
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 200-209.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2021.02.013
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Cheng-si1( ), QIN Min1, TAN Ming-juan2, MIAO Ting-ting1, SHAO Tian-ye1, LIU Xin-jian1, WANG Yong1,*(
), QIN Min1, TAN Ming-juan2, MIAO Ting-ting1, SHAO Tian-ye1, LIU Xin-jian1, WANG Yong1,*( )
)
Received:2021-02-09
Revised:2021-03-12
Online:2021-04-30
Published:2021-04-30
Contact:
WANG Yong
E-mail:zcs1003678028@163.com;yongwsh@njmu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHAO Cheng-si, QIN Min, TAN Ming-juan, MIAO Ting-ting, SHAO Tian-ye, LIU Xin-jian, WANG Yong. Effect of praziquantel on impaired renal function in mice with acute infection of Schistosoma japonicum[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 200-209.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2021.02.013
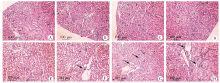
Fig. 2
Kidney tissue sections of mice with acute infection of Schistosoma japonicum (HE staining,× 100) A-D: At different time points in the health control group, the renal tissues showed no inflammatory cell infiltration, the size of glomerulus was normal with no mesangial cell proliferation, and no pathological damage was found. E-H: At different time points in the infection group, the renal tissues showed increased inflammatory cell infiltration, enlarged glomerulus and mesangial cell proliferation, with the progression of infection. The black arrows indicate inflammatory cells or glomeruli with mesangial hyperplasia.
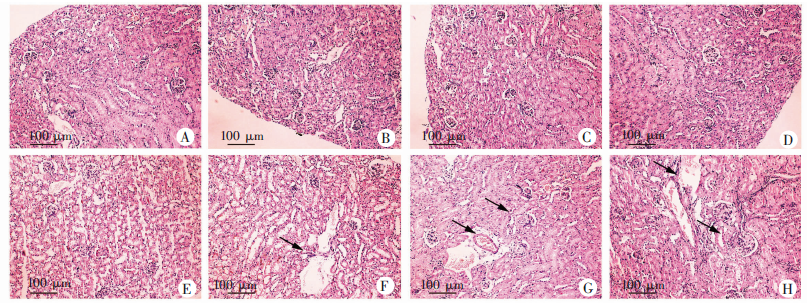
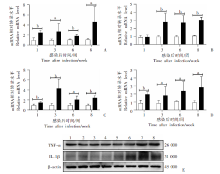
Fig. 3
Levels of inflammatory factors in kidneys of mice with acute infection of S. japonicum A-D: Relative transcription levels of TNF-α, TGF-β, IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA; E: Protein expression levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in mice kidney, 1-4: Health control group; 5-8: Weeks 1, 3, 6, and 8 after infection in the infection group. a: P < 0.05; b: P < 0.01.
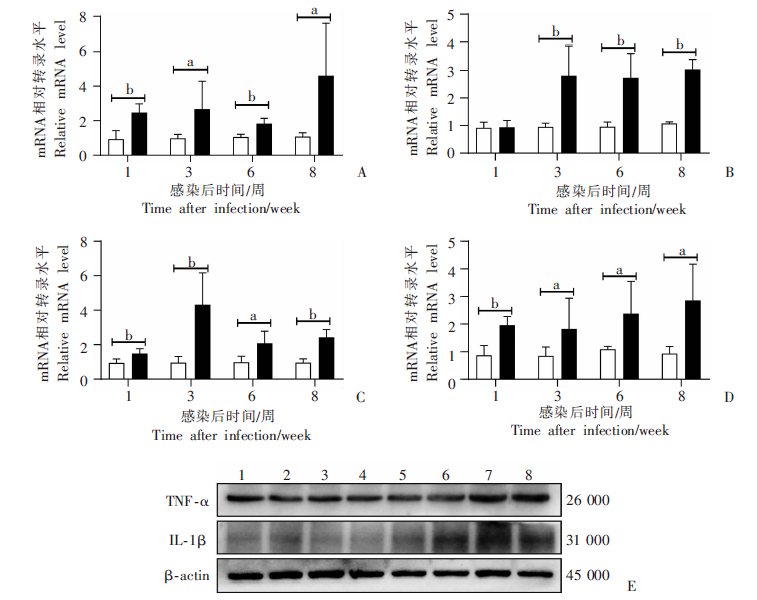
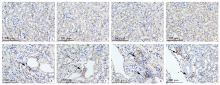
Fig. 4
Macrophage infiltration in renal tissues in mice with acute infection of S. japonicum detected by immunohistochemistry(× 200) A-D: In the health control group,there were fewer F4/80-positive cells. E-H: At weeks 1, 3, 6, and 8 in the infection group, the renal tissues showed increased F4/80-positive cells. The black arrows indicate the F4/80-positive cells.
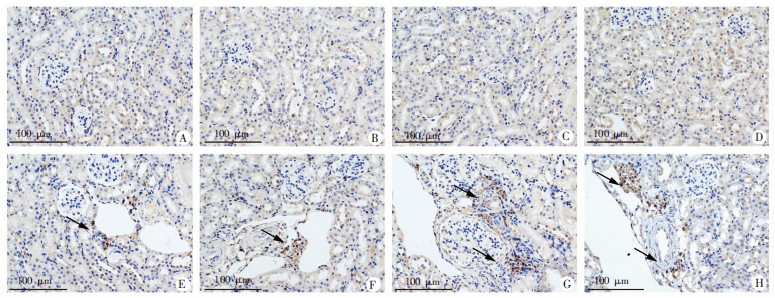
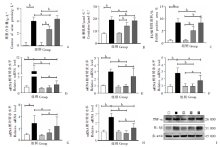
Fig. 6
Changes on renal function and inflammation in mice with acute infection of S. japonicum treated with praziquantel A: Urine protein content; B: Serum creatinine level; C: Immunohistochemical positive area; D-H: Relative transcription levels of renal inflammatory factors TNF-α, TGF-β, IL-1β, IL-6 and chemokine CCL2 mRNA ; I: Protein levels of TNF-α and IL-1β. a: P < 0.05; b: P < 0.01.
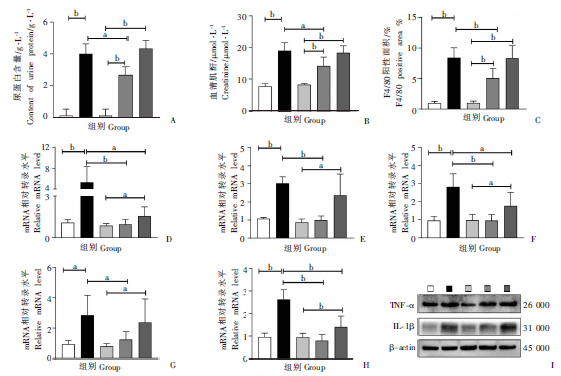
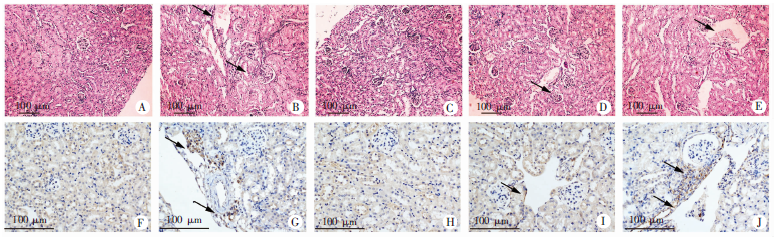
Fig. 7
Changes on renal injury (HE staining, × 100)and macrophage infiltration (immunohistochemistry, × 200)in mice with acute infection of S. japonicum treated with praziquantel A-D: HE staining of the kidney slice (× 100); F-J: F4/80 immunohistochemistry on the kidney slice (× 200). A: There was no inflammatory cell infiltration in health control group, and the size of glomerulus was normal and no mesangial cell proliferated, with no detection of pathological damage; B: Inflammatory cell infiltration was increased, glomerulus was enlarged with more mesangial cell proliferation in infection group; C: There was no inflammatory cell infiltration, the size of glomerulus was normal with no mesangial cell proliferation, and no pathological damage was found in health control with praziquantel-treatment group; D: Inflammatory cell infiltration was reduced, and the enlarged glomerulus decreased with less mesangial cell proliferation in infection with praziquantel-treatment group; E: Inflammatory cell infiltration was increased, glomerulus was enlarged with more mesangial cell proliferation in praziquantel treatment group. The black arrows indicate inflammatory cells or glomeruli with mesangial hyperplasia; F: Fewer F4/80-positive cells in health control group; G: Increased F4/80-positive cells in infection group; H: Fewer F4/80 positive-cells in health control with praziquantel-treatment group; I: Fewer F4/80-positive cells in infection with praziquantel-treatment group; J: Increased F4/80-positive cells in praziquantel treatment group. The black arrows indicate the F4/80-positive cells.
| [1] | Yang JR, Xu MX, Tan XD. Healthy China Strategy and schistosomiasis control[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2020,32(4):419-422. (in Chinese) |
| ( 杨晋如, 徐明星, 谭晓东. 健康中国战略与血吸虫病防控[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2020,32(4):419-422.) | |
| [2] | Guan Z, Lu S, Li SZ, et al. Epidemic status and prevention and control challenges of schistosomiasis among floating population in China[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2017,35(6):598-603. (in Chinese) |
| ( 关周, 吕山, 李石柱, 等. 我国流动人口血吸虫病流行现状及防控挑战[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2017,35(6):598-603.) | |
| [3] |
Andersson KL, Chung RT. Hepatic schistosomiasis[J]. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol, 2007,10(6):504-512.
pmid: 18221611 |
| [4] | Sun YJ, Li ZQ, Lu FL. Research progress on immunopathological mechanism of egg granuloma of Schistosoma japonicum[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2019,37(6):97-101, 106. (in Chinese) |
| ( 孙钰浚, 李钊琪, 吕芳丽. 日本血吸虫虫卵肉芽肿免疫病理机制研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2019,37(6):97-101, 106.) | |
| [5] |
Gryseels B. Schistosomiasis[J]. Infect Dis Clin N Am, 2012,26(2):383-397.
doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2012.03.004 pmid: 94278209134268421 |
| [6] | Andrade ZA, Queiroz ACD. Renal lesions in hepatosplenic schistosomiasis[J]. Rev Inst Med Trop São Paulo, 1968,10(1):36-40. |
| [7] |
Colley DG, Secor WE. Immunology of human schistosomiasis[J]. Parasite Immunol, 2014,36(8):347-357.
doi: 10.1111/pim.2014.36.issue-8 |
| [8] |
Neves PDMM, Bezerra KS, Silveira MAD, et al. Schistosoma mansoni and membranous nephropathy[J]. Kidney Int, 2016,89(4):959-959.
doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2015.12.015 |
| [9] | Neves PDMDM, Jorge LB, Cavalcante LB, et al. Schistosomiasis-associated glomerulopathy: Clinical aspects, pathological characteristics, and renal outcomes[J]. Clin nephrol, 2020,93(5):251-261. |
| [10] | Fabiana, Oliveira, Goncalves, et al. Schistosoma mansoni associated glomerulopathy with IgA mesangial deposits: case report[J]. J Brasileira De Nefrologia, 2017,39(1):86-90. |
| [11] | Rodrigues VL, Otoni A, Voieta I, et al. Glomerulonephritis in schistosomiasis mansoni: a time to reappraise[J]. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop, 2010,43(6):638-642. |
| [12] | Burke ML, Jones MK, Gobert GN, et al. Immunopathogenesis of human schistosomiasis[J]. Parasite Immunol, 2009,31(4):163-176. |
| [13] | Abensur H, Nussenzveig I, Saldanha LB, et al. Nephrotic syndrome associated with hepatointestinal schistosomiasis[J]. Rev Inst Med Trop São Paulo, 1992,34(4):273-276. |
| [14] | Sobh MA, Moustafa FE, Sally SM, et al. Characterisation of kidney lesions in early schistosomal-specific nephropathy[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 1988,3(4):392-398. |
| [15] | Yan ZZ, Hochman A, Zhou ZY, et al. Immune complex nephropathy of Schistosoma japonicum[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 1986,4(1):14-17. (in Chinese) |
| ( 严自助, Hochman A, 周中源, 等. 日本血吸虫免疫复合物肾病的实验研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 1986,4(1):14-17.) | |
| [16] | Chisty MM, Nargis M, Sato H, et al. Schistosoma mansoni: kinetics of glomerulonephritis in Mongolian gerbils and its correlation with intensity and duration of infection[J]. Parasite Paris France, 2002,9(2):143-151. |
| [17] | Sobh M, Moustafa F, Hamid S, et al. Schistosomal-specific nephropathy in Syrian golden hamsters: treatment by induction of antigen excess[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 1996,11(11):2178-2184. |
| [18] | Xu DW, Bao XQ, Wang YZ, et al. Study on immune response of Schistosoma japonicum nephropathy[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 1989,1(2):47-50. (in Chinese) |
| ( 须大卫, 包献清, 王雅珍, 等. 日本血吸虫肾病免疫反应的研究[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 1989,1(2):47-50.) | |
| [19] | Donate-Correa Luis-Rodríguez Martín-Núez, et al. Inflammatory targets in diabetic nephropathy[J]. J Clin Med, 2020,9(2):458-470. |
| [20] | Meng XM. Inflammatory Mediators and Renal Fibrosis[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019,1165:381-406. |
| [21] | Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Lan HY. Inflammatory processes in renal fibrosis[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2014,10(9):493-503. |
| [22] | Chung ACK, Lan HY. Chemokines in renal injury[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2011,22(5):802-809. |
| [23] | Lee SB, Kalluri R. Mechanistic connection between inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Kidney Int, 2010,78(Suppl 119):S22-26. |
| [24] | Liu YH. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis[J]. Nat Revs Nephrol, 2011,7(12):684-696. |
| [25] | Boor P, Ostendorf T, Floege J. Renal fibrosis: novel insights into mechanisms and therapeutic targets[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2010,6(11):643-656. |
| [26] | Watkins BM. Drugs for the control of parasitic diseases: current status and development in schistosomiasis[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2003,19(11):477-478. |
| [27] | Wang W, Zhao CS, Miu TT, et al. Inhibitory effect of praziquanl on proliferation and inflammatory response of spleen macrophages in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2020,38(3):263-270. (in Chinese) |
| ( 王伟, 赵成思, 缪婷婷, 等. 吡喹酮治疗对日本血吸虫感染小鼠脾巨噬细胞增殖和炎症反应的抑制作用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2020,38(3):263-270.) | |
| [28] | Liang YJ, Jie L, Quan Y, et al. New insight into the antifibrotic effects of praziquantel on mice in infection with Schistosoma japonicum[J]. PLoS One, 2011,6(5):e20247. |
| [29] | Liu J, Kong D, Qiu J, et al. Praziquantel ameliorates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad signalling via upregulating Smad7 in hepatic stellate cells[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2019,176(24):4666-4680. |
| [30] | Barsoum R. The changing face of schistosomal glomerulopathy[J]. Kidney Int, 2005,66(6):2472-2484. |
| [31] | Hillyer GV, Lewert RM. Studies on renal pathology in hamsters infected with Schistosoma mansoni and S. japonicum[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 1974,23(3):404-411. |
| [32] | Bezerra D, Duarte, Alexandre L, et al. Acute kidney injury in schistosomiasis: a retrospective cohort of 60 patients in Brazil[J]. J Parasitol, 2015,101(2):244-247. |
| [33] | Kano K, Milgrom KF. Immune complex disease[J]. Vox Sang, 1980,38(3):121-137. |
| [34] | Gong FL. Medical immunology[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 227-228. (in Chinese) |
| ( 龚非力. 医学免疫学[M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 227-228.) | |
| [35] | Balow JE, Cho ME, Austin HA. Immunologic renal diseases[M]. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2008: 462. |
| [36] | Anders HJ, Ryu M. Renal microenvironments and macrophage phenotypes determine progression or resolution of renal inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Kidney Int, 2011,80(9):915-925. |
| [37] | Eardley KS, Kubal C, Zehnder D, et al. The role of capillary density, macrophage infiltration and interstitial scarring in the pathogenesis of human chronic kidney disease[J]. Kidney Int, 2008,74(4):495-504. |
| [38] | Nishida M, Hamaoka K. Macrophage phenotype and renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy[J]. Nephron Expl Nephrol, 2008,110(1):e31-36. |
| [1] | TAN Xiao, ZHU Qi, LIU Zhongqi, LI Jia, PENG Dingjin. Immunogenicity of Schistosoma japonicum Sj26gst mRNA vaccine candidate [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 546-551. |
| [2] | LIU Huaman, Bikash Giri, FANG Chuantao, ZHENG Yameng, WU Huixin, ZENG Minhao, LI Shan, CHENG Guofeng. Identification of gender associated m6A modified circRNA in Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 552-558. |
| [3] | LU Junxia, XU Junying, ZHAO Bin, WANG Qianwen, LI Wenhua, GENG Yuqing, HOU Jun, WU Xiangwei, CHEN Xueling. Echinococcus granulosus infection induces macrophages to express CD73 and A2AR to suppress inflammatory response [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 559-566. |
| [4] | LAN Weiming, XU Hui, XU Yin, QIU Tingting, XIE Shuying, DENG Fenglin, HU Shaoliang, LIU Huan, GUO Jiagang, ZENG Xiaojun. Study on early warning of high risk environment of Schistosoma japonicum infection by quantitative real-time PCR [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 502-505. |
| [5] | JIAO Hongjie, QI Wenjing, GUO Gang, BAO Jianling, WU Chuanchuan, SONG Chuanlong, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao, YAN Mei. Polarization effect of Echinococcus granulosus antigen B on the mouse macrophage RAW264.7 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 23-28. |
| [6] | WANG Xiao-ling, ZHANG Wei, YI Cun, CHEN Xiang-yu, YANG Wen-bin, XU Bin, HU Wei. The effect of SjGPR89 protein on the growth and development of Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 701-707. |
| [7] | CHEN Guo, ZHU Dan-dan, DUAN Yi-nong. Research progress of immune regulation protein B7 family on immune regulation during Schistosoma japonicum infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 774-779. |
| [8] | YAN Xiao-lan, WEN Li-yong, XIONG Yan-hong, ZHENG Bin, ZHANG Jian-feng, WANG Tian-ping, YU Li-ling, XU Guo-zhang, LIN Dan-dan, ZHOU Xiao-nong. Interpretation of Criteria for Detection of Antibody against Schistosoma japonicum—Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 798-800. |
| [9] | LI Jia-ming, WANG Yi-xuan, YANG Ning-ai, MA Hui-hui, LAN Min, LIU Chun-lan, ZHAO Zhi-jun. Effects of ROP16 protein of Toxoplasma gondii on polarization and apoptosis of MH-S cells and their related mechanisms [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 579-586. |
| [10] | TANG Xian-shi, JI Wen-xiang, XIONG Chun-rong, ZHOU Yong-hua, XU Yong-liang, TONG De-sheng. Study on anxiety-like behavior of mice with late-stage infection of Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 622-628. |
| [11] | LIANG Le, ZHANG Jing, SHEN Yu-juan, HU Yuan, CAO Jian-ping. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate promotes liver egg granuloma formation and fibrosis in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 441-445. |
| [12] | OUYANG Bing, LI Ren-xi. One case of Diphyllobothrium latum infection caused by raw salmon [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 295-298. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xiao-cheng, GAO Yuan, HU Yuan, CAO Jian-ping. Preliminary study on the changes of plymorphonucler myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the spleen of mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 330-336. |
| [14] | GAO Yuan, ZHANG Xiao-cheng, HU Yuan, CAO Jian-ping. Study on the inhibitory effect of natural killer cells on liver fibrosis of schistosomiasis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 168-174. |
| [15] | SUN Ye-ting, JIANG Nan, JIANG Yan-yan, LI Teng, JIANG Xiao-feng, CAO Jian-ping, SHEN Yu-juan. Study on the polarization of MDSC stimulated by Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex-derived exosomes in vitro [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 175-180. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||