
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2020, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 293-298.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2020.03.006
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Sheng-lin, DENG Wang-ping, LI Yin-long, WANG Li-ping, ZHANG Li-juan, LV Shan, XU Jing*( )
)
Received:2020-01-02
Online:2020-06-30
Published:2020-07-07
Contact:
Jing XU
E-mail:xujing@nipd.chinacdc.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Sheng-lin, DENG Wang-ping, LI Yin-long, WANG Li-ping, ZHANG Li-juan, LV Shan, XU Jing. Establishment of recombinase polymerase amplification technique for rapid detection of Schistosoma japonicum nucleic acid[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 293-298.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2020.03.006
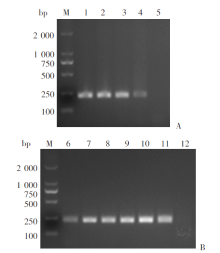
Fig. 1
Optimization of the RPA reaction conditions A: Amplification results under different reaction temperatures; B: Amplification results after different reaction durations. M: DNA marker; 1-5: Reactions at temperatures of 40, 35, 30, 25 and 20 ℃; 6-11: Reactions for 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 min; 12: ddH2O
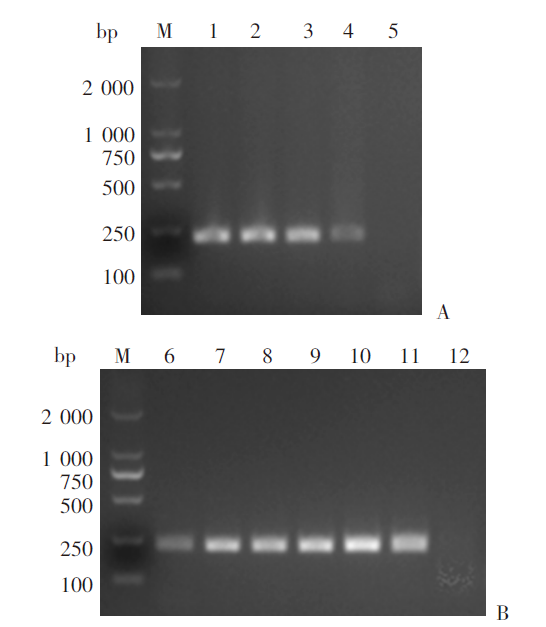
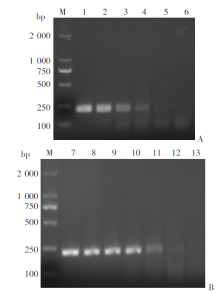
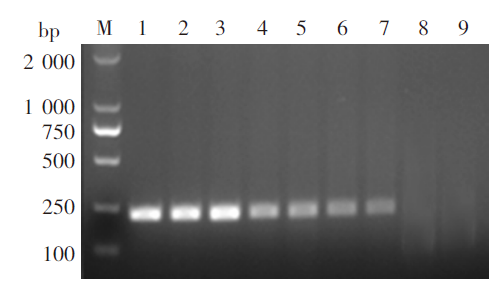
Fig. 3
Sensitivity of the RPA assay A: Sensitivity of the RPA method against genomic DNA; B: Sensitivity of the RPA method against recombinant plasmid. M: DNA marker; 1-5: Genomic DNA at concentrations of 100 pg/μl, 10 pg/μl, 1 pg/μl, 100 fg/μl, and 10 fg/μl, respectively; 7-12: Plasmid concentrations of 106 copies/μl, 105 copies/μl, 104 copies/μl, 103 copies/μl, 102 copies/μl and 10 copies/μl, respectively; 6, 13: ddH2O
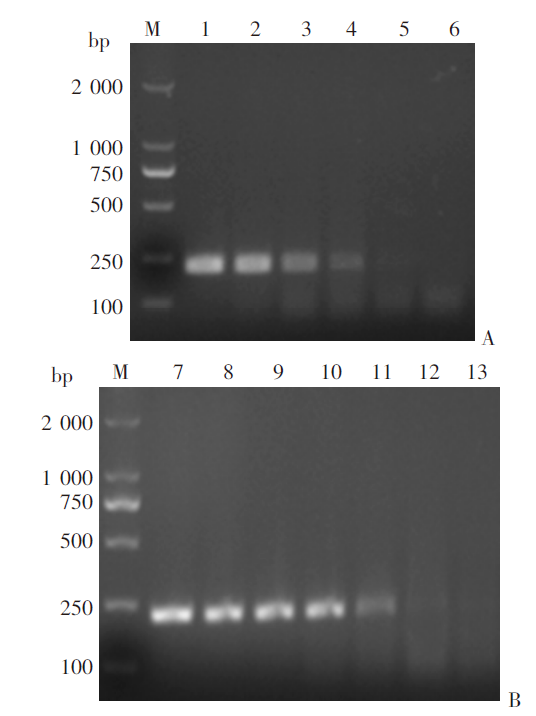
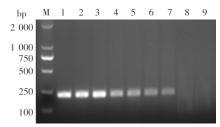
Fig. 5
Agarose gel electrophoresis of RPA products from mixed DNA of positively- and negatively-infected snails M: DNA marker; 1: Genomic DNA of S. japonicum adults; 2-8: The mixed snail DNA at ratios of 1 : 10, 1 : 50, 1 : 100, 1 : 250, 1 : 500, 1 : 1000 and 1 : 2 000, respectively; 8: ddH2O
| [1] |
Colley DG, Bustinduy AL, Secor WE, et al. Human schistosomiasis[J]. Lancet, 2014,383(9936):2253-2264.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61949-2 pmid: 24698483 |
| [2] |
Zhang LJ, Mwanakasale V, Xu J, et al. Diagnostic performance of two specific Schistosoma japonicum immunological tests for screening Schistosoma haematobium in school children in Zambia[J]. Acta Trop, 2020,202:105285.
doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2019.105285 pmid: 31786108 |
| [3] | Dang H, Jin JN, Xu J, et al. Surveillance of schistosomiasis in People’s Republic of China in 2015[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2017,29(3):273-280. (in Chinese) |
| ( 党辉, 金嘉宁, 许静, 等. 2015年全国血吸虫病监测分析[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2017,29(3):273-280.) | |
| [4] | Qin ZQ, Xu J, Feng T, et al. Field evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) platform for the detection of Schistosoma japonicum infection in Oncomelania hupensis snails[J]. Trop Med Infect Dis, 2018,3(4):124-133. |
| [5] | Yan J, Hu T, Lei ZL. The endemic situation and challenges of major parasitic diseases in China[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2015,33(6):412-417. (in Chinese) |
| ( 严俊, 胡桃, 雷正龙. 全国重点寄生虫病的防控形势与挑战[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2015,33(6):412-417.) | |
| [6] | Yang K, Li SZ. Application of big data mining technology in monitoring and early-warning of schistosomiasis[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2015,33(6):461-465. (in Chinese) |
| ( 杨坤, 李石柱. 大数据挖掘技术应用于血吸虫病监测预警研究的探讨[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2015,33(6):461-465.) | |
| [7] |
Wang W, Li YZ, Li HJ, et al. Immunodiagnostic efficacy of detection of Schistosoma japonicum human infections in China: a meta analysis[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Med, 2012,5(1):15-23.
doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(11)60238-1 pmid: 22182637 |
| [8] | Wang SP, He X, Zhou YF. Demand for and the development of detection techniques for source of schistosome infection in China[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2015,33(6):456-460. (in Chinese) |
| ( 汪世平, 何鑫, 周云飞. 我国血吸虫病传染源快速检测技术的需求与发展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2015,33(6):456-460.) | |
| [9] | Zhao S, Liu YH, Li T, et al. Rapid detection of Schistosoma japonicum specific gene fragment by recombinase aided isothermal amplification combined with fluorescent probe[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2019,37(1):23-27. (in Chinese) |
| ( 赵松, 刘燕红, 李婷, 等. 结合重组酶介导的核酸等温扩增和荧光探针快速检测日本血吸虫基因片段[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2019,37(1):23-27.) | |
| [10] | Dang-Trinh MA, Angeles JMM, Moendeg KJ, et al. Utilization of real time PCR for the assessment of egg burden in the organs of Schistosoma japonicum experimentally infected mice[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2018,189:61-65. |
| [11] | Zhang X, He CC, Liu JM, et al. Nested-PCR assay for detection of Schistosoma japonicum infection in domestic animals[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2017,6(1):86-92. |
| [12] | Zheng WB, Wu YD, Ma JG, et al. Recombinase polymerase amplification and its applications in parasite detection[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2015,33(5):382-386. (in Chinese) |
| ( 郑文斌, 吴耀东, 马剑钢, 等. 重组酶聚合酶扩增技术及其在寄生虫检测中的应用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2015,33(5):382-386.) | |
| [13] |
Lai MY, Ooi CH, Lau YL. Rapid detection of Plasmodium knowlesi by isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assay[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2017,97(5):1597-1599.
pmid: 28820700 |
| [14] |
Daher RK, Stewart G, Boissinot M, et al. Recombinase polymerase amplification for diagnostic applications[J]. Clin Chem, 2016,62(7):947-958.
doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2015.245829 pmid: 27160000 |
| [15] | Liu W, Liu HX, Zhang L, et al. A novel isothermal assay of Borrelia burgdorferi by recombinase polymerase amplification with lateral flow detection[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016,17(8):1250. |
| [16] | Feng T, Qin ZQ, Xu J, et al. Efficacy evaluation of a loop mediated isothermal amplification technique in detection of DNA of Schistosoma japonicum eggs in fecal samples[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2017,35(3):230-234. (in Chinese) |
| ( 冯婷, 秦志强, 许静, 等. 环介导等温扩增法检测粪样中日本血吸虫虫卵DNA的效果评估[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2017,35(3):230-234.) | |
| [17] | Zhu HQ, Xu J, Zhu R, et al. Comparison of the miracidium hatching test and modified Kato-Katz method for detecting Schistosoma japonicum in low prevalence areas of China[J]. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health, 2014,45(1):20-25. |
| [18] | Yue Y, Zhang JZ, Zhang MJ. Application of NASBA and RPA in detection of pathogenic bacteria[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2019,40(8):1018-1022. (in Chinese) |
| ( 岳苑, 张建中, 张茂俊. NASBA和RPA两种等温扩增技术在病原茵检测中的应用研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2019,40(8):1018-1022.) | |
| [19] |
Piepenburg O, Williams CH, Stemple DL, et al. DNA Detection using recombination proteins[J]. PLoS Biol, 2006,4(7):e204.
pmid: 16756388 |
| [20] | Zhang HC, Wei YY, Yang ZF, et al. Establishment of RPA isothermal detection method for African classical swine fever virus[J]. Mod J Animal Husb Vet Med, 2019(11):13-16. (in Chinese) |
| ( 张皓淳, 魏园园, 杨作丰, 等. 非洲猪瘟病毒RPA等温检测方法的建立[J]. 现代畜牧兽医, 2019(11):13-16.) | |
| [21] |
Kersting S, Rausch V, Bier FF, et al. Rapid detection of Plasmodium falciparum with isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow analysis[J]. Malar J, 2014,13:99.
pmid: 24629133 |
| [22] |
Rosser A, Rollinson D, Forrest M, et al. Isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) of Schistosoma haematobium DNA and oligochromatographic lateral flow detection[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2015,8:446.
pmid: 26338510 |
| [23] | Poulton K, Webster B. Development of a lateral flow recombinase polymerase assay for the diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni infections[J]. Anal Biochem, 2018,546:65-71. |
| [24] | Wang SL, Wang LP, Wu LL, et al. Diagnostic value of nucleic acid detection in schistosomiasis japonica: a meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2020,32(1):15-22. (in Chinese) |
| ( 王盛琳, 王丽萍, 吴铃铃, 等. 核酸检测技术对日本血吸虫病诊断价值的meta分析[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2020,32(1):15-22.) | |
| [25] |
Crannell ZA, Castellanos-Gonzalez A, Irani A, et al. Nucleic acid test to diagnose cryptosporidiosis: lab assessment in animal and patient specimens[J]. Anal Chem, 2014,86(5):2565-2571.
pmid: 24479858 |
| [26] |
Kumagai T, Lu SH, Wang TP, et al. Detection of early and single infections of Schistosoma japonicum in the intermediate host snail, Oncomelania hupensis, by PCR and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2010,83(3):542-548.
doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.10-0016 pmid: 20810818 |
| [27] | Sun K, Xing WW, Yu XL, et al. Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick for rapid and visual detection of Schistosoma japonicum[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2016,9:476. |
| [28] | Xing WW, Yu XL, Feng JT, et al. Field evaluation of a recombinase polymerase amplification assay for the diagnosis of Schistosoma japonicum infection in Hunan Province of China[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2017,17:164. |
| [29] | Zhao S, Li T, Yang K, et al. Establishment of a recombinase-aided isothermal amplification technique to detect Schistosoma japonicum specific gene fragments[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2018,30(3):273-277, 306. (in Chinese) |
| ( 赵松, 李婷, 杨坤, 等. 重组酶介导的日本血吸虫特异性基因片段核酸等温扩增检测方法的建立[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2018,30(3):273-277, 306.) | |
| [30] | Cheng G, Li D, Zhuang DF, et al. The influence of natural factors on the spatio-temporal distribution of Oncomelania hupensis[J]. Acta Trop, 2016,164:194-207. |
| [1] | TAN Xiao, ZHU Qi, LIU Zhongqi, LI Jia, PENG Dingjin. Immunogenicity of Schistosoma japonicum Sj26gst mRNA vaccine candidate [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 546-551. |
| [2] | LIU Huaman, Bikash Giri, FANG Chuantao, ZHENG Yameng, WU Huixin, ZENG Minhao, LI Shan, CHENG Guofeng. Identification of gender associated m6A modified circRNA in Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 552-558. |
| [3] | LAN Weiming, XU Hui, XU Yin, QIU Tingting, XIE Shuying, DENG Fenglin, HU Shaoliang, LIU Huan, GUO Jiagang, ZENG Xiaojun. Study on early warning of high risk environment of Schistosoma japonicum infection by quantitative real-time PCR [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 502-505. |
| [4] | WANG Xiao-ling, ZHANG Wei, YI Cun, CHEN Xiang-yu, YANG Wen-bin, XU Bin, HU Wei. The effect of SjGPR89 protein on the growth and development of Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 701-707. |
| [5] | CHEN Guo, ZHU Dan-dan, DUAN Yi-nong. Research progress of immune regulation protein B7 family on immune regulation during Schistosoma japonicum infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 774-779. |
| [6] | YAN Xiao-lan, WEN Li-yong, XIONG Yan-hong, ZHENG Bin, ZHANG Jian-feng, WANG Tian-ping, YU Li-ling, XU Guo-zhang, LIN Dan-dan, ZHOU Xiao-nong. Interpretation of Criteria for Detection of Antibody against Schistosoma japonicum—Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 798-800. |
| [7] | TANG Xian-shi, JI Wen-xiang, XIONG Chun-rong, ZHOU Yong-hua, XU Yong-liang, TONG De-sheng. Study on anxiety-like behavior of mice with late-stage infection of Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 622-628. |
| [8] | LIANG Le, ZHANG Jing, SHEN Yu-juan, HU Yuan, CAO Jian-ping. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate promotes liver egg granuloma formation and fibrosis in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 441-445. |
| [9] | WANG Li-ping, LV Chao, QIN Zhi-qiang, XU Jing, DENG Wang-ping. Establishment and preliminary evaluation of a visualized detection technique for Schistosoma mansoni nucleic acid based on recombinase polymerase amplification [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 337-343. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yi-long, YE Run, LE Bin, CHEN Wen-zhu, PAN Wei-qing, ZHANG Dong-mei. A reverse transcriptase aid-enzymatic recombinase isothermal amplification-based method for detection of West Nile virus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 344-348. |
| [11] | GAO Yuan, ZHANG Xiao-cheng, HU Yuan, CAO Jian-ping. Study on the inhibitory effect of natural killer cells on liver fibrosis of schistosomiasis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 168-174. |
| [12] | JIANG Feng, CHEN Run, DU Ning-ning, ZHU Meng-yi, ZHONG Hao, CHEN Hui, XI Xu-xia, ZHAN Xiao-dong, LI Chao-pin. Investigation of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pet dogs and cats in Wuhu City [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(1): 124-126. |
| [13] | HONG Yang, LIN Jiao-jiao. Research progress on proteomics in Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 725-730. |
| [14] | SHI Liang, XIONG Chun-rong, LIU Mao-mao, WEI Xiu-shen, ZHANG Jian-feng, WANG Xin-yao, WANG Tao, HANG De-rong, YANG Hai-tao, YANG Kun. Evaluation of efficacy of visual intelligent recognition model for Oncomelania hupensis based on deep learning technology [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 764-770. |
| [15] | HUANG Ai-long, ZHANG Bei, SHEN Han-yu, CHEN Guo, LI Jing, ZHU Dan-dan, DUAN Yi-nong. Expression and function of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 in the liver of mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(5): 621-626. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||