
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 771-778.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2021.06.007
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
HOU Jiao1( ), WEN Hao1, WANG Ming-kun2, LI Wen-ding1, LI liang1, LI Jing2, ZHANG Chuan-shan1,2, WANG Hui1,2,*(
), WEN Hao1, WANG Ming-kun2, LI Wen-ding1, LI liang1, LI Jing2, ZHANG Chuan-shan1,2, WANG Hui1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-04-14
Revised:2021-05-28
Online:2021-12-30
Published:2021-12-05
Contact:
WANG Hui
E-mail:houj526@163.com;wangh0923@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
HOU Jiao, WEN Hao, WANG Ming-kun, LI Wen-ding, LI liang, LI Jing, ZHANG Chuan-shan, WANG Hui. Changes of macrophage subsets and polarization in spleen of mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 771-778.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2021.06.007
Table 1
Primers for real-time quantitative PCR of macrophage polarization genes
| 引物 Primer | NCBI基因 ID NCBI Gene ID | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequence (5′→3′) | 片段长度/bp Fragment length/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β-F | 16176 | CCTCGTGCTGTCGGACCCATA | 344 |
| IL-1β-R | CAGGCTTGTGCTCTGCTTGTGA | ||
| IFN-γ-F | 15978 | TAGCCAAGACTGTGATTGCGG | 159 |
| IFN-γ-R | AGACATCTCCTCCCATCAGCAG | ||
| CXCL11-F | 56066 | GAACAGGAAGGTCACAGCCATAGC | 180 |
| CXCL11-R | TCAACTTTGTCGCAGCCGTTACTC | ||
| CCR7-F | 12775 | TGTACGAGTCGGTGTGCTTC | 162 |
| CCR7-R | GGTAGGTATCCGTCATGGTCTTG | ||
| CD86-F | 12524 | CTGGACTCTACGACTTCACAATG | 131 |
| CD86-R | AGTTGGCGATCACTGACAGTT | ||
| MRC1-F | 17533 | CATGAGGCTTCTCCTGCTTCT | 143 |
| MRC1-R | TTGCCGTCTGAACTGAGATGG | ||
| Retnla-F | 57262 | GGTCCCAGTGCATATGGATGAGA-CCATAGA | 296 |
| Retnla-R | CACCTCTTCACTCGAGGGACAGTT-GGCAGC | ||
| ARG1-F | 11846 | CAGAAGAATGGAAGAGTCAG | 250 |
| ARG1-R | CAGATATGCAGGGAGTCACC | ||
| GAPDH-F | 14433 | GATGCAGGGATGATGTTCTG | 106 |
| GAPDH-R | GTGAAGGTCGGTAACGG |
Fig. 1
Spleen weight, spleen coefficient and number of spleen lymphocytes in mice at different time points after infection with E. multilocularis protoscoleces A: Spleen weight; B: Spleen coefficient; C: Number of splenic lymphocytes. 1: Control group; 2: Mild infection group; 3: Moderate infection group; 4: Heavy infection group. a, P < 0.05; b, P < 0.01.
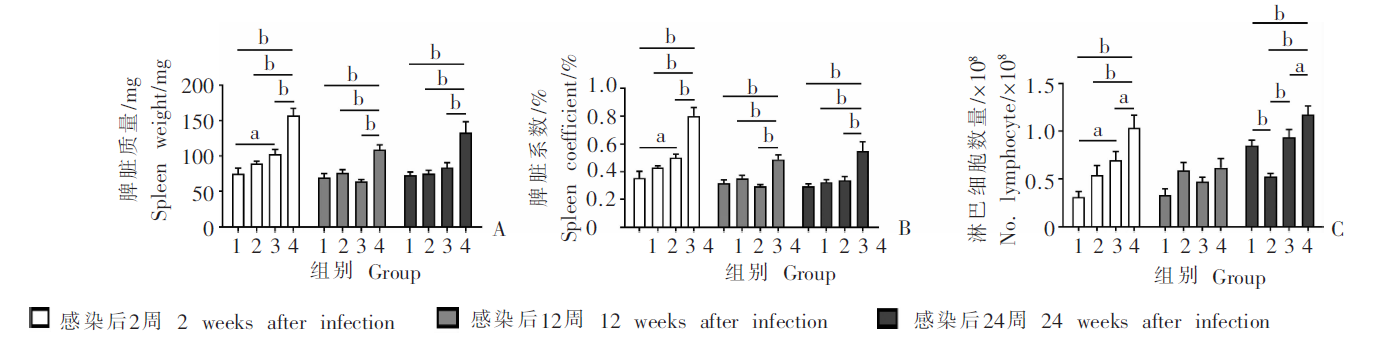
Fig. 2
Changes in the proportion and number of splenic macrophages at different time points in mice infected with E. multilocularis protoscoleces A: Representative diagram of flow cytometry analysis; B: Proportion of macrophage in spleen; C: Number of splenic macrophages. 1: Control group; 2: Mild infection group; 3: Moderate infection group; 4: Heavy infection group. a, P < 0.05 ; b, P < 0.01.
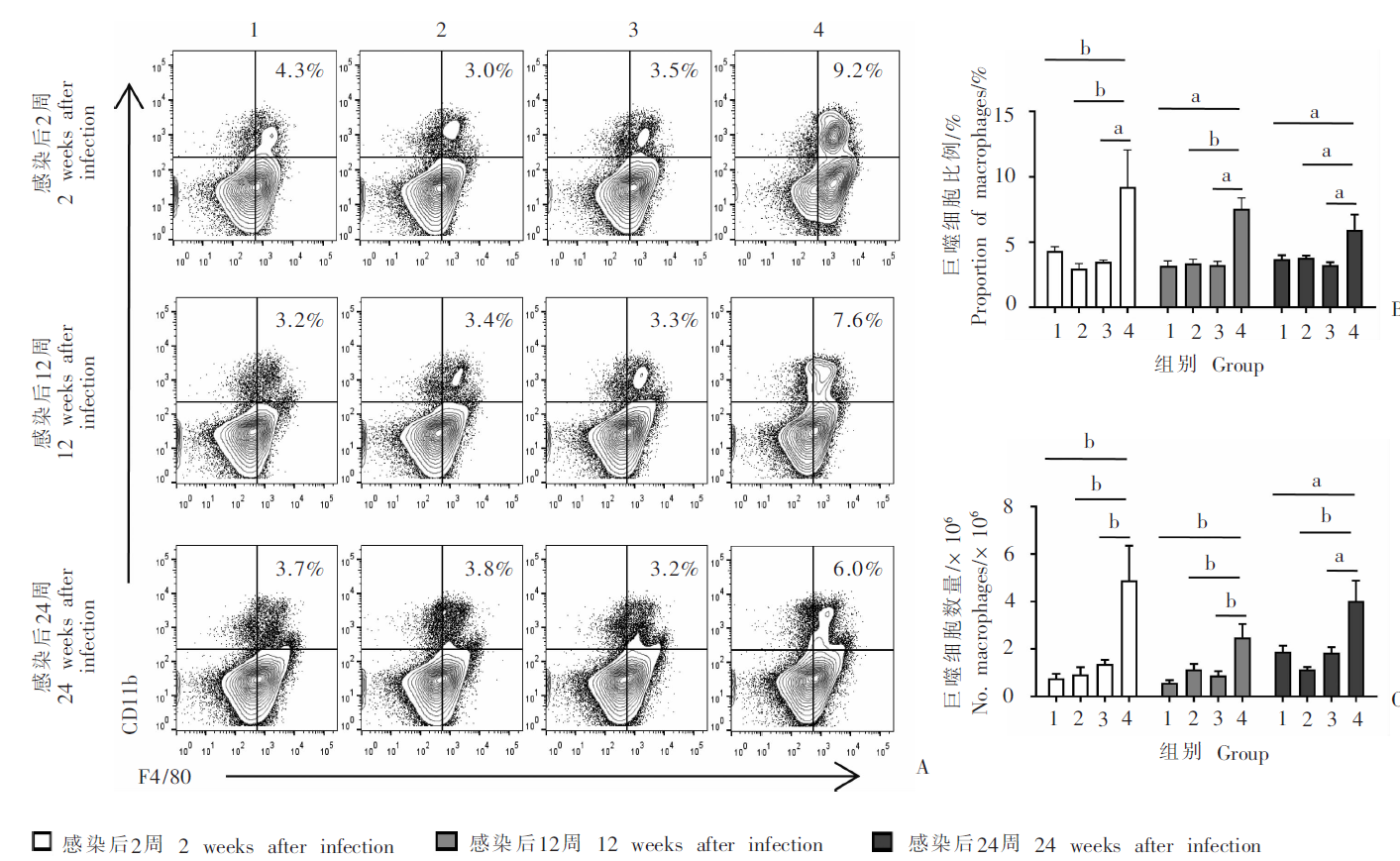
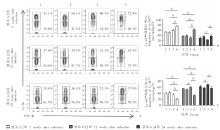
Fig. 3
Changes of Ly-6Chigh and Ly-6Clow macrophage subsets in spleen of mice infected with E. multilocularis protoscoleces at different time points A: Representative diagram of flow cytometry analysis; B,C: Proportion of Ly-6Chigh and Ly-6Clow macrophage subsets in spleen. 1: Control group; 2: Mild infection group; 3: Moderate infection group; 4: Heavy infection group. a, P < 0.05; b, P < 0.01.
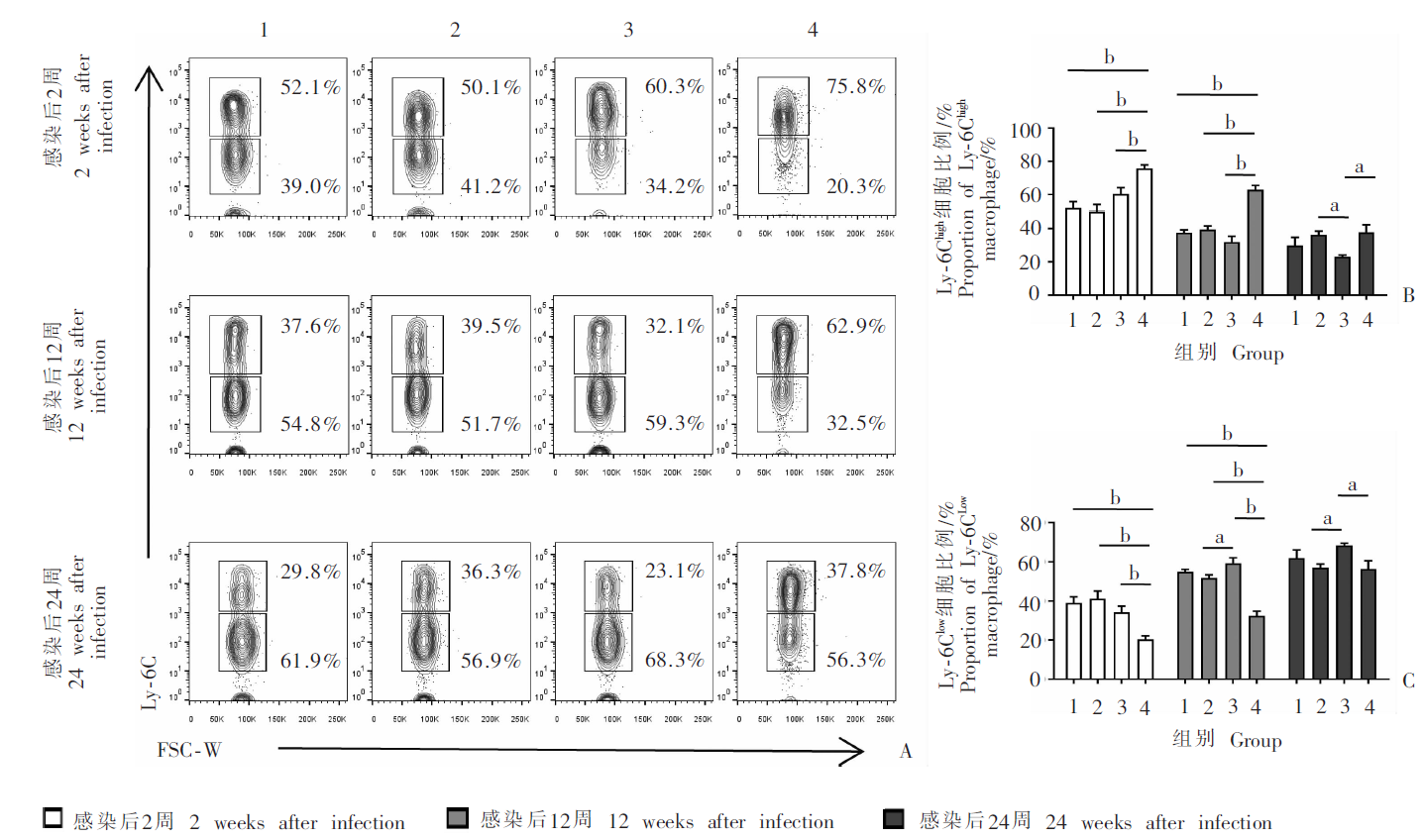
Table 2
Relative level of mRNA transcription of macrophage polarization genes in spleen of mice infected with E. multilocularis protoscoleces
| 巨噬细胞极化相关基因Macrophage polarization related gene | 感染后2周2 weeks after infection | 感染后12周12 weeks after infection | 感染后24周 24 weeks after infection | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 低感染组 | 中感染组 | 高感染组 | 对照组 | 低感染组 | 中感染组 | 高感染组 | 对照组 | 低感染组 | 中感染组 | 高感染组 | |
| Control group | Mild infection group | Moderate infection group | Heavy infection group | Control group | Mild infection group | Moderate infection group | Heavy infection group | Control group | Mild infection group | Moderate infection group | Heavy infection group | |
| M1 | ||||||||||||
| IL-1β | 1.2 ± 0.9 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 0.7 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 1.8 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 3.4 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 4.6 ± 1.8b | 1.0 ± 1.3 | 2.8 ± 1.5 |
| IFN-γ | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 2.5 | 1.8 ± 2.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 0.9 ± 0.9 |
| CXCL11 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.6 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 2.1 | 1.6 ± 2.0 | 0.7 ± 0.8 | 0.6 ± 0.6 | 2.3 ± 3.6 | 1.9 ± 2.7 | 1.7 ± 1.0 | 6.1 ± 7.2 | 28.2 ± 36.3a |
| CCR7 | 1.1 ± 0.6 | 2.3 ± 0.7 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.2a | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 2.2 ± 1.5 | 0.7 ± 0.6 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.8 |
| CD86 | 1.3 ± 1.0 | 1.9 ± 1.1 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 2.1 ± 1.7 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1a |
| M2 | ||||||||||||
| MRC1 | 1.2 ± 0.9 | 2.1 ± 1.9 | 1.3 ± 1.1 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 1.0 ± 0.9 | 2.7 ± 2.3 | 1.9 ± 1.2 | 1.8 ± 1.5 | 2.9 ± 1.3 | 3.6 ± 3.2 | 5.2 ± 2.9a |
| Retnla | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.9 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 1.0 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 1.1 ± 0.6 | 1.6 ± 1.1 | 0.8 ± 0.8 | 0.7 ± 1.0 | 6.8 ± 5.3 | 201.8 ± 176.4b |
| ARG1 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 1.0 | 0.6 ± 0.5 | 0.7 ± 0.6 | 2.8 ± 4.8 | 2.2 ± 2.3 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 12.1 ± 28.2 | 1.2 ± 0.8 | 0.7 ± 0.6 | 5.0 ± 4.3 | 51.2 ± 69.6b |
| [1] | Wen H, Vuitton L, Tuxun T, et al. Echinococcosis: advances in the 21st century[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2019, 32(2): e00075-18. |
| [2] | Tuerhongjiang T, Shao YM, Wen H, et al. Consensus on Chinese terminology in the clinical field of echinococcosis[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2021, 39(1): 76-84. (in Chinese) |
| (吐尔洪江·吐逊, 邵英梅, 温浩, 等. 棘球蚴病临床领域相关中文专业术语专家共识[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(1): 76-84.) | |
| [3] | Wang TP, Cao ZG. Current status of echinococcosis control in China and the existing challenges[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018, 36(3): 291-296. (in Chinese) |
| (汪天平, 操治国. 中国棘球蚴病防控进展及其存在的问题[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018, 36(3): 291-296.) | |
| [4] | Abudusalamu A, Shao YM, Tuerganaili A, et al. Establishment and innovative practice of integrative system of prevention, diagnosis and management for echinococcosis in China[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2019, 37(4): 388-394. (in Chinese) |
| (阿卜杜萨拉姆·艾尼, 邵英梅, 吐尔干艾力·阿吉, 等. 中国棘球蚴病防诊治体系建设与创新实践[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2019, 37(4): 388-394.) | |
| [5] |
Aji T, Dong JH, Shao YM, et al. Ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation as alternative to allotransplantation for end-stage hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(5): 1037-1046.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.07.006 |
| [6] |
Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2008, 8(12): 958-969.
doi: 10.1038/nri2448 pmid: 19029990 |
| [7] |
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines[J]. Immunity, 2014, 41(1): 14-20.
doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008 pmid: 25035950 |
| [8] |
Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, et al. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling[J]. J Pathol, 2013, 229(2): 176-185.
doi: 10.1002/path.4133 |
| [9] | Kong D, Zhou C, Guo H, et al. Praziquantel targets M1 macrophages and ameliorates splenomegaly in chronic schistosomiasis[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2017, 62(1): e00005-17. |
| [10] |
Faz-López B, Mayoral-Reyes H, Hernández-Pando R, et al. A dual role for macrophages in modulating lung tissue damage/repair during L2 Toxocara canis infection[J]. Pathogens, 2019, 8(4): 280.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040280 |
| [11] |
Wang H, Zhang CS, Fang BB, et al. Dual role of hepatic macrophages in the establishment of the Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode in mice[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 11: 600635.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.600635 |
| [12] | Lewis SM, Williams A, Eisenbarth SC. Structure and function of the immune system in the spleen[J]. Sci Immunol, 2019, 4(33): eaau6085. |
| [13] | Audia S, Samson M, Guy J, et al. Immunologic effects of rituximab on the human spleen in immune thrombocytopenia[J]. Blood, 2011, 118(16): 4394-400. |
| [14] | Wang H, Li J, Guo BP, et al. Establishment of secondary hydatid disease infection in mice with cystic and alveolar Echinococcus cysts cultured in vitro[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2016, 32(9): 784-788. (in Chinese) |
| (王慧, 李军, 郭宝平, 等. 微囊法棘球蚴继发感染小鼠动物模型的建立[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2016, 32(9): 784-788.) | |
| [15] |
Zhang CS, Shao YM, Yang ST, et al. T-cell tolerance and exhaustion in the clearance of Echinococcus multilocularis: role of inoculum size in a quantitative hepatic experimental model[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 11153.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11703-1 |
| [16] | He YS, Hui HY, Yu R, et al. Effects of asparagus on organ indexes and blood biochemistry in high-fat diet mice[J]. Chin J Microecol, 2018, 30(11): 1261-1265. (in Chinese) |
| (何云山, 惠华英, 喻嵘, 等. 芦笋对高脂饮食小鼠脏器指数及血生化的影响[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2018, 30(11): 1261-1265.) | |
| [17] |
Bronte V, Pittet MJ. The spleen in local and systemic regulation of immunity[J]. Immunity, 2013, 39(5): 806-818.
doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.010 |
| [18] |
Meinderts SM, Oldenborg PA, Beuger BM, et al. Human and murine splenic neutrophils are potent phagocytes of IgG-opsonized red blood cells[J]. Blood Adv, 2017, 1(14): 875-886.
doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017004671 pmid: 29296731 |
| [19] |
Muraille E, Leo O, Moser M. TH1/TH2 paradigm extended: macrophage polarization as an unappreciated pathogen-driven escape mechanism?[J]. Front Immunol, 2014, 5: 603.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00603 pmid: 25505468 |
| [20] | Xu J, Zhang H, Chen L, et al. Schistosoma japonicum infection induces macrophage polarization[J]. J Biomed Res, 2014, 28(4): 299-308. |
| [21] | Gui T, Shimokado A, Sun Y, et al. Diverse roles of macrophages in atherosclerosis: from inflammatory biology to biomarker discovery[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2012, 2012: 693083. |
| [1] | LU Junxia, XU Junying, ZHAO Bin, WANG Qianwen, LI Wenhua, GENG Yuqing, HOU Jun, WU Xiangwei, CHEN Xueling. Echinococcus granulosus infection induces macrophages to express CD73 and A2AR to suppress inflammatory response [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 559-566. |
| [2] | CAO Deping, LI Jiajing, SONG Mengwei, MO Gang. Experimental observation on the changes of hepatic stellate cells stimulated in vitro with tissue protein of Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 440-445. |
| [3] | DU Tao, HU Chunhui, GAN Xuehui, GAO Pan, ZHANG Fabin. Anti-Echinococcus multilocularis effect of total alkaloids of Sophora moorcroftiana in water solution and tablet forms in vitro and in vivo [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 15-22. |
| [4] | JIAO Hongjie, QI Wenjing, GUO Gang, BAO Jianling, WU Chuanchuan, SONG Chuanlong, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao, YAN Mei. Polarization effect of Echinococcus granulosus antigen B on the mouse macrophage RAW264.7 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 23-28. |
| [5] | HOU Xin-ling, LI De-wei, SHI Yang, WANG Mao-lin, ZIBIGU Rousu, ABIDAN Ainiwaer, ZHENG Xu-ran, KANG Xue-jiao, WANG Hui, LI Jing, ZHANG Chuan-shan. Changes of ST2+ T cell subset function and their immune checkpoint molecule expression in the peritoneal cavity of mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 708-716. |
| [6] | LI Jia-ming, WANG Yi-xuan, YANG Ning-ai, MA Hui-hui, LAN Min, LIU Chun-lan, ZHAO Zhi-jun. Effects of ROP16 protein of Toxoplasma gondii on polarization and apoptosis of MH-S cells and their related mechanisms [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 579-586. |
| [7] | HUANG Yuan-yuan, YAO Shi-jie, BIAN Zhi-fang, WEN Yi-xin, ZHENG Li, CAO Ya-ming. Immunoprotective effect of dexamethasone on experimental cerebral malaria in mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 446-453. |
| [8] | SONG Peng, CAI Yu-chun, LU Yan, AI Lin, CHEN Mu-xin, CHEN Shao-hong, CHEN Jia-xu. Establishment of mouse infection model of Babesia microti Lishui isolate and consequent pathological changes [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 493-499. |
| [9] | WU Liang-liang, YANG Ling-fei, SONG Tao. Ultrasound and pathological manifestations of lesions in SD rats with hepatic Echinococcus multilocularis infection established by different methods [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 549-552. |
| [10] | ZHONG Shun-hu, SUN Yue, GUO Xiao-la, ZHENG Ya-dong, CHEN Yi-xia. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in splenic lymphocytes in Echinococcus multilocularis-infected mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 288-294. |
| [11] | ZHUO Yi-cheng, YANG Hai-cheng, LIU Cheng-hao, ZHANG Bao-cai, DUO Xiao-yong, ZHANG Shi-jie. Effect of osteopontin expression level on the growth and development of Echinococcus multilocularis protoscoleces [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 299-304. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xiao-cheng, GAO Yuan, HU Yuan, CAO Jian-ping. Preliminary study on the changes of plymorphonucler myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the spleen of mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 330-336. |
| [13] | WANG Jie, WEN Hong-yang, CHEN Ying, AN Ran, LUO Qing-li, SHEN Ji-long, DU Jian. Construction and identification of macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene knockout strain of Toxoplasma gondii [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 349-354. |
| [14] | SUN Ye-ting, JIANG Nan, JIANG Yan-yan, LI Teng, JIANG Xiao-feng, CAO Jian-ping, SHEN Yu-juan. Study on the polarization of MDSC stimulated by Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex-derived exosomes in vitro [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 175-180. |
| [15] | CAI Ren, REN Yuan, MI Rong-sheng, GUO Gang, QI Wen-jing, ZHANG Zhuang-zhi, GUO Bao-ping. Characteristics of alveolar echinococcosis cases and genetic polymorphism of the parasite from Xinyuan County, Xinjiang [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 181-186. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||