
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 27-35.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2024.01.004
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIE Xiaoman( ), SUN Hang, DAI Lisha, ZHU Wenju, WANG Lilei, XIE Huanhuan, DONG Hongjie, ZHANG Junmei, WANG Qi, ZHOU Beibei, ZHAO Guihua, XU Chao, YIN Kun*(
), SUN Hang, DAI Lisha, ZHU Wenju, WANG Lilei, XIE Huanhuan, DONG Hongjie, ZHANG Junmei, WANG Qi, ZHOU Beibei, ZHAO Guihua, XU Chao, YIN Kun*( )
)
Received:2023-08-09
Revised:2023-10-04
Online:2024-02-28
Published:2024-03-12
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:CLC Number:
XIE Xiaoman, SUN Hang, DAI Lisha, ZHU Wenju, WANG Lilei, XIE Huanhuan, DONG Hongjie, ZHANG Junmei, WANG Qi, ZHOU Beibei, ZHAO Guihua, XU Chao, YIN Kun. Effect of Toxoplasma gondii infection on m6A methylation modification of transcripts in mice brain tissue[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(1): 27-35.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2024.01.004
Table 1
Transcriptome sequencing quality control data for T. gondii infected and uninfected mouse brain tissues
| 样品 Sample | 序列条数 No. sequence | 总碱基个数 Total base | 平均质量值 Mean Qual |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组a Control group a | |||
| C1 | 3 180 872 | 3 848 393 167 | 10.16 |
| C2 | 3 668 346 | 4 418 900 151 | 9.92 |
| C3 | 3 404 079 | 4 080 017 275 | 10.08 |
| C4 | 3 012 064 | 3 881 576 763 | 10.12 |
| C5 | 3 378 209 | 4 330 477 402 | 10.12 |
| C6 | 3 547 332 | 4 760 557 767 | 10.23 |
| TgCtwh6感染组 TgCtwh6 infection group | |||
| T1 | 3 653 250 | 4 295 421 375 | 10.10 |
| T2 | 3 441 401 | 3 658 768 263 | 9.75 |
| T3 | 3 117 499 | 3 720 974 204 | 10.10 |
| LHG感染组 LHG infection group | |||
| L1 | 2 678 488 | 3 652 926 862 | 10.19 |
| L2 | 3 228 485 | 3 724 541 278 | 10.03 |
| L3 | 2 973 916 | 3 700 213 104 | 10.08 |
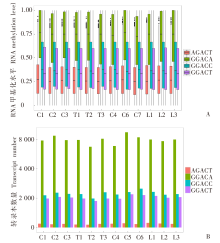
Fig. 1
The distribution of the methylation level of mouse infected or uninfected with T. gondii A: Methylation level distribution of four m6A methylation motifs; B: The transcripts corresponding to hypermethylation sites of four m6A methylation motifs. C1-C3: The control group for the TgCtwh6 infection group; T1-T3: The TgCtwh6 infection group; C4-C6: The control group for the LHG infection group; L1-L3: The LHG infection group.
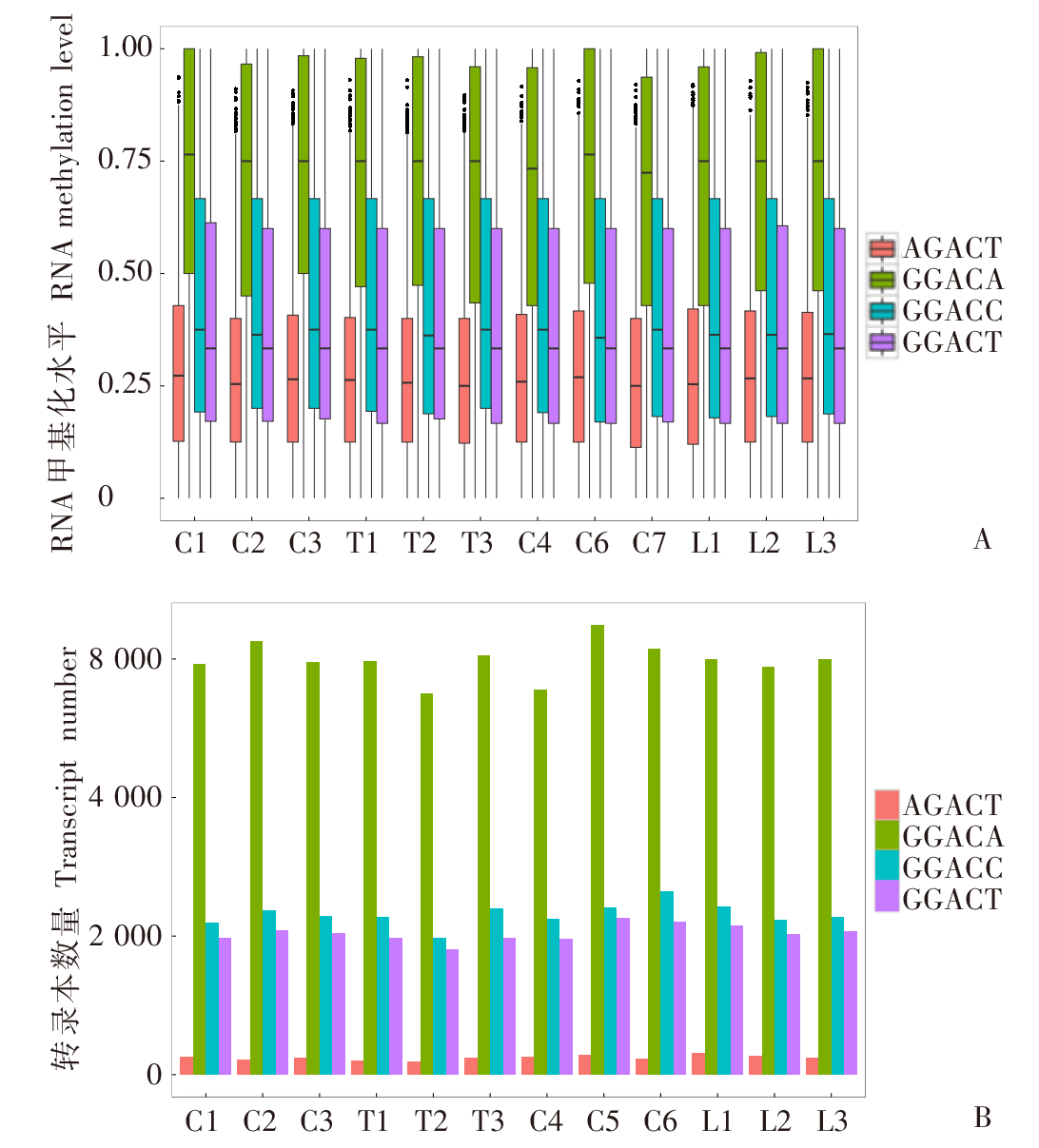
Table 2
Statistical results of differential methylation loci of 4 m6A motifs in mice brains between T. gondii-infected groups and control group
| 模体 Motif | 差异甲基化位点 DML | 高差异甲基位点Hyper DML | 低差异甲基位点 Hypo DML |
|---|---|---|---|
| GGACA | 2 504 | 1 187 | 1 317 |
| GGACC | 2 408 | 1 142 | 1 266 |
| GGACT | 2 376 | 1 123 | 1 253 |
| AGACT | 1 945 | 930 | 1 015 |
| 合计 Total | 9 233 | 4 382 | 4 851 |

Fig. 3
The biological process branch enrichment analysis of the GO pathway of the transcript where the differential methylation loci is located A: Biological process enrichment results of all transcripts where DML is located; B: Biological process enrichment results of the transcript where the DML of GGACA motif is located.
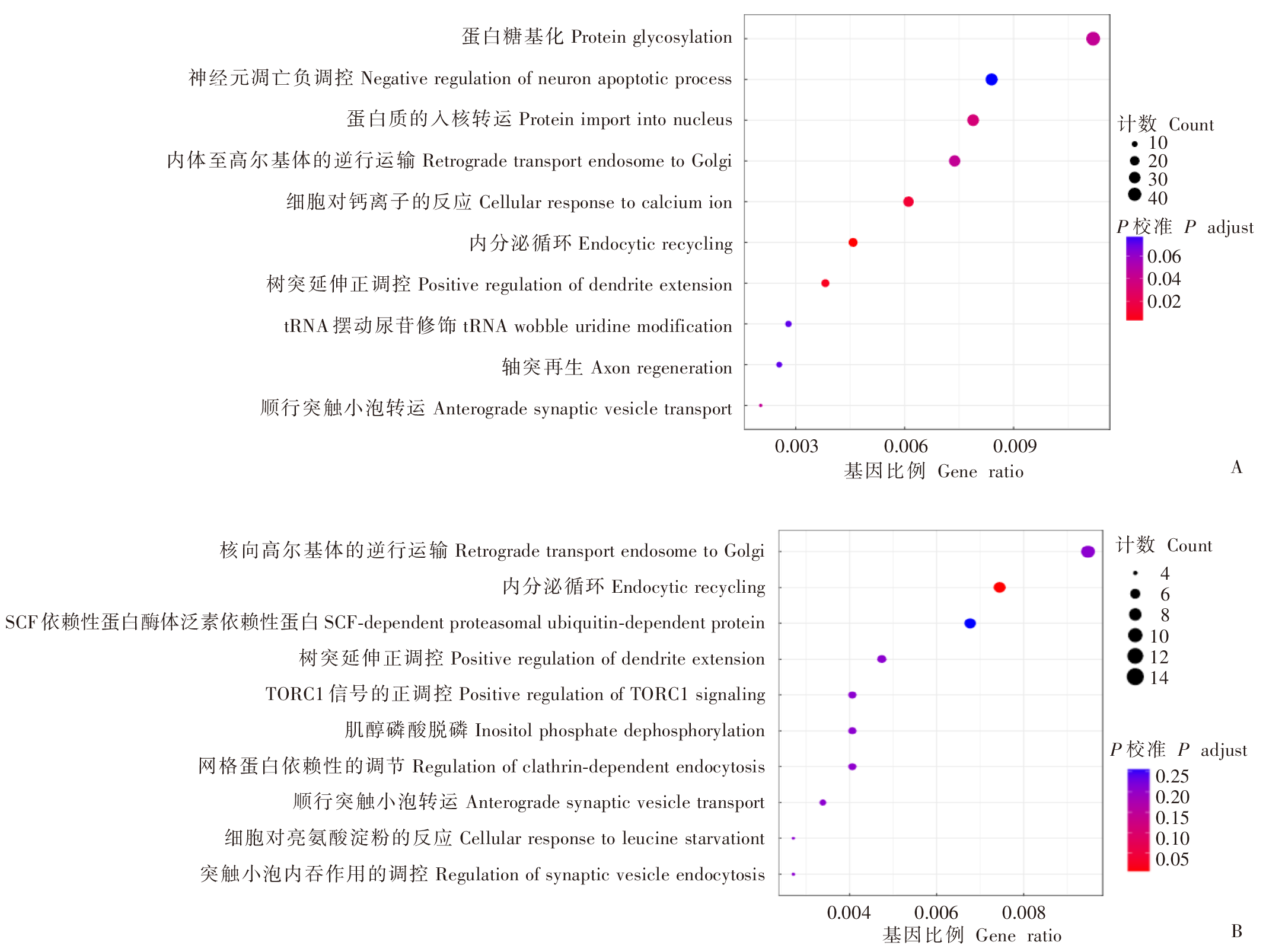
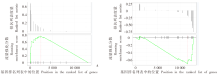
Fig. 4
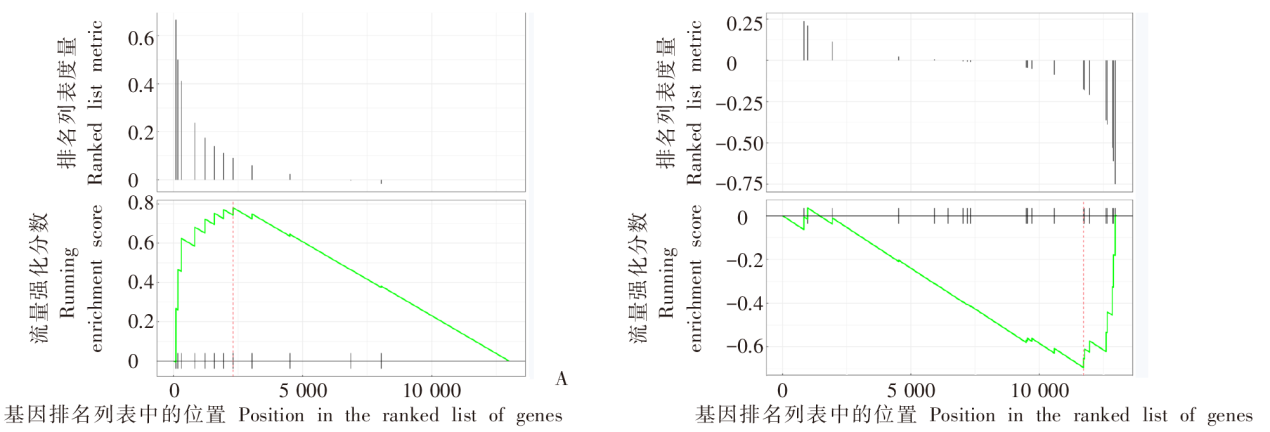
GSEA enrichment analysis diagram in the brain of T. gondii infected mice A: GSEA analysis of the subset of negative regulation pathways of fibroblast proliferation; B: GSEA analysis diagram of a subset of Hippo signal pathways. The green curve upward indicates the pathway tends to be up-regulated, while downward indicates the pathway tends to be down-regulated. The core transcripts within this subset are shown to the right of the red dashed line.
| [1] | Molan A, Nosaka K, Hunter M, et al. Global status of Toxoplasma gondii infection: systematic review and prevalence snapshots[J]. Trop Biomed, 2019, 36(4): 898-925. |
| [2] |
Pan M, Lyu CC, Zhao JL, et al. Sixty years (1957—2017) of research on toxoplasmosis in china: an overview[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8: 1825.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01825 |
| [3] |
Robert-Gangneux F, Dardé ML. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2012, 25(2): 264-296.
doi: 10.1128/CMR.05013-11 pmid: 22491772 |
| [4] | Elsheikha HM, Marra CM, Zhu XQ. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of cerebral toxoplasmosis[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2020, 34(1): e00115-e00119. |
| [5] |
Yin K, Xu C, Zhao GH, et al. Epigenetic manipulation of psychiatric behavioral disorders induced by Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 803502.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.803502 |
| [6] |
Hsu PC, Groer M, Beckie T. New findings: depression, suicide, and Toxoplasma gondii infection[J]. J Am Assoc Nurse Pract, 2014, 26(11): 629-637.
doi: 10.1002/2327-6924.12129 |
| [7] |
Boillat M, Hammoudi PM, Dogga SK, et al. Neuroinflammation-associated aspecific manipulation of mouse predator fear by Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Cell Rep, 2020, 30(2): 320-334.e6.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.12.019 |
| [8] |
Hari Dass SA, Vyas A. Toxoplasma gondii infection reduces predator aversion in rats through epigenetic modulation in the host medial amygdala[J]. Mol Ecol, 2014, 23(24): 6114-6122.
doi: 10.1111/mec.2014.23.issue-24 |
| [9] |
Syn G, Anderson D, Blackwell JM, et al. Epigenetic dysregulation of host gene expression in Toxoplasma infection with specific reference to dopamine and amyloid pathways[J]. Infect Genet Evol, 2018, 65: 159-162.
doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.07.034 |
| [10] |
Holmes MJ, Padgett LR, Bastos MS, et al. m6A RNA methylation facilitates pre-mRNA 3'-end formation and is essential for viability of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2021, 17(7): e1009335.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009335 |
| [11] |
Farhat DC, Bowler MW, Communie G, et al. A plant-like mechanism coupling m6A reading to polyadenylation safeguards transcriptome integrity and developmental gene partitioning in Toxoplasma[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e68312.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.68312 |
| [12] |
Baumgarten S, Bryant JM, Sinha A, et al. Transcriptome-wide dynamics of extensive m6A mRNA methylation during Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage development[J]. Nat Microbiol, 2019, 4(12): 2246-2259.
doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0521-7 pmid: 31384004 |
| [13] |
Zhang N, Ding CH, Zuo YX, et al. N6-methyladenosine and neurological diseases[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2022, 59(3): 1925-1937.
doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02739-0 pmid: 35032318 |
| [14] | Imanishi M. Mechanisms and strategies for determining m6A RNA modification sites by natural and engineered m6A effector proteins[J]. Chem Asian J, 2022, 17(16): e202200367. |
| [15] |
Xiao S, Cao S, Huang QT, et al. The RNA N6-methyladenosine modification landscape of human fetal tissues[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2019, 21(5): 651-661.
doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0315-4 |
| [16] |
Oerum S, Meynier V, Catala M, et al. A comprehensive review of m6A/m6Am RNA methyltransferase structures[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(13): 7239-7255.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab378 pmid: 34023900 |
| [17] |
Zhao GH, Zhang LX, Dai LS, et al. Development of Toxoplasma gondii Chinese Ⅰ genotype wh6 strain in cat intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Korean J Parasitol, 2022, 60(4): 241-246.
doi: 10.3347/kjp.2022.60.4.241 |
| [18] | Zhao GH, Dai LS, Zhu JJ, et al. Development research of Toxoplasma gondii Chinese Ⅲ genotype strain isolated from humans in the definitive host[J]. J Pathog Biol, 2022, 17(2): 174-179. (in Chinese) |
| (赵桂华, 代莉莎, 朱进进, 等. 人源中国Ⅲ型刚地弓形虫分离株在终末宿主内的发育研究[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2022, 17(2): 174-179.) | |
| [19] |
Lorenz DA, Sathe S, Einstein JM, et al. Direct RNA sequencing enables m6A detection in endogenous transcript isoforms at base-specific resolution[J]. RNA, 2020, 26(1): 19-28.
doi: 10.1261/rna.072785.119 |
| [20] |
Liu HB, Liu XJ, Zhang SM, et al. Systematic identification and annotation of human methylation marks based on bisulfite sequencing methylomes reveals distinct roles of cell type-specific hypomethylation in the regulation of cell identity genes[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2016, 44(1): 75-94.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1332 pmid: 26635396 |
| [21] |
Yu GC, Wang LG, Han YY, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters[J]. OMICS, 2012, 16(5): 284-287.
doi: 10.1089/omi.2011.0118 pmid: 22455463 |
| [22] |
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(43): 15545-15550.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102 pmid: 16199517 |
| [23] |
Vignon M, Bastide A, Attina A, et al. Multiplexed LC-MS/MS quantification of salivary RNA modifications in periodontitis[J]. J Periodontal Res, 2023, 58(5): 959-967.
doi: 10.1111/jre.v58.5 |
| [24] |
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Zhang MM, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the transcriptome-wide m6A methylome in colorectal cancer by MeRIP sequencing[J]. Epigenetics, 2021, 16(4): 425-435.
doi: 10.1080/15592294.2020.1805684 |
| [25] |
Krusnauskas R, Stakaitis R, Steponaitis G, et al. Identification and comparison of m6A modifications in glioblastoma non-coding RNAs with MeRIP-seq and Nanopore dRNA-seq[J]. Epigenetics, 2023, 18(1): 2163365.
doi: 10.1080/15592294.2022.2163365 |
| [26] |
Sendinc E, Shi Y. RNA m6A methylation across the transcriptome[J]. Mol Cell, 2023, 83(3): 428-441.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.01.006 pmid: 36736310 |
| [27] |
He HY, Hu L. Cysteine-rich intestinal protein 1 enhances the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via Ras signaling[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2022, 38(1): 49-58.
doi: 10.1002/kjm2.v38.1 |
| [28] |
Imp BM, Rubin LH, Tien PC, et al. Monocyte activation is associated with worse cognitive performance in HIV-infected women with virologic suppression[J]. J Infect Dis, 2017, 215(1): 114-121.
doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw506 pmid: 27789726 |
| [29] |
Bichsel SJ, Tamaskovic R, Stegert MR, et al. Mechanism of activation of NDR (nuclear Dbf2-related) protein kinase by the hMOB1 protein[J]. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(34): 35228-35235.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404542200 pmid: 15197186 |
| [30] |
Hergovich A. MOB control: reviewing a conserved family of kinase regulators[J]. Cell Signal, 2011, 23(9): 1433-1440.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.04.007 pmid: 21539912 |
| [31] |
Hong AW, Meng ZP, Guan KL. The Hippo pathway in intestinal regeneration and disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 13(6): 324-337.
doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.59 pmid: 27147489 |
| [32] |
Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry[J]. Mol Syst Biol, 2007, 3: 89.
pmid: 17353931 |
| [33] |
Hutloff A, Dittrich AM, Beier KC, et al. ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28[J]. Nature, 1999, 397(6716): 263-266.
doi: 10.1038/16717 |
| [34] |
Simpson TR, Quezada SA, Allison JP. Regulation of CD4 T cell activation and effector function by inducible costimulator (ICOS)[J]. Curr Opin Immunol, 2010, 22(3): 326-332.
doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2010.01.001 pmid: 20116985 |
| [35] |
Carreno BM, Collins M. The B7 family of ligands and its receptors: new pathways for costimulation and inhibition of immune responses[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2002, 20: 29-53.
pmid: 11861596 |
| [36] |
Villegas EN, Lieberman LA, Mason N, et al. A role for inducible costimulator protein in the CD28-independent mechanism of resistance to Toxoplasma gondii[J]. J Immunol, 2002, 169(2): 937-943.
pmid: 12097399 |
| [37] |
Wilson EH, Zaph C, Mohrs M, et al. B7RP-1-ICOS interactions are required for optimal infection-induced expansion of CD4+ Th1 and Th2 responses[J]. J Immunol, 2006, 177(4): 2365-2372.
pmid: 16887998 |
| [38] |
O’Brien CA, Batista SJ, Still KM, et al. IL-10 and ICOS differentially regulate T cell responses in the brain during chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection[J]. J Immunol, 2019, 202(6): 1755-1766.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801229 |
| [39] |
Suzuki Y, Lutshumba J, Chen KC, et al. IFN-γ production by brain-resident cells activates cerebral mRNA expression of a wide spectrum of molecules critical for both innate and T cell-mediated protective immunity to control reactivation of chronic infection with Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2023, 13: 1110508.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1110508 |
| [1] | ZHENG Guangfu, LIU Xianbing, JIANG Yuzhu, LI Xinyu, HU Xuemei, ZHANG Haixia. Imvolvement of placental neutrophils and IL-17 in adverse pregnancy outcome caused by Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnant mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(1): 48-54. |
| [2] | XUE Yushan, LIN Ping, CHENG Xunjia, FENG Meng. Damage caused by chronic infection of Toxoplasma gondii on the host central nervous system and its mechanism [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 527-531. |
| [3] | JIANG Wenjing, MENG Yali, ZHAO Lina, WANG Chunmiao, ZHANG Xiaolei. Immunoprotection of nuclei acid vaccine dual-targeting rhoptry protein 18 and surface antigen 30 of Toxoplasma gondii in mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 532-538. |
| [4] | LIANG Kejia, LIU Cong, LI Yanlin, LI Xiaoge, LIU Yan, LI Zhenkui. Research advances on transcriptional regulation in plasmodium sexual stages [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 619-624. |
| [5] | ZHAO Ziqi, LV Fangli. Study on the inhibitory effect of artemether liposome on Toxoplasma gondii proliferation in vitro [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 446-451. |
| [6] | ZHANG Chi, CHEN Jiating, XIN Zixuan, YANG Lili, YANG Zihan, PENG Hongjuan. Transcriptome analysis of mice brain chronically infected with Toxoplasma gondii and validation of the kynurenine pathway associated with depression [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 270-278. |
| [7] | OU Yangran, LIU Xingzhuo, HUANG Shiguang, LYU Fangli. Effect of locking galectin-receptor interaction on the immunopathology of small intestine of Toxoplasma gondii-infected mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 279-285. |
| [8] | XU Shaojie, CHEN Shenbo, CHEN Junhu. Research progress on transcription regulation of rif gene in Plasmodium falciparum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 374-379. |
| [9] | DU Juan, LI Jia, WU Di, YU Qi, ZHANG Wei, BAI Runian, GUO Junlin, LIU Qingbin, LEI Qili, GU Chuanhui, WANG Meng, ZHAO Haojun. Seroepidemiological survey of Toxoplasma gondii infection in dogs and cats in Beijing 2022 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 389-392. |
| [10] | LI Jia-ming, WANG Yi-xuan, YANG Ning-ai, MA Hui-hui, LAN Min, LIU Chun-lan, ZHAO Zhi-jun. Effects of ROP16 protein of Toxoplasma gondii on polarization and apoptosis of MH-S cells and their related mechanisms [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 579-586. |
| [11] | ZOU Wei-hao, WU Wei-ling, LIAO Yuan-peng, CHEN Min, PENG Hong-juan. Preparation and application of monoclonal antibody against Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoite antigen 1 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 587-593. |
| [12] | DAI Li-sha, ZHANG Li-xin, YIN Kun. Research advances in Toxoplasma gondii induced host mental-behavioural disorders [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 642-646. |
| [13] | WANG Ting, YANG Qing-li, LENG Jing, LI Bao-ying, SHEN Ji-qing, DAI Yue. Expression of the high mobility group box 1 homologous protein of Clonorchis sinensis and its effect on nuclear transcription factor-κB activation in mouse macrophages [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 305-308. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yi-long, YE Run, LE Bin, CHEN Wen-zhu, PAN Wei-qing, ZHANG Dong-mei. A reverse transcriptase aid-enzymatic recombinase isothermal amplification-based method for detection of West Nile virus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 344-348. |
| [15] | WANG Jie, WEN Hong-yang, CHEN Ying, AN Ran, LUO Qing-li, SHEN Ji-long, DU Jian. Construction and identification of macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene knockout strain of Toxoplasma gondii [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 349-354. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||