
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2020, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 317-323.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2020.03.010
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN He-jie1, JIANG Hui-jiao1, LIANG Qian2, Wu Jie1, GUI Xian-wei1, ZOU Hai-liang1, XING Zhi-kun1, WANG Er-qiang3, CHEN Xue-ling3, WU Xiang-wei1,*( )
)
Received:2019-11-27
Online:2020-06-30
Published:2020-07-07
Contact:
Xiang-wei WU
E-mail:wxwshz@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHEN He-jie, JIANG Hui-jiao, LIANG Qian, Wu Jie, GUI Xian-wei, ZOU Hai-liang, XING Zhi-kun, WANG Er-qiang, CHEN Xue-ling, WU Xiang-wei. Effects of supernatant of different hepatoma cells on the vitality of Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces in vitro[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 317-323.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2020.03.010

Fig. 1
The morphology of cells cultured with Huh7, Hepa1-6, and HepG2 supernatant for 48 h under an inverted microscope(× 100) A: Cells cultured with Huh7 supernatant had a polygonal shape; B: Cells cultured with Hepa1-6 supernatant were round and bright;C: Cells cultured with HepG2 supernatant had a spindle shape
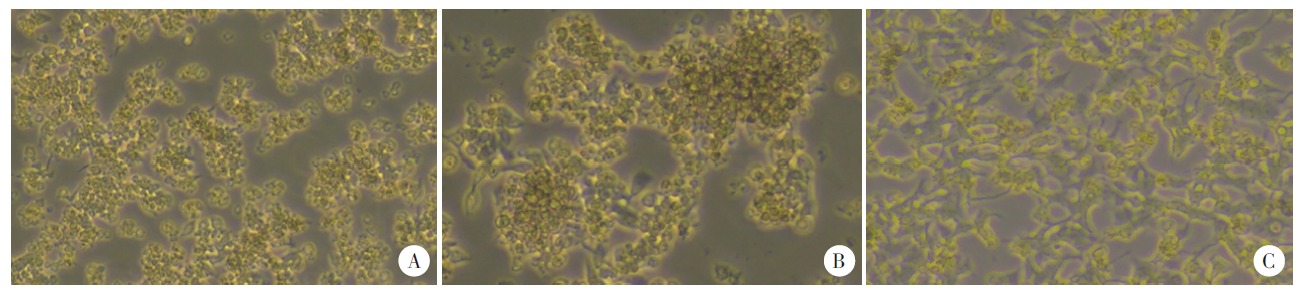
Table 1
Survival rate of Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces under different treatments(/%)
| 组别Group | 培养时间/d Culture duration/d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
| 无血清组Serum-free group | 99.1 ± 1.7 | 76.3 ± 0.2 | 46.5 ± 1.1 | 18.0 ± 1.5 |
| Huh7上清共培养组Huh7 Co-culture group | 94.9 ± 1.8 | 78.0± 1.0 | 46.2 ± 3.6 | 19.0 ± 1.7 |
| Hepa1-6上清共培养组Hepa1-6 Co-culture group | 97.7 ± 2.0 | 83.0 ± 2.1 | 55.9 ± 2.3 | 36.1 ± 1.0a |
| HepG2上清共培养组HepG2 Co-culture group | 97.8 ± 2.3 | 88.2 ± 1.4 | 68.7 ± 1.1 | 45.7 ± 0.4a |
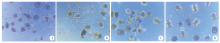
Fig. 2
Morphology of four groups of protoscoleces after seven days of treatment under an inverted microscope A, B: In the serum-free group and the Huh7 group, most of the protoscoleces were stained blue, with partial loss of morphology; C: The Hepa1-6 group showed more blue protoscoleces, and the number of cells with dye rejection increased; D: The HepG2 group has a small number of blue protoscoleces and good transmittance
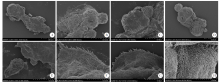
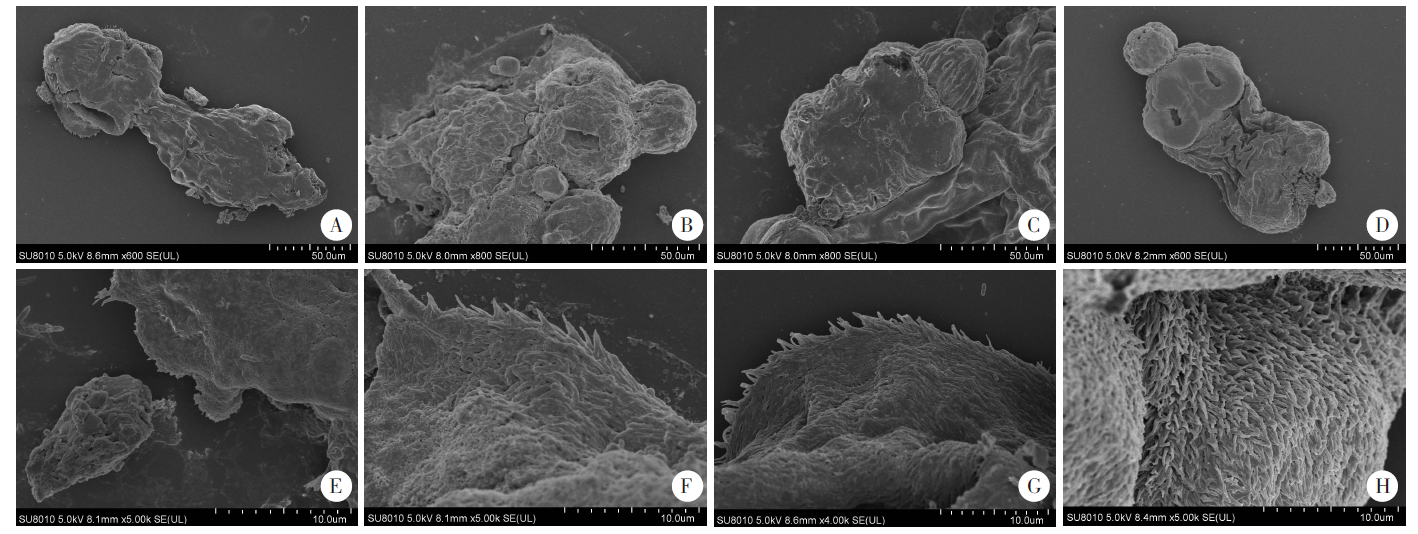
Fig. 3
Ultrastructure of the Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces after seven days of treatment under a scanning electron microscope A-D: The overall morphology of the head segment (× 800); E-H: The ultrastructure of the protoscoleces (× 5 000); A, E: In the serum-free group, the protoscoleces had discontinuous surface structure and deformed suckers; B, F: In the Huh7 group, the protoscoleces had a solid body and the hooks were detached; C, G: In the Hepa1-6 group, the protoscoleces had well-maintained morphology, regular arrangement of hairs, but partial loss of hairs; D, H: In the HepG2 group, the protoscoleces had dense morphology, regular arrangement of microhairs and a complete apical chuck
| [1] | Qi YF, Wu WP. Progress on the epidemiology of echinococcosis[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2013,31(2):143-148. (in Chinese) |
| ( 齐颜凤, 伍卫平. 棘球蚴病流行病学研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2013,31(2):143-148.) | |
| [2] | Wang TP, Cao ZG. Current status of echinococcosis control in China and the existing challenges[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018,36(3):291-296. (in Chinese) |
| ( 汪天平, 操治国. 中国棘球蚴病防控进展及其存在的问题[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018,36(3):291-296.) | |
| [3] |
Romig T, Deplazes P, Jenkins D, et al. Ecology and life cycle patterns of Echinococcus species[J]. Adv Parasitol, 2017,95:213-314.
pmid: 28131364 |
| [4] | Brunetti E, Kern P, Vuitton DA, et al. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans[J]. Acta Trop, 2010,114(1):1-16. |
| [5] | Hemphill A, Gottstein B. Immunology and morphology studies on the proliferation of in vitro cultivated Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes[J]. Parasitol Res, 1995,81(7):605-614. |
| [6] | Jura H, Bader A, Hartmann M, et al. Hepatic tissue culture model for study of host-parasite interactions in alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Infect Immun, 1996,64(9):3484-3490. |
| [7] | Spiliotis M, Tappe D, Sesterhenn L, et al. Long-term in vitro cultivation of Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes under axenic conditions[J]. Parasitol Res, 2004,92(5):430-432. |
| [8] | Wang JW. Establishment of an anaerobic culture model for Echinococcus multilocularis in vitro and study on the factors influencing the growth and development of Echinococcus multilocularis in vitro[D]. Xiamen: Xianmen University, 2011: 14-24. (in Chinese) |
| ( 王季武. 泡球蚴体外厌氧培养模型建立及影响体外培养泡球蚴生长发育因素研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2011: 14-24.) | |
| [9] | Mohammadzadeh T, Sadjjadi SM, Rahimi H. Still and moving image evidences for mating of Echinococcus granulosus reared in culture media[J]. Iran J Parasitol, 2014,9(1):129-133. |
| [10] | Wang T, Zheng XT, Qi WJ, et al. Establishment of amouse model to complete the life-cycle of Echinococcus granulosus in laboratory[J]. J Xinjiang Med Univ, 2018,41(6):724-727. (in Chinese) |
| ( 王甜, 郑雪婷, 齐文静, 等. 在实验室完成细粒棘球绦虫生活史小鼠模型的建立[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2018,41(6):724-727.) | |
| [11] |
Wang J, Gottstein B. Immunoregulation in larval Echinococcus multilocularis infection[J]. Parasite Immunol, 2016,38(3):182-192.
doi: 10.1111/pim.12292 pmid: 26536823 |
| [12] | Wang H, Li J, Guo BP, et al. In vitro culture of Echinococcus multilocularis producing protoscoleces and mouse infection with the cultured vesicles[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2016,9(1):411. |
| [13] | Wang H, Li J, Guo BP, et al. Establishment of secondary hydatid disease infection in mice with cystic and alveolar Echinococcus cysts cultured in vitro[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2016,32(9):784-788. (in Chinese) |
| ( 王慧, 李军, 郭宝平, 等. 微囊法棘球蚴继发感染小鼠动物模型的建立[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2016,32(9):784-788.) | |
| [14] | Fabbri J, Maggiore MA, Pensel PE, et al. In vitro and in vivo efficacy of carvacrol against Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Acta Trop, 2016,164:272-279. |
| [15] | Wang JH, Goepfert C, Mueller N, et al. Larval Echinococcus multilocularis infection reduces dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis in mice by attenuating T helper type 1/type 17-mediated immune reactions[J]. Immunology, 2018,154(1):76-88. |
| [16] | Rahimi HR, Mohammadzadeh T, Sadjjadi SM, et al. BALB/c mice immunity to hydatidosis induced by in-vitro reared Echinococcus granulosus adult worm antigens[J]. Iran J Immunol, 2017,14(2):123-133. |
| [17] | Lu JH, Guo ZM, Yu XB, et al. The cell line establishment and immunogenic study of Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Acad J Sun Yat-Sen Univ Med Sci, 2001,22(2):81-84. (in Chinese) |
| ( 陆家海, 郭中敏, 余新炳, 等. 细粒棘球蚴细胞系培育及其免疫研究[J]. 中山医科大学学报, 2001,22(2):81-84.) | |
| [18] | Zhang YL, Wang TT, Zhou XT, et al. In vitro cultivation of Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes and observation of their growth[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2007,25(2):93-96. (in Chinese) |
| ( 张亚楼, 王婷婷, 周晓涛, 等. 泡球蚴组织体外培养的生长发育观察[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2007,25(2):93-96.) | |
| [19] | Schuster FL, Sullivan JJ. Cultivation of clinically significant hemoflagellates[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2002,15(3):374-389. |
| [20] |
Dezaki ES, Yaghoubi MM, Spiliotis M, et al. Comparison of ex vivo harvested and in vitro cultured materials from Echinococcus granulosus by measuring expression levels of five genes putatively involved in the development and maturation of adult worms[J]. Parasitol Res, 2016,115(11):4405-4416.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-016-5228-6 pmid: 27515372 |
| [21] | Yang CQ, Li XY. Study on the optimum culture conditions of Hepa1-6 cells[J]. J Anhui Agric Sci, 2010,38(28):15507-15509. (in Chinese) |
| ( 杨慈清, 李小英. Hepa1-6细胞的最佳培养条件研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010,38(28):15507-15509.) | |
| [22] | Cheng H, Liao ZL, Chen HY, et al. Effect of low concentration of cerium oxide nanomaterials on hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation[J]. J Reg Anat Oper Surg, 2016,25(4):244-247. (in Chinese) |
| ( 程姮, 廖忠莉, 陈虹燕, 等. 低浓度氧化铈纳米材料对肝癌细胞增殖能力的影响[J]. 局解手术学杂志, 2016,25(4):244-247.) | |
| [23] | Zhang Y. The methodology of culturing Huh7 liver cancer stem cells and the molecular mechanism of celastrol inhibits Huh7 liver cancer stem cells[D]. Hefei: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 2017. (in Chinese) |
| ( 张悦. Huh7肝癌干细胞培养的方法学建立及雷公藤红素抑制Huh7肝癌干细胞的作用机制研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽中医药大学, 2017.) | |
| [24] | Liu YJ, Xu J, Huang HY, et al. Inhibitory effect of the excretory/scretory proteins of Trichinella spiralis on proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma hep G2 cell line[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2015,33(4):315-317. (in Chinese) |
| ( 刘英杰, 徐静, 黄红莹, 等. 旋毛虫排泄分泌蛋白对人肝癌HepG2细胞增殖的抑制作用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2015,33(4):315-317.) | |
| [25] |
Tian ZJ, An W. ERK1/2 contributes negative regulation to STAT3 activity in HSS-transfected HepG2 cells[J]. Cell Res, 2004,14(2):141-147.
doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290213 pmid: 15115615 |
| [26] | He XM, Zheng LD, Zhang T, et al. Research H9 and HepG-2 in vitro co-culture supernatants affect HepG-2 proliferation, migration and apoptosis[J]. Chin J Immunol, 2016,32(2):154-158, 164. (in Chinese) |
| ( 何雪梅, 郑良栋, 张婷, 等. H9与HepG-2体外共培养上清对HepG-2增殖迁移及凋亡的影响[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2016,32(2):154-158, 164.) | |
| [27] | Han ZY, Deng Z, Wang ZY, et al. Effects of different culture media and feeder cells on the culture of Echinococcus multilocularis in vitro[J]. Chin J Tissue Eng Res, 2019,23(19):3080-3085. (in Chinese) |
| ( 韩振阳, 邓子, 王泽宇, 等. 不同培养基与饲养细胞组合对多房棘球绦虫体外培养模型的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(19):3080-3085.) | |
| [28] |
Ponce-Gordo F, Cuesta-Bandera C. Echinococcus granulosus: observations on strobilar development in in vitro monophasic culture[J]. J Helminthol, 1995,69(2):173-175.
doi: 10.1017/s0022149x00014085 pmid: 7636162 |
| [29] | Spiliotis M, Lechner S, Tappe D, et al. Transient transfection of Echinococcus multilocularis primary cells and complete in vitro regeneration of metacestode vesicles[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2008,38(8/9):1025-1039. |
| [1] | LU Junxia, XU Junying, ZHAO Bin, WANG Qianwen, LI Wenhua, GENG Yuqing, HOU Jun, WU Xiangwei, CHEN Xueling. Echinococcus granulosus infection induces macrophages to express CD73 and A2AR to suppress inflammatory response [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 559-566. |
| [2] | WU Xiaoying, HU Yuan, CAO Jianping. Preparation of Echinococcus granulosus peptide embedded in chitosan quaternary ammonium salt nanoparticles [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 300-305. |
| [3] | LI Benfu, WANG Zhengqing, XU Qian, ZI Jinrong, YAN Xinliu, PENG Jia, LI Jianxiong, CAI Xuan, WU Fangwei, YANG Yaming. Sequence analysis of mitochondrial co1 and nd1 genes in Echinococcus granulosus in Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 306-311. |
| [4] | GUO Gang, REN Yuan, JIAO Hongjie, WU Juan, GUO Baoping, QI Wenjing, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao. Effect of intraperitoneal inoculation with Echinococcus microcysts on the infection and pathogenicity of E. multilocularis in mouse liver [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 156-162. |
| [5] | JIAO Hongjie, QI Wenjing, GUO Gang, BAO Jianling, WU Chuanchuan, SONG Chuanlong, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao, YAN Mei. Polarization effect of Echinococcus granulosus antigen B on the mouse macrophage RAW264.7 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 23-28. |
| [6] | WU De-fang, FU Yong, REN Bin, ZHANG Yao-gang, XU Xiao-lei, PANG Ming-quan, FAN Hai-ning. Genetic diversity and differentiation time of human isolates of Echinococcus granulosus and E. multilocularis from Qinghai [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 610-615. |
| [7] | QIAO Shi-yuan, ZHOU Xue, LIU Cheng-hao, JIANG Hui-jiao, BU Yuan-yuan, CHEN Xue-ling, WU Xiang-wei. Effect of albendazole-loaded vesicles on the vitality of protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 324-329. |
| [8] | SUN Ye-ting, JIANG Nan, JIANG Yan-yan, LI Teng, JIANG Xiao-feng, CAO Jian-ping, SHEN Yu-juan. Study on the polarization of MDSC stimulated by Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex-derived exosomes in vitro [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 175-180. |
| [9] | ZHOU Wen-zheng, SUN Jun-gang, ZHAO Xi-bin, CAO Li. Therapeutic effect of intensity modulated radiation therapy on secondary femur infection with Echinococcus granulosus in rats [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 443-448. |
| [10] | TIAN Meng-xiao, ZANG Xiao-yan, GUO Gang, QI Wen-jing, GUO Bao-ping, REN Yuan, LI Jun, ZHANG Wen-bao. Expression and activity assay of serine protease in Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 233-239. |
| [11] | FAN Jun-jie, HAN Xiu-min, Nur Fazleen Binti Idris, LI Kai, TAN Qing-qing, CAO Wen-qiao, LI Xiang, LIAO Peng, YE Bin. Bioinformatics characteristics and immunoreactivity of protein kinase A of Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 682-687. |
| [12] | SHI Chun-li, YANG Hui, PAN Wen, ZHANG Xin, ZHU Xiao-ting, ZHAO Jia-qing. Proteomic analysis of human proteins in extracellular vesicles secreted by protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 695-701. |
| [13] | YU Xiao-dong, YALI Ya-sen, WANG Jia-ling, LI Meng, YE Jian-rong. Establishment of BALB/c mouse model of Echinococcus granulosus-induced sensitization and changes of related immune cells [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(4): 412-416. |
| [14] | CAO Sheng-kui, ZHANG Xiao-fan, WEI Yu-huan, PAN Jia-ming, CAO Jian-ping, SHEN Yu-juan, CHEN Jia-xu. Expression and function of arginase in livers of mice infected with Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 304-309. |
| [15] | ZHOU Hong-rang, MAO Guang-yao, WANG Xiao-ling, CHEN Mu-xin, YU Qing, WANG Ying, Ai Lin, XIAO Ning. Establishment and application of a multiplex recombinase-aided isothermal amplification technique for identifying Echinococcus granulosus and Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 310-316. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||