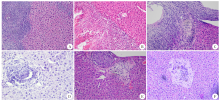
Fig. 5
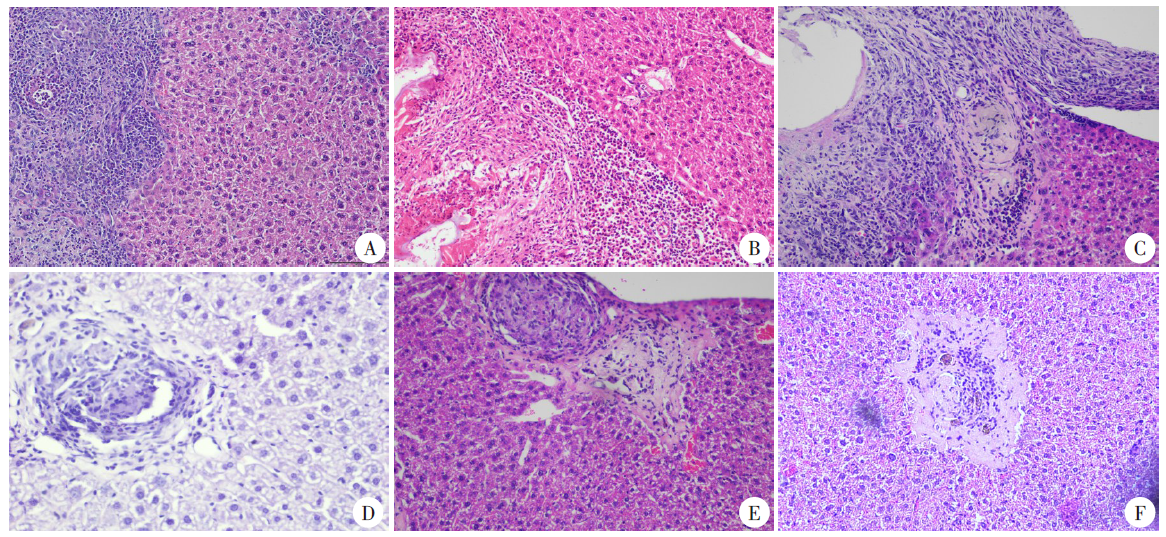
Pathological changes in the mice liver of different groups infected with Em protoscoleces through hepatic portal vein (HE staining, × 200) A-C: The Em liver infection group, a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrated 1 month after hepatic portal vein infection with the protoscolex of E. multilocular (A), inflammatory cells were relatively reduced compared with the previous period and more neutrophils were present at 3 months after infection (B),and the lesions were accompanied by a large number of connective tissue hyperplasia 6 months later (C); D-F: The Eg/Em infection group, the inflammatory infiltration of the lesions was less one month after the hepatic portal vein was infected with the protoscolex of E. multilocular (D), hyperplasia of collagen fibres was predominant around the lesion at 3 months after infection (E),and the lesions in the near recovery period could be seen six months later (F).
| [1] | Han S, Kui Y, Xue CZ, et al. The endemic status of echinococcosis in China from 2004 to 2020[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2022, 40(4): 475-480. (in Chinese) |
| (韩帅, 蒉嫣, 薛垂召, 等. 2004—2020年全国棘球蚴病疫情分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(4): 475-480.) | |
| [2] | Zheng CJ, Yang L, Zhang GJ, et al. Interpretation of technical scheme for echinococcosis control (edition 2019)[J]. J Trop Dis Parasitol, 2020, 18(4): 193-196, 201. (in Chinese) |
| (郑灿军, 杨柳, 张光葭, 等. 《包虫病防治技术方案(2019年版)》解读[J]. 热带病与寄生虫学, 2020, 18(4):193- 196, 201.) | |
| [3] |
Pohnan R, Ryska M, Hytych V, et al. Echinococcosis mimicking liver malignancy: a case report[J]. Int J Surg Case Rep, 2017, 36: 55-58.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2017.04.032 |
| [4] |
Siles-Lucas M, Casulli A, Cirilli R, et al. Progress in the pharmacological treatment of human cystic and alveolar echinococcosis: compounds and therapeutic targets[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2018, 12(4): e0006422.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006422 |
| [5] |
Yang C, He JY, Yang XW, et al. Surgical approaches for definitive treatment of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: results of a survey in 178 patients[J]. Parasitology, 2019, 146(11): 1414-1420.
doi: 10.1017/S0031182019000891 pmid: 31267889 |
| [6] |
Larrieu E, Herrero E, Mujica G, et al. Pilot field trial of the EG95 vaccine against ovine cystic echinococcosis in Rio Negro, Argentina: early impact and preliminary data[J]. Acta Trop, 2013, 127(2): 143-151.
doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.04.009 pmid: 23632258 |
| [7] |
Zhang WB, Li J, You H, et al. Short report: Echinococcus granulosus from Xinjiang, PR China: cDNAS encoding the EG95 vaccine antigen are expressed in different life cycle stages and are conserved in the oncosphere[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2003, 68(1): 40-43.
doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2003.68.40 |
| [8] |
Bowles J, Blair D, McManus DP. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing[J]. Mol Biochem Parasitol, 1992, 54(2): 165-173.
doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90109-W |
| [9] |
Nakao M, Xiao N, Okamoto M, et al. Geographic pattern of genetic variation in the fox tapeworm Echinococcus multilocularis[J]. Parasitol Int, 2009, 58(4): 384-389.
doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2009.07.010 |
| [10] |
Alvarez Rojas CA, Kronenberg PA, Aitbaev S, et al. Genetic diversity of Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato in Kyrgyzstan: the A2 haplotype of E. multilocularis is the predominant variant infecting humans[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2020, 14(5): e0008242.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008242 |
| [11] | Shang JY, Zhang GJ, Yu WJ, et al. Genetic polymorphism of Echinococcus multilocularis in northwestern China inferred from cox1 gene sequences[J]. J Pathog Biol, 2021, 16(2): 137-142. (in Chinese) |
| (尚婧晔, 张光葭, 喻文杰, 等. 中国西北部地区多房棘球绦虫cox1基因多态性研究[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2021, 16(2): 137-142.) | |
| [12] |
Konyaev SV, Yanagida T, Ingovatova GM, et al. Molecular identification of human echinococcosis in the Altai region of Russia[J]. Parasitol Int, 2012, 61(4): 711-714.
doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2012.05.009 pmid: 22609955 |
| [13] |
Laurimäe T, Kronenberg PA, Alvarez Rojas CA, et al. Long-term (35 years) cryopreservation of Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes[J]. Parasitology, 2020, 147(9): 1048-1054.
doi: 10.1017/S003118202000075X pmid: 32364108 |
| [14] | Liu HD, Wang HB, Fan HN, et al. Alveolar echinococcosis and immune evasion[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018, 36(6): 655-660. (in Chinese) |
| (刘寒冬, 王宏宾, 樊海宁, 等. 多房棘球蚴病的免疫逃避机制[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018, 36(6): 655-660.) | |
| [15] | Zhang LH, Chen G, Chong SG, et al. Research progress on the immune regulation mechanism in alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2022, 40(1): 109-113, 120. (in Chinese) |
| (张伶慧, 陈根, 种世桂, 等. 多房棘球蚴病中免疫细胞调控机制的研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(1): 109-113, 120.) | |
| [16] |
Zheng HJ, Zhang WB, Zhang L, et al. The genome of the hydatid tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Nat Genet, 2013, 45(10): 1168-1175.
doi: 10.1038/ng.2757 |
| [17] |
Tsai IJ, Zarowiecki M, Holroyd N, et al. The genomes of four tapeworm species reveal adaptations to parasitism[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7443): 57-63.
doi: 10.1038/nature12031 |
| [18] | Guo BP. Study on correlation between pathogenic differences and mitochondrial genetic markers in Echinococcus multilocularis[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2019: 29-97. (in Chinese) |
| (郭宝平. 多房棘球绦虫致病差异与线粒体遗传标志相关性的研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2019: 29-97.) | |
| [19] | Shang JY, Zhang GJ, Yu WJ, et al. Advances in researches on the genetic diversity of Echinococcus multilocularis[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2020, 38(5): 637-641, 646. (in Chinese) |
| (尚婧晔, 张光葭, 喻文杰, 等. 多房棘球绦虫遗传多态性研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2020, 38(5): 637-641, 646.) | |
| [20] | Yin J. Clinical characteristics of patients with hepatic alveolar hydatid and cystic echinococcosis mixed infection[D]. Xining: Qinghai University, 2019: 36-44. (in Chinese) |
| (尹杰. 肝泡型合并囊型包虫混合感染患者的临床特点分析[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2019: 36-44.) |
| [1] | XUE Yushan, LIN Ping, CHENG Xunjia, FENG Meng. Damage caused by chronic infection of Toxoplasma gondii on the host central nervous system and its mechanism [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 527-531. |
| [2] | GUO Shuai, HE Biao, GAO Yuanli, FAN Yongling, ZHU Feng, DING Yan, LIU Taiping, XU Wenyue. Specie-specific analysis of plasmodia infecting rats and mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 539-545. |
| [3] | LU Junxia, XU Junying, ZHAO Bin, WANG Qianwen, LI Wenhua, GENG Yuqing, HOU Jun, WU Xiangwei, CHEN Xueling. Echinococcus granulosus infection induces macrophages to express CD73 and A2AR to suppress inflammatory response [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 559-566. |
| [4] | LIU Wenhu, HUANG Ming, LIANG Jin, LIU Jianxiong, WEN Zhaomeng, MA Shaobo. A case of ventricular cysticercosis complicated with hydrocephalus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 644-646. |
| [5] | ZHANG Li, MIAO Feng, SHEN Yanmei. A case of Capillaria hepatica infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 650-652. |
| [6] | LI Xiaoli, LI Shaogang, WU Zhaoyong. Clinical characteristics of patients with intestinal Diphyllobothrium tapeworm infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 459-463. |
| [7] | ZHENG Yuhua, TIE Ping, BAI Yongfei, YAN Changfu, WANG Ting, WANG Jingying, TIAN Xiaodong, DAI Peifang. Investigation on visceral leishmaniasis in domestic dogs and sandfly density in epidemic area in Shanxi Province from 2021 to 2022 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 470-475. |
| [8] | LI Yuqiong, YU Youli, GAO Junrong, LIU Yunyun, LI Hongbing, NIU Xiaohao. Enterocytozoon bieneusi infection in dairy cows and its genotype identification in Yinchuan area of Ningxia Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 476-479. |
| [9] | WANG Feng, WU Fan, LI Linlin, HUANG Qingqing. Prevalence of parasitic infections in wild mice in Wuhu City, Anhui Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 516-519. |
| [10] | ZHU Canmin, PENG Weijian, WANG Dili, ZHOU Huajing, JIN Qiangjian, CHANG Chang. A case of acute primary amoebic meningoencephalitis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 524-526. |
| [11] | WU Xiaoying, HU Yuan, CAO Jianping. Preparation of Echinococcus granulosus peptide embedded in chitosan quaternary ammonium salt nanoparticles [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 300-305. |
| [12] | LI Benfu, WANG Zhengqing, XU Qian, ZI Jinrong, YAN Xinliu, PENG Jia, LI Jianxiong, CAI Xuan, WU Fangwei, YANG Yaming. Sequence analysis of mitochondrial co1 and nd1 genes in Echinococcus granulosus in Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 306-311. |
| [13] | ZHANG Mizhen, HUANG Jilei, ZHU Huihui, ZHOU Changhai, ZHU Tingjun, QIAN Menbao, CHEN Yingdan, LI Shizhu. Epidemiological analysis of soil-transmitted nematode infections in China in 2020 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 331-335. |
| [14] | LI Chang, DU Xinyue, YAN Min, WANG Zhaojun. Research advances on the role and mechanism of neutrophil extracellular traps in parasitic infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 219-222. |
| [15] | ZHENG Dan, LIN Chenxin, CAI Wuwei, XIE Hangguo. Investigation of Anisakis spp. infection in marine fish in Fujian Province, 2019—2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 238-240. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||