
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 437-443.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2021.04.003
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Qi-qi( ), LIU Cong-shan, HUO Le-le, WEI Yu-fen, JIANG Bin, YIN Meng, XUE Jian, TAO Yi, ZHANG Hao-bing*(
), LIU Cong-shan, HUO Le-le, WEI Yu-fen, JIANG Bin, YIN Meng, XUE Jian, TAO Yi, ZHANG Hao-bing*( )
)
Received:2021-03-02
Revised:2021-04-23
Online:2021-08-30
Published:2021-06-23
Contact:
ZHANG Hao-bing
E-mail:15288939978@163.com;zhanghb@nipd.chinacdc.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
SHI Qi-qi, LIU Cong-shan, HUO Le-le, WEI Yu-fen, JIANG Bin, YIN Meng, XUE Jian, TAO Yi, ZHANG Hao-bing. Affect of aminoalcohol compound HT24 on the expression of tubulin in Echinococcus multilocularis protoscoleces[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 437-443.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2021.04.003
Table 1
The primer sequence for qPCR
| 基因名称Gene name | 引物序列 (5′→3′) Primer sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| α9 | F: ATCTGCCGGCGCAACC |
| R: CGAAATGACAGGAGCATAAGTG | |
| β2 | F: AGGCTTGCGACTGCTTG |
| R: CCGTGTCCGACACCTTAGGT | |
| β4 | F: GTCCCTTCTCCCAAGGTGTC |
| R: TGTCGATGCAATAGGTCTCA | |
| β6 | F: CACGGGTTCTGGTATGGGT |
| R: ACGGTATCAGAGACCTTAG | |
| EF-1α | F: TTTGAGAAAGAGGCGGCTGAGATG |
| R: TAATAAAGTCACGATGACCGGGCG |
Fig. 2
The morphological changes of E. multilocularis protoscoleces 3 days after HT24 treatment in vitro(× 20) A: Control group, the protoscoles showed normal morphology; B, C: low- and medium-concentration groups, the protoscoles were swollen, and hooks detached from the rostellum; D: High-concentration group, the protoscoles died and dwindled.
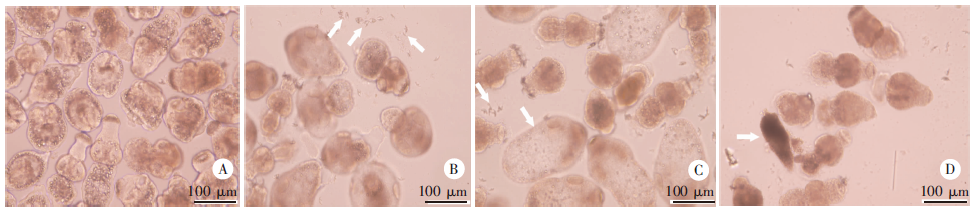
Fig. 3
The transmission electron microscopic observation of tubulin of E. multilocularis protoscoleces 3, 5, and 7 days after HT24 treatment in vitro(× 70 000) A: Control group, the cell membrane was intact, the cilia in the cytoplasm were arranged neatly; B, C, D: Low-, medium-, and high-concentration groups, the cell membrane was broken, and the cilia in the cytoplasm were cracked and spilled out of the cell.
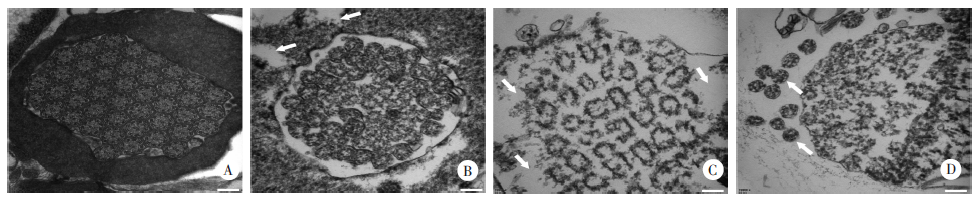
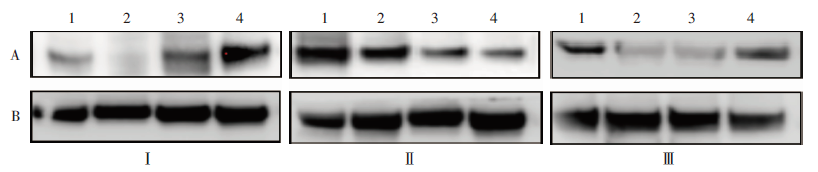
Fig. 5
Western blotting of β-tubulin protein expression in E. multilocularis protoscoleces 3, 5, and 7 days after HT24 treatment A: β-tubulin; B: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; 1-4: Low-, medium-, high-concentration group; 4: Control group; Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ: 3, 5, 7 days after HT24 treatment.
| [1] | Wang LY, Wu WP. Natural factors of alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2009, 25(1):63-66. (in Chinese) |
| (王立英, 伍卫平. 泡球蚴病流行的自然因素[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2009, 25(1):63-66.) | |
| [2] | Eckert J, Gemmell MA, Meslin FX, et al. WHO/OIE manual on echinococcosis in human and animals: a public health problem of global concern[M]. Paris: World Organization for Animal Health, 2001: 1-17. |
| [3] | Holmes P. Investing to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases[R]. Geneva: WHO, 2015, 7(4244):596-596. |
| [4] | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization. Multicriteria-based ranking for risk management of food borne parasites[R]. Rome: FAO Headquarters, 2012. |
| [5] |
Eckert J, Deplazes P. Biological, epidemiological, and clinical aspects of echinococcosis, a zoonosis of increasing concern[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2004, 17(1):107-135.
doi: 10.1128/CMR.17.1.107-135.2004 |
| [6] |
Ammann RW, Eckert J. Cestodes. Echinococcus[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 1996, 25(3):655-689.
doi: 10.1016/S0889-8553(05)70268-5 |
| [7] | WHO Informal Working Group on Echinococcosis. Guidelines for treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans[J]. Bull World Health Organ, 1996, 74(3):231-242. |
| [8] | Kern P, Menezes da Silva A, Akhan O, et al. The echinococcoses: diagnosis, clinical management and burden of disease[J]. Adv Parasitol, 2017, 96:259-369. |
| [9] |
Jura H, Bader A, Frosch M. In vitro activities of benzimidazoles against Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 1998, 42(5):1052-1056.
pmid: 9593125 |
| [10] |
Reuter S, Jensen B, Buttenschoen K, et al. Benzimidazoles in the treatment of alveolar echinococcosis: a comparative study and review of the literature[J]. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2000, 46(3):451-456.
doi: 10.1093/jac/46.3.451 |
| [11] |
Reuter S, Buck A, Manfras B, et al. Structured treatment interruption in patients with alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Hepatology, 2004, 39(2):509-517.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1527-3350 |
| [12] | Zhu WJ, Han XM, Guo YM. Progress in researches of benzimidazole in treatment of echinococcosis[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2017, 29(4):530-533. (in Chinese) |
| (朱文君, 韩秀敏, 郭亚民. 苯并咪唑类药物治疗包虫病研究进展[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2017, 29(4):530-533.) | |
| [13] |
Liu C, Yin J, Xue J, et al. In vitro effects of amino alcohols on Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Acta Trop, 2018, 182:285-290.
doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.08.031 |
| [14] |
Brehm K, Kronthaler K, Jura H, et al. Cloning and characterization of beta-tubulin genes from Echinococcus multilocularis[J]. Mol Biochem Parasitol, 2000, 107(2):297-302.
doi: 10.1016/S0166-6851(00)00178-X |
| [15] | Pierce RJ, Dubois-Abdesselem F, Lancelot J, et al. Targeting schistosome histone modifying enzymes for drug development[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2012, 18(24):3567-3578. |
| [16] |
Parker AL, Teo WS, McCarroll JA, et al. An emerging role for tubulin isotypes in modulating cancer biology and chemotherapy resistance[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(7):1434.
doi: 10.3390/ijms18071434 |
| [17] |
Nogales E. Structural insight into microtubule function[J]. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct, 2001, 30:397-420.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.30.1.397 |
| [18] |
Subramanian R, Kapoor TM. Building complexity: insights into self-organized assembly of microtubule-based architectures[J]. Dev Cell, 2012, 23(5):874-885.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.10.011 pmid: 23153484 |
| [19] |
Mao J, Wang D, Wang Z, et al. Combretastatin A-1 phosphate, a microtubule inhibitor, acts on both hepatocellular carcinoma cells and tumor-associated macrophages by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Cancer Lett, 2016, 380(1):134-143.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.06.020 |
| [20] | Liu M, Zhu YQ, Huang JF, et al. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C regulates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by specifically binding to β-tubulin[J]. Acad J Second Mil Med Univ, 2021, 42(1):14-20. (in Chinese) |
| (刘梦, 朱怡卿, 黄金凤, 等. 泛素结合酶E2C通过特异性结合β-微管蛋白参与调控肝细胞癌进展[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2021, 42(1):14-20.) | |
| [21] |
Froidevaux-Klipfel L, Poirier F, Boursier C, et al. Modulation of septin and molecular motor recruitment in the microtubule environment of the taxol-resistant human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231[J]. Proteomics, 2011, 11(19):3877-3886.
doi: 10.1002/pmic.201000789 pmid: 21761557 |
| [22] |
Kavallaris M, Kuo DY, Burkhart CA, et al. Taxol-resistant epithelial ovarian tumors are associated with altered expression of specific beta-tubulin isotypes[J]. J Clin Invest, 1997, 100(5):1282-1293.
pmid: 9276747 |
| [23] |
Banerjee A. Increased levels of tyrosinated alpha-, beta(Ⅲ)-, and beta(Ⅳ)-tubulin isotypes in paclitaxel-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2002, 293(1):598-601.
doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00269-3 |
| [24] |
Tamura D, Arao T, Nagai T, et al. Slug increases sensitivity to tubulin-binding agents via the downregulation of βⅢ and βⅣα-tubulin in lung cancer cells[J]. Cancer Med, 2013, 2(2):144-154.
doi: 10.1002/cam4.2013.2.issue-2 |
| [25] |
Kusel JR, McVeigh P, Thornhill JA. The schistosome excretory system: a key to regulation of metabolism, drug excretion and host interaction[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2009, 25(8):353-358.
doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2009.05.003 pmid: 19617001 |
| [26] |
Bahia D, Avelar LG, Vigorosi F, et al. The distribution of motor proteins in the muscles and flame cells of the Schistosoma mansoni miracidium and primary sporocyst[J]. Parasitology, 2006, 133(Pt 3):321-329.
pmid: 16740180 |
| [27] |
Valverde-Islas LE, Arrangoiz E, Vega E, et al. Visualization and 3D reconstruction of flame cells of Taenia solium (Cestoda)[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(3):e14754.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014754 |
| [28] |
Rohde K, Watson NA, Roubal FR. Ultrastructure of the protonephridial system of Anoplodiscus cirrusspiralis (Monogenea Monopisthocotylea)[J]. Int J Parasitol, 1992, 22(4):443-457.
pmid: 1644519 |
| [1] | CAO Deping, LI Jiajing, SONG Mengwei, MO Gang. Experimental observation on the changes of hepatic stellate cells stimulated in vitro with tissue protein of Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 440-445. |
| [2] | GUO Gang, REN Yuan, JIAO Hongjie, WU Juan, GUO Baoping, QI Wenjing, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao. Effect of intraperitoneal inoculation with Echinococcus microcysts on the infection and pathogenicity of E. multilocularis in mouse liver [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 156-162. |
| [3] | DU Tao, HU Chunhui, GAN Xuehui, GAO Pan, ZHANG Fabin. Anti-Echinococcus multilocularis effect of total alkaloids of Sophora moorcroftiana in water solution and tablet forms in vitro and in vivo [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 15-22. |
| [4] | HOU Xin-ling, LI De-wei, SHI Yang, WANG Mao-lin, ZIBIGU Rousu, ABIDAN Ainiwaer, ZHENG Xu-ran, KANG Xue-jiao, WANG Hui, LI Jing, ZHANG Chuan-shan. Changes of ST2+ T cell subset function and their immune checkpoint molecule expression in the peritoneal cavity of mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 708-716. |
| [5] | WU Liang-liang, YANG Ling-fei, SONG Tao. Ultrasound and pathological manifestations of lesions in SD rats with hepatic Echinococcus multilocularis infection established by different methods [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 549-552. |
| [6] | ZHONG Shun-hu, SUN Yue, GUO Xiao-la, ZHENG Ya-dong, CHEN Yi-xia. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in splenic lymphocytes in Echinococcus multilocularis-infected mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 288-294. |
| [7] | ZHUO Yi-cheng, YANG Hai-cheng, LIU Cheng-hao, ZHANG Bao-cai, DUO Xiao-yong, ZHANG Shi-jie. Effect of osteopontin expression level on the growth and development of Echinococcus multilocularis protoscoleces [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 299-304. |
| [8] | ABUDUAINI Abulizi, PAIZULA Shalayiadang, TALAITI Tuergan, ZHANG Rui-qing, WANG Hui, ZHANG Chuan-shan, SHAO Ying-mei, TUERGANAILI Aji. Affect of Echinococcus multilocularis protein-mediated NK cell surface receptor NKG2A on the function of NK cells [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(1): 36-42. |
| [9] | HOU Jiao, WEN Hao, WANG Ming-kun, LI Wen-ding, LI liang, LI Jing, ZHANG Chuan-shan, WANG Hui. Changes of macrophage subsets and polarization in spleen of mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 771-778. |
| [10] | LI Ling-hui, WANG Wei, HOU Xin-ling, SHI Yang, LI De-wei, LI Liang, WANG Hui, LI Jing, ZHANG Chuan-shan. Affects of Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode infection on the natural killer T cells and their subsets in mouse spleen [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(3): 311-317. |
| [11] | GUO Bao-ping, GUO Gang, ZHANG Li, XIANG Jing-jing, WANG Xiao-ping, REN Yuan, QI Wen-jing, ZHANG Hui, LI Jun, ZHANG Wen-bao, WANG Hai-yan. Investigation on infection of Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode in small rodents in Chabchar County, Xinjiang [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(3): 327-332. |
| [12] | XU Kai, WANG Hai-jiu, ZHANG Li, ZHANG Yao-gang, FAN Hai-ning, REN Li, REN Bin, WANG Zhi-xin. Research progress on the mechanisms underlying the impairment of host hepatocytes by Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 256-259. |
| [13] | ZHU Ji-hai, CAO De-ping, ZHAO Jun, LIU Jun, SHI Hu-xiang, LIU Yan. Investigation of differentially expressed genes in liver tissues of patients with alveolar echinococcosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(1): 48-54. |
| [14] | ZHU Ji-hai, CAO De-ping, QIE Yangrangzhong, LIU Jun, ZHAO Jun, LIU Yan. Effect of Elsholtzia eriostachya in combination with albendazole in treatment of secondary Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode infection in rats [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 688-694. |
| [15] | SHANG Jing-ye, ZHANG Guang-jia, YU Wen-jie, HE Wei, LIAO Sha, LI Rui-rui, HUANG Yan, LIU Yang, ZHONG Bo. Advances in researches on the genetic diversity of Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(5): 637-641. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||