
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 532-538.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2023.05.002
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIANG Wenjing( ), MENG Yali, ZHAO Lina, WANG Chunmiao, ZHANG Xiaolei*(
), MENG Yali, ZHAO Lina, WANG Chunmiao, ZHANG Xiaolei*( )
)
Received:2023-03-21
Revised:2023-05-10
Online:2023-10-30
Published:2023-11-06
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:CLC Number:
JIANG Wenjing, MENG Yali, ZHAO Lina, WANG Chunmiao, ZHANG Xiaolei. Immunoprotection of nuclei acid vaccine dual-targeting rhoptry protein 18 and surface antigen 30 of Toxoplasma gondii in mice[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 532-538.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2023.05.002
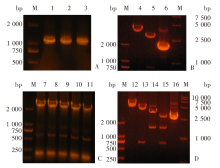
Fig. 2
PCR and enzyme digestion identification of recombinant plasmids pVAX1-p30 and pVAX1-rop18-p30 A, B: PCR and restriction enzymes identification of pVAX1-p30; C, D: PCR and restriction enzymes identification of of pVAX1-rop18-p30. M: DNA marker; 1-3: Monoclony of pVAX1-p30; 4-5: NheⅠsingle enzyme digestion, NheⅠ and AflⅡdouble enzyme digestion of pVAX1-p30; 6: Plasmid of pVAX1-p30; 7-11: Monoclony of pVAX1-rop18-p30; 12-15: NheⅠsingle enzyme digestion; NheⅠ and AflⅡ double enzyme digestion; HindⅢ and BamHⅠdouble enzyme digestion; Nhe Ⅰ, AflⅡ, HindⅢ and BamHⅠenzyme digestion of pVAX1-rop18-p30; 16: Plasmid pVAX1-rop18-p30.
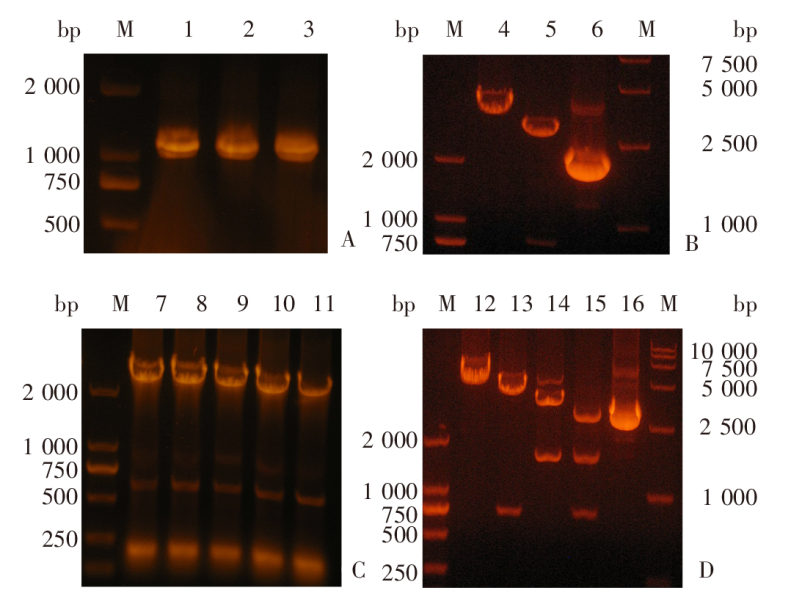
Table 1
Antibody levels in mouse serum before and after immunization with pVAX1-rop18-p30, pVAX1-p30, pVAX1-rop18 nucleic acid vaccine detected by ELISA (A450 value)
| 组别 Group | 免疫前 Before immunization | 免疫后13 d 13 d post-immunization | 免疫后27 d 27 d post-immunization | 免疫后41 d 41 d post-immunization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pVAX1-rop18-p30组 pVAX1-rop18-p30 group | 0.107 ± 0.022 | 0.136 ± 0.016 | 0.329 ± 0.027a | 0.788 ± 0.025a,b |
| pVAX1-rop18组 pVAX1-rop18 group | 0.108 ± 0.024 | 0.134 ± 0.031 | 0.315 ± 0.024a | 0.512 ± 0.027a |
| pVAX1-p30组 pVAX1-p30 plasmid group | 0.107 ± 0.018 | 0.143 ± 0.024 | 0.290 ± 0.082a | 0.498 ± 0.027a |
| pVAX1组 pVAX1 group | 0.106 ± 0.021 | 0.119 ± 0.019 | 0.124 ± 0.021 | 0.122 ± 0.014 |
| PBS组 PBS group | 0.108 ± 0.012 | 0.113 ± 0.023 | 0.110 ± 0.010 | 0.109 ± 0.011 |
| [1] |
Mutka T, Seyfang A, Yoo JY, et al. Adverse pregnancy outcomes in Toxoplasma gondii seropositive Hispanic women[J]. J Obstet Gynaecol Res, 2023, 49(3): 893-903.
doi: 10.1111/jog.v49.3 |
| [2] |
Wang JL, Zhang NZ, Li TT, et al. Advances in the development of anti-Toxoplasma gondii vaccines: challenges, opportunities, and perspectives[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2019, 35(3): 239-253.
doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2019.01.005 |
| [3] |
El Hajj H, Lebrun M, Fourmaux MN, et al. Inverted topology of the Toxoplasma gondii ROP5 rhoptry protein provides new insights into the association of the ROP2 protein family with the parasitophorous vacuole membrane[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2007, 9(1): 54-64.
doi: 10.1111/cmi.2007.9.issue-1 |
| [4] | Anuradha B, Preethi C. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma IgG antibodies in HIV positive patients in and around Khammam, Telangana State[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2014, 8(9): DL01-DL02. |
| [5] |
Lopes AP, Granada S, Oliveira AC, et al. Toxoplasmosis in dogs: first report of Toxoplasma gondii infection in any animal species in Angola[J]. Pathog Glob Health, 2014, 108(7): 344-346.
doi: 10.1179/2047773214Y.0000000160 |
| [6] |
Luo HQ, Li K, Zhang H, et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in zoo and domestic animals in Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Parasite, 2017, 24: 7.
doi: 10.1051/parasite/2017007 |
| [7] |
Nzelu IN, Kwaga JKP, Kabir J, et al. Detection and genetic characterisation of Toxoplasma gondii circulating in free-range chickens, pigs and seropositive pregnant women in Benue State, Nigeria[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2021, 15(6): e0009458.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009458 |
| [8] |
Kim K, Weiss LM. Toxoplasma: the next 100 years[J]. Microbes Infect, 2008, 10(9): 978-984.
doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2008.07.015 |
| [9] |
Boothroyd JC, Dubremetz JF. Kiss and spit: the dual roles of Toxoplasma rhoptries[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2008, 6(1): 79-88.
pmid: 18059289 |
| [10] | Zhang X, Gan XF, Cheng ZY, et al. Advances in the study of rhoptry proteins 2 of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. J Pathog Biol, 2015, 10(6): 574-576, 579. (in Chinese) |
| (张贤, 甘小凤, 程正阳, 等. 弓形虫棒状体蛋白2家族成员研究进展[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2015, 10(6): 574-576, 579.) | |
| [11] |
Fentress SJ, Sibley LD. The secreted kinase ROP18 defends Toxoplasma’s border[J]. Bioessays, 2011, 33(9): 693-700.
doi: 10.1002/bies.201100054 pmid: 21773979 |
| [12] |
El Hajj H, Demey E, Poncet J, et al. The ROP2 family of Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry proteins: proteomic and genomic characterization and molecular modeling[J]. Proteomics, 2006, 6(21): 5773-5784.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1615-9861 |
| [13] |
Yuan ZG, Zhang XX, Lin RQ, et al. Protective effect against toxoplasmosis in mice induced by DNA immunization with gene encoding Toxoplasma gondii ROP18[J]. Vaccine, 2011, 29(38): 6614-6619.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.06.110 |
| [14] | Xu TJ, Li YK, Lin XL, et al. Effect of molecular adjuvant Ov-ASP-1 on SAG1 nucleic acid vaccine of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Heilongjiang Anim Sci Vet Med, 2019(5): 118-122. (in Chinese) |
| (徐焘杰, 李元凯, 林霞琳, 等. 分子佐剂Ov-ASP-1对弓形虫SAG1核酸疫苗的影响[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2019(5): 118-122.) | |
| [15] |
Debard N, Buzoni-Gatel D, Bout D. Intranasal immunization with SAG1 protein of Toxoplasma gondii in association with cholera toxin dramatically reduces development of cerebral cysts after oral infection[J]. Infect Immun, 1996, 64(6): 2158-2166.
doi: 10.1128/iai.64.6.2158-2166.1996 pmid: 8675321 |
| [16] |
Nielsen HV, Lauemøller SL, Christiansen L, et al. Complete protection against lethal Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice immunized with a plasmid encoding the SAG1 gene[J]. Infect Immun, 1999, 67(12): 6358-6363.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.12.6358-6363.1999 pmid: 10569750 |
| [17] | Qi NS, Sun MF, Liao SQ, et al. Invasion-associated factors of apicomplexa[J]. Chin J Anim Vet Sci, 2012, 43(2): 167-174. (in Chinese) |
| (戚南山, 孙铭飞, 廖申权, 等. 顶复门原虫入侵相关因子的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2012, 43(2): 167-174.) | |
| [18] | Li B, Wei F, Liu Q, et al. Construction and identification of Toxoplasma gondii ROP18 in transgenic Leishmania tarentolae[J]. Prog Vet Med, 2012, 33(2): 1-4. (in Chinese) |
| (李博, 魏峰, 刘全, 等. 弓形虫ROP18基因重组蜥蜴利什曼原虫的构建及鉴定[J]. 动物医学进展, 2012, 33(2): 1-4.) | |
| [19] |
Garcia JL. Vaccination concepts against Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Expert Rev Vaccines, 2009, 8(2): 215-225.
doi: 10.1586/14760584.8.2.215 pmid: 19196201 |
| [20] |
Chen J, Li ZY, Petersen E, et al. DNA vaccination with genes encoding Toxoplasma gondii antigens ROP5 and GRA15 induces protective immunity against toxoplasmosis in Kunming mice[J]. Expert Rev Vaccines, 2015, 14(4): 617-624.
doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.1011133 pmid: 25749394 |
| [21] | Guo LL, Zhang XL, Zhang JS, et al. Construction of eukaryotic expression vector containing rop18-rop12 of Toxoplasma gondii RH strain[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2015, 33(3): 161-166. (in Chinese) |
| (郭玲玲, 张晓磊, 张进顺, 等. 刚地弓形虫RH株rop18-rop12复合基因真核表达载体的构建[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2015, 33(3): 161-166.) | |
| [22] | Liu RR, Zhang XL, Zhang JS, et al. Construction and identification of a dual promoter eukaryotic expression vector for rop10 and rop18 of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. J Pathog Biol, 2018, 13(6): 612-616. (in Chinese) |
| (刘荣荣, 张晓磊, 张进顺, 等. 刚地弓形虫rop10-rop18真核表达载体的构建与鉴定[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2018, 13(6): 612-616.) | |
| [23] | Zhao HZ, Li LH, Song ZX, et al. Research progress of genetic engineering vaccine for Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Hubei J Anim Vet Sci, 2019, 40(4): 10-12. (in Chinese) |
| (赵海忠, 李良华, 宋忠旭, 等. 弓形虫基因工程疫苗研究进展[J]. 湖北畜牧兽医, 2019, 40(4): 10-12.) | |
| [24] |
Kalef DA. Leishmania mexicana recombinant filamentous acid phosphatase as carrier for Toxoplasma gondii surface antigen 1 expression in Leishmania tarentolae[J]. J Parasi Dis, 2021, 45(4): 1135-1144.
doi: 10.1007/s12639-021-01413-x |
| [25] | Zhan GQ, Wu ST, Li GG, et al. Study on the cellular immune responses induced by p30 DNA vaccine of Toxoplasma gondii in mice[J]. Chin J Parasit Dis Contr, 2001(4): 257-259. (in Chinese) |
| (占国清, 吴少庭, 李国光, 等. 弓形虫表面抗原p30 DNA疫苗免疫小鼠诱导细胞免疫应答的研究[J]. 中国寄生虫病防治杂志, 2001(4): 257-259.) | |
| [26] |
Angus CW, Klivington-Evans D, Dubey JP, et al. Immunization with a DNA plasmid encoding the SAG1 (P30) protein of Toxoplasma gondii is immunogenic and protective in rodents[J]. J Infect Dis, 2000, 181(1): 317-324.
pmid: 10608781 |
| [27] | Zhuang HH, Pan LT, Yao CQ, et al. Preparation of Toxoplasma gondii SAG1 recombinant antibody and identification of its epitope[J]. Chin J Vet Sci, 2021, 41(6): 1080-1085, 1104. (in Chinese) |
| (庄浩瀚, 潘灵韬, 姚晨倩, 等. 弓形虫SAG1重组抗体制备及抗原表位鉴定[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2021, 41(6): 1080-1085, 1104.) | |
| [28] | Zhao HG, Fan ZG, Huang FY, et al. Immune response in mice induced by complex gene vaccine pcSAG1-ROP5 of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2013, 31(1): 1-5. (in Chinese) |
| (赵焕阁, 范志刚, 黄风迎, 等. 弓形虫复合基因疫苗pcSAG1-ROP5诱导小鼠免疫应答的研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2013, 31(1): 1-5.) | |
| [29] | Qi TN, Shi C, Wang ZY, et al. Construction and expression of eukaryotic expression recombinant plasmid of SAG1-GRA1 gene of Toxoplasma gondii[J]. J Guizhou Med Univ, 2020, 45(3): 286-291. (in Chinese) |
| (綦廷娜, 石畅, 汪政勇, 等. 弓形虫SAG1-GRA1复合基因真核表达重组质粒的构建与表达[J]. 贵州医科大学学报, 2020, 45(3): 286-291.) | |
| [30] |
Wu LM, Yang HJ, Wang JL, et al. A novel combined DNA vaccine encoding Toxoplasma gondii SAG1 and ROP18 provokes protective immunity against a lethal challenge in mice[J]. Acta Parasitol, 2021, 66(4): 1387-1395.
doi: 10.1007/s11686-021-00415-2 |
| [31] | Ni XT. Construction of recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum expressing ROP18 and SAG1 and their protective efficacy against Toxoplasma gondii infection[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2016: 30-36. (in Chinese) |
| (倪晓婷. 弓形虫ROP18和SAG1乳酸杆菌活载体疫苗株的构建及其免疫效果评价[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2016: 30-36.) |
| [1] | XUE Yushan, LIN Ping, CHENG Xunjia, FENG Meng. Damage caused by chronic infection of Toxoplasma gondii on the host central nervous system and its mechanism [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 527-531. |
| [2] | ZHAO Ziqi, LV Fangli. Study on the inhibitory effect of artemether liposome on Toxoplasma gondii proliferation in vitro [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 446-451. |
| [3] | ZHANG Chi, CHEN Jiating, XIN Zixuan, YANG Lili, YANG Zihan, PENG Hongjuan. Transcriptome analysis of mice brain chronically infected with Toxoplasma gondii and validation of the kynurenine pathway associated with depression [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 270-278. |
| [4] | OU Yangran, LIU Xingzhuo, HUANG Shiguang, LYU Fangli. Effect of locking galectin-receptor interaction on the immunopathology of small intestine of Toxoplasma gondii-infected mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 279-285. |
| [5] | DU Juan, LI Jia, WU Di, YU Qi, ZHANG Wei, BAI Runian, GUO Junlin, LIU Qingbin, LEI Qili, GU Chuanhui, WANG Meng, ZHAO Haojun. Seroepidemiological survey of Toxoplasma gondii infection in dogs and cats in Beijing 2022 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 389-392. |
| [6] | LI Jia-ming, WANG Yi-xuan, YANG Ning-ai, MA Hui-hui, LAN Min, LIU Chun-lan, ZHAO Zhi-jun. Effects of ROP16 protein of Toxoplasma gondii on polarization and apoptosis of MH-S cells and their related mechanisms [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 579-586. |
| [7] | ZOU Wei-hao, WU Wei-ling, LIAO Yuan-peng, CHEN Min, PENG Hong-juan. Preparation and application of monoclonal antibody against Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoite antigen 1 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 587-593. |
| [8] | DAI Li-sha, ZHANG Li-xin, YIN Kun. Research advances in Toxoplasma gondii induced host mental-behavioural disorders [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 642-646. |
| [9] | WANG Jie, WEN Hong-yang, CHEN Ying, AN Ran, LUO Qing-li, SHEN Ji-long, DU Jian. Construction and identification of macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene knockout strain of Toxoplasma gondii [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 349-354. |
| [10] | WANG Zhen-xun, XIONG Si-si, SUN Xia-hui, WANG Yong-liang, PAN Ge, HE Shen-yi, CONG Hua. Differential expression and action mechanism of lncRNA102796 in the brain of mice with chronic infection of Toxoplasma gondii [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 187-193. |
| [11] | JIANG Feng, CHEN Run, DU Ning-ning, ZHU Meng-yi, ZHONG Hao, CHEN Hui, XI Xu-xia, ZHAN Xiao-dong, LI Chao-pin. Investigation of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pet dogs and cats in Wuhu City [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(1): 124-126. |
| [12] | LU Fei, ZHUO Xun-hui, LU Shao-hong. Research progress on the interaction between host cell autophagy and apicomplexa protozoa infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 826-831. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xiao-han, FENG Ying, CHEN Ran, SANG Xiao-yu, YANG Na. Advances in research of structure, function and regulatory mechanism of Toxoplasma gondii conoid [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 832-835. |
| [14] | WANG Long-jiang, LI Jin, YIN Kun, XU Chao, LIU Gong-zhen, HUANG Bing-cheng, WEI Qing-kuan, SUN Hui. Comparative analysis of transcriptomes in Toxoplasma gondii before and after invasion in human foreskin fibroblasts [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 480-486. |
| [15] | LIAO Wen-zhong, XU Li-qing, YAO Li-jie, CHEN Min, PENG Hong-juan. Characterization of ubiquitinated protein profile change in host cells caused by Toxoplasma gondii infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 487-493. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||