
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2020, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 159-165.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2020.02.005
• ORIGNAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wen-qi ZHENG1, Xue-min FENG2, Ya-ming CAO3, Yan-qiu HAN1, Jun-rui WANG1,*( )
)
Received:2019-08-29
Online:2020-04-30
Published:2020-05-11
Contact:
Jun-rui WANG
E-mail:wangjunrui123@yeah.net
Supported by:CLC Number:
Wen-qi ZHENG, Xue-min FENG, Ya-ming CAO, Yan-qiu HAN, Jun-rui WANG. Bioinformatics analysis and enzymatic activity test of quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase from Plasmodium berghei[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(2): 159-165.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2020.02.005
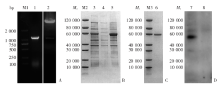
Fig. 3
rPbQSOX vector construction, prokaryotic expression, as well as SDS-PAGE and Western blotting analyses A: PCR product of PbQSOX and double-digestion product of pET30a(+)-PbQSOX plasmid; B: Prokaryotic expression of rPbQSOX; C: Purification of rPbQSOX; D: Western blotting results of rPbQSOX. M1: DNA marker; M2, M3: Protein marker; 1: PCR product of PbQSOX gene; 2: Double-digestion product of pET30a(+)-PbQSOX plasmid with Nde Ⅰ and Hind Ⅲ; 3: Ultrasonic homogenate; 4: Sediments after ultrasonic homogenization; 5: Supernatant after ultrasonic homogenization; 6: Purified rPbQSOX; 7: Culture solutions after IPTG induction; 8: Negative control without induction
| [1] | World Health Organization: World malaria report 2019[M] report 2019[M]. Geneva: WHO Press, 2019: 12-13. |
| [2] | Lei ZL, Wang LY . Control situation and primary task of key parasitic diseases in China[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2012,30(1):1-5. (in Chinese) |
| ( 雷正龙, 王立英 . 全国重点寄生虫病防治形势与主要任务[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2012,30(1):1-5.) | |
| [3] | Zhang L, Feng J, Zhang SS , et al. The progress of national malaria elimination and epidemiological characteristics of malaria in China in 2017[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018,36(3):201-209. (in Chinese) |
| ( 张丽, 丰俊, 张少森 , 等. 2017年全国疟疾疫情特征及消除工作进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018,36(3):201-209.) | |
| [4] | Liu HE, Su PC, Chen X , et al. Advances in the study of the resistance of Plasmodium vivax to common anti-malarial drugs[J]. J Pathog Biol, 2018,13(9):1049-1051, 1053. (in Chinese) |
| ( 刘怀鄂, 苏品璨, 陈熙 , 等. 常用抗间日疟药物抗药性机制研究进展[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2018,13(9):1049-1051, 1053.) | |
| [5] | Gatton ML, Chitnis N, Churcher T , et al. The importance of mosquito behavioural adaptations to malaria control in Africa[J]. Evolution, 2013,67(4):1218-1230. |
| [6] | Cowman AF, Healer J, Marapana D , et al. Malaria: biology and disease[J]. Cell, 2016,167(3):610-624. |
| [7] | Tuju J, Kamuyu G, Murungi LM , et al. Vaccine candidate discovery for the next generation of malaria vaccines[J]. Immunology, 2017,152(2):195-206. |
| [8] | Freedman RB, Hirst TR, Tuite MF . Protein disulphide isomerase: building bridges in protein folding[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 1994,19(8):331-336. |
| [9] | Kiermeier F, Mashaley R . Influence of raw milk processing on the aflatoxin M content of milk products (author′s transl)[J]. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch, 1977,164(3):183-187. |
| [10] | Ostrowski MC, Kistler WS . Properties of a flavoprotein sulfhydryl oxidase from rat seminal vesicle secretion[J]. Biochemistry, 1980,19(12):2639-2645. |
| [11] | Hoober KL, Joneja B , White HB 3rd, et al. A sulfhydryl oxidase from chicken egg white[J]. J Biol Chem, 1996,271(48):30510-30516. |
| [12] | Jaje J, Wolcott HN, Fadugba O , et al. A flavin-dependent sulfhydryl oxidase in bovine milk[J]. Biochemistry, 2007,46(45):13031-13040. |
| [13] | Heckler EJ, Alon A, Fass D , et al. Human quiescin-sulfhydryl oxidase, QSOX1: probing internal redox steps by mutagenesis[J]. Biochemistry, 2008,47(17):4955-4963. |
| [14] | Thorpe C, Hoober KL, Raje S , et al. Sulfhydryl oxidases: emerging catalysts of protein disulfide bond formation in eukaryotes[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2002,405(1):1-12. |
| [15] | Alon A, Heckler EJ, Thorpe C , et al. QSOX contains a pseudo-dimer of functional and degenerate sulfhydryl oxidase domains[J]. FEBS Lett, 2010,584(8):1521-1525. |
| [16] | Haque SJ, Majumdar T, Barik S . Redox-assisted protein folding systems in eukaryotic parasites[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2012,17(4):674-683. |
| [17] | Kodali VK, Thorpe C . Quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase from Trypanosoma brucei: catalytic activity and mechanism of a QSOX family member with a single thioredoxin domain[J]. Biochemistry, 2010,49(9):2075-2085. |
| [18] | Katchman BA, Antwi K, Hostetter G , et al. Quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase 1 promotes invasion of pancreatic tumor cells mediated by matrix metalloproteinases[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2011,9(12):1621-1631. |
| [19] | Mebazaa A, Vanpoucke G, Thomas G , et al. Unbiased plasma proteomics for novel diagnostic biomarkers in cardiovascular disease: identification of quiescin Q6 as a candidate biomarker of acutely decompensated heart failure[J]. Eur Heart J, 2012,33(18):2317-2324. |
| [20] | Poillet L, Pernodet N, Boyer-Guittaut M , et al. QSOX1 inhibits autophagic flux in breast cancer cells[J]. PLoS One, 2014,9(1):e86641. |
| [21] | Song H, Zhang B, Watson MA , et al. Loss of Nkx3.1 leads to the activation of discrete downstream target genes during prostate tumorigenesis[J]. Oncogene, 2009,28(37):3307-3319. |
| [22] | Basu S, Leonard JC, Desai N , et al. Divergence of Erv1-associated mitochondrial import and export pathways in trypanosomes and anaerobic protists[J]. Eukaryotic Cell, 2013,12(2):343-355. |
| [23] | Alon A, Grossman I, Gat Y , et al. The dynamic disulphide relay of quiescin sulphydryl oxidase[J]. Nature, 2012,488(7411):414-418. |
| [24] | Chivers PT, Laboissière MC, Raines RT . The CXXC motif: imperatives for the formation of native disulfide bonds in the cell[J]. EMBO J, 1996,15(11):2659-2667. |
| [25] | Raje S, Thorpe C . Inter-domain redox communication in flavoenzymes of the quiescin/sulfhydryl oxidase family: role of a thioredoxin domain in disulfide bond formation[J]. Biochemistry, 2003,42(15):4560-4568. |
| [26] | Okuda A, Matsusaki M, Higashino Y , et al. Disulfide bond formation activity of soybean quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase[J]. FEBS J, 2014,281(23):5341-5355. |
| [27] | Zheng WY, Zhang WY, Hu W , et al. Exploring the smallest active fragment of HsQSOX1b and finding a highly efficient oxidative engine[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(7):e40935. |
| [1] | LIANG Kejia, LIU Cong, LI Yanlin, LI Xiaoge, LIU Yan, LI Zhenkui. Research advances on transcriptional regulation in plasmodium sexual stages [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 619-624. |
| [2] | SUN Jun. The biological significance of malarial hemozoin’s formation [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 209-212. |
| [3] | ZHONG Shun-hu, SUN Yue, GUO Xiao-la, ZHENG Ya-dong, CHEN Yi-xia. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed miRNAs in splenic lymphocytes in Echinococcus multilocularis-infected mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 288-294. |
| [4] | GE Jie-yun, LIU Lei, SUN Yi-fan, CHENG Yang. Advances in research on the vacuolar membrane function and the associated proteins of plasmodium parasitophorous vacuole [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 402-410. |
| [5] | LU Fei, ZHUO Xun-hui, LU Shao-hong. Research progress on the interaction between host cell autophagy and apicomplexa protozoa infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 826-831. |
| [6] | SU Ya-jing, QIAO Xia, WANG Peng-tao, KANG Yu-ting, YANG Ning-ai, JIA Wei, ZHAO Zhi-jun. Gene expression profiling of human lung adenocarcinoma of A549 cells induced by Toxoplasma virulence-related effector ROP16Ⅲ [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 473-480. |
| [7] | LI Mei, TU Hong, XIA Zhi-gui, WANG Zhen-yu, ZHOU He-jun. Thermal stability of diagnostic targets Plasmodium falciparum histidine rich protein Ⅱ and Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase in rapid detection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 245-248. |
| [8] | LIU Hong, LIU Yao-bao, CAO Jun. Research advance and application of whole-genome sequencing of Plasmodium [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 265-270. |
| [9] | LUO Fei, TAN Yan, ZHOU Shuang, YUAN Yi, LI Shan-shan, XU Jing-ru, ZHOU Yang. Assessment and analysis of malaria diagnostic capacity by microscopy at primary health institutions in Chongqing [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(1): 93-99. |
| [10] | HE Cheng, PAN Shuai, XU Mei-zhen, YUAN Fei, HE Jing-mei, LIU Zhuan-zhuan. Proteome-based identification and bioinformatics analysis of protein phosphatases of Toxoplasma gondii [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(1): 120-124. |
| [11] | GUO Chu-tong, OUYANG Chun-yan, HE Jun-xian, JI Shu-yu, YANG Li-teng, LIU Xiao-yu. Cloning, expression, purification and immunogenicity analysis of the tenth-class allergen of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 723-729. |
| [12] | ZHU Ling-qian, FENG Xin-yu, HU Wei, LI Shi-zhu. Functions and roles of miRNA during the infection of Anopheles by Plasmodium [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 742-748. |
| [13] | ZHOU Shui-mao, TU Zu-wu, YANG Yan, CHEN Fang, JIA Xi-shuai. Evaluation of the efficacy of loop-mediated isothermal amplification in detecting Plasmodium falciparum and other species of Plasmodium [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(4): 423-428. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yan, XU Ai-fang, ZHANG Jia-qi, YAO Li-nong, GU Kai-long, XUE Li-zhi, PAN Ke-nv. Differential diagnosis of a case of Babesia microti infection previously misdiagnosed as malaria [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(4): 445-448. |
| [15] | Rui YANG, Yu-ting ZHENG, Xiao-yu YANG, Li-min DONG, Zu-rui LIN, Yao-wu ZHOU, Xu-can ZENG, Hong-bin LI, Jin-yong JIANG. Investigation on malaria vectors in Jinghong, a border area in Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(4): 406-410. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||