
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 43-49.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.01.006
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHAO Han1( ), LI Si-yuan1, LI Jun2,*(
), LI Si-yuan1, LI Jun2,*( )
)
Received:2021-06-18
Revised:2021-07-25
Online:2022-02-28
Published:2022-01-13
Contact:
LI Jun
E-mail:1257460268@qq.com;xjlijun@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
SHAO Han, LI Si-yuan, LI Jun. The affect of metformin on autophagy and apoptosis of Echinococcus multilocularis cysts and protoscoleces[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(1): 43-49.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.01.006
Fig. 1
Affects of different metformin concentrations on the viability of Echinococcus multilocularis cysts(× 100) A, E: Control group; B-D: after 24 h of co-cultivation, the apoptotic cells in the cysts and the cysts turbidity increases as the concentration of metformin increases; F-H: after 48 h of co-cultivation, the cysts are less viable as metformin concentration increases and the formation of apoptotic bodies can be seen when metformin concentration reaches 10 mmol/L.
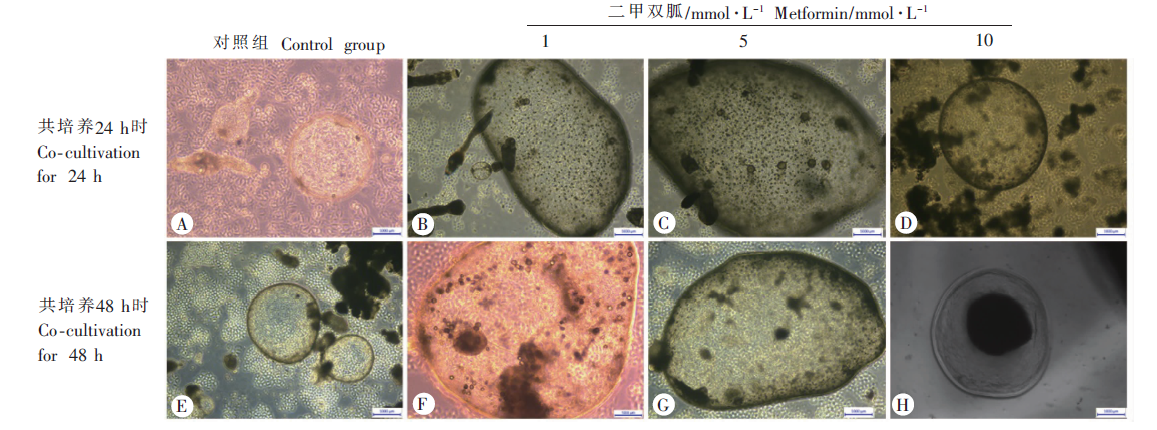
Fig. 2
Affect of different concentrations of metformin on the viability of protoscoleces of E. multilocularis (HE staining, × 100) A, E: Control group; B-D: After 24 h of co-cultivation, the proportion of red stained protoscoleces increases with the concentration of metformin; F-H: After co-cultivation with metformin for 48 h, the viability of protoscoleces reduced as the concentration of metformin increases, and all protoscoleces showed red-stained in the 10 mmol/L group.
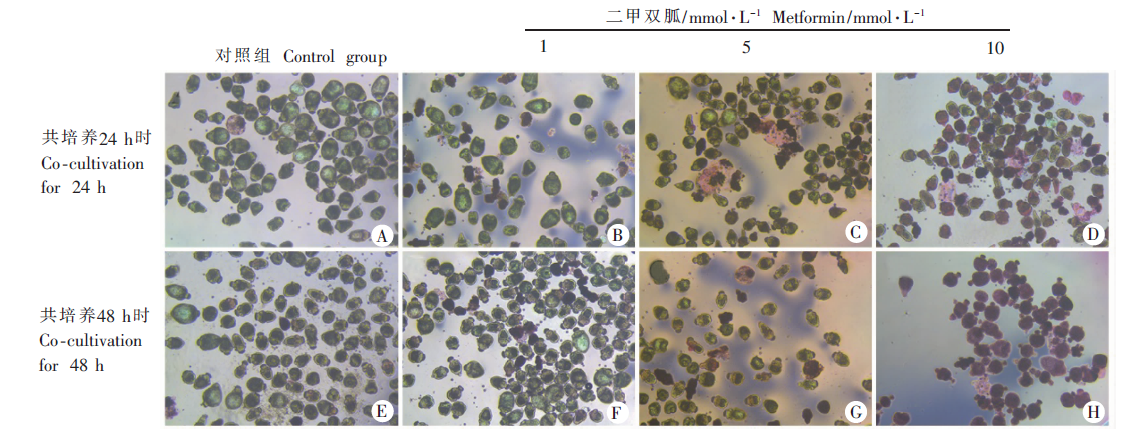
Table 1
Expression of apoptotic proteins in E. multilocularis cysts and protoscoleces after treatment by metformin at different concentrations
| 蛋白Protein | 相对表达量 Relative expression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mmol/L二甲双胍 1 mmol/L Metformin | 5 mmol/L二甲双胍 5 mmol/L Metformin | 10 mmol/L二甲双胍 10 mmol/L Metformin | 对照组 Control group | |
| 囊泡 Vesicles B细胞淋巴瘤/白血病-2 Bcl-2 | 0.82 ± 0.05 | 0.89 ± 0.02 | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 1.09 ± 0.07 |
| 剪切的半胱氨酸肽酶3 Cleaved-caspase3 | 1.00 ± 0.09 | 1.34 ± 0.06 | 1.61 ± 0.05 | 0.67 ± 0.01 |
| 半胱氨酸肽酶9 Caspase9 | 0.94 ± 0.02 | 1.03 ± 0.11 | 0.78 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.05 |
| 原头节Protoscoleces B细胞淋巴瘤/白血病-2 Bcl-2 | 1.05 ± 0.12 | 0.60 ± 0.06 | 0.84 ± 0.12 | 1.55 ± 0.12 |
| 剪切的半胱氨酸肽酶3 Cleaved-caspase3 | 0.66 ± 0.09 | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | 0.46 ± 0.07 |
| 半胱氨酸肽酶9 Caspase9 | 0.72 ± 0.02 | 0.75 ± 0.05 | 0.97 ± 0.10 | 0.54 ± 0.07 |
Table 2
The expression of AMPK pathway-related proteins and autophagy-related proteins after E. multilocularis cysts and protoscoleces were treated with metformin at different concentrations
| 蛋白 Protein | 相对表达量 Relative expression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mmol/L二甲双胍 1 mmol/L Metformin | 5 mmol/L二甲双胍 5 mmol/L Metformin | 10 mmol/L二甲双胍 10 mmol/L Metformin | 对照组 Control group | |
| 囊泡 Vesicles 蛋白轻链3Ⅱ LC3-Ⅱ | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 0.86 ± 0.13 | 1.07 ± 0.06 | 0.75 ± 0.10 |
| 自噬基因14 Atg14 | 1.28 ± 0.21 | 1.33 ± 0.23 | 1.44 ± 0.23 | 0.52 ± 0.14 |
| 雷帕霉素机械靶蛋白 mTOR | 1.47 ± 0.27 | 1.42 ± 0.25 | 1.58 ± 0.31 | 0.63 ± 0.11 |
| 磷酸化的一磷酸腺苷依赖的蛋白激酶 P-AMPK | 0.77 ± 0.11 | 0.83 ± 0.12 | 0.69 ± 0.11 | 0.53 ± 0.09 |
| 原头节 Protoscoleces 蛋白轻链3Ⅱ LC3-Ⅱ | 0.84 ± 0.14 | 1.45 ± 0.23 | 1.68 ± 0.24 | 0.33 ± 0.07 |
| 自噬基因14 Atg14 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 1.16 ± 0.10 | 1.33 ± 0.11 | 0.55 ± 0.09 |
| 雷帕霉素机械靶蛋白 mTOR | 1.10 ± 0.02 | 1.49 ± 0.11 | 1.25 ± 0.03 | 0.59 ± 0.06 |
| 磷酸化的一磷酸腺苷依赖的蛋白激酶 P-AMPK | 1.18 ± 0.09 | 1.52 ± 0.09 | 1.27 ± 0.19 | 0.20 ± 0.01 |
| [1] | Wen H, Vuitton L, Tuxun T, et al. Echinococcosis: advances in the 21st century[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2019, 32(2): 1-2. |
| [2] |
Siles-Lucas M, Casulli A, Cirilli R, et al. Progress in the pharmacological treatment of human cystic and alveolar echinococcosis: compounds and therapeutic targets[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2018, 12(4): e0006422.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006422 |
| [3] |
Stojkovic M, Mickan C, Weber TF, et al. Pitfalls in diagnosis and treatment of alveolar echinococcosis: a sentinel case series[J]. BMJ Open Gastroenterol, 2015, 2(1): e000036.
doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2015-000036 |
| [4] |
Spiliotis M, Lechner S, Tappe D, et al. Transient transfection of Echinococcus multilocularis primary cells and complete in vitro regeneration of metacestode vesicles[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2008, 38(8/9): 1025-1039.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.11.002 |
| [5] | Spiliotis M, Brehm K. Axenic in vitro cultivation of Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode vesicles and the generation of primary cell cultures[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2009, 470(1): 245-262. |
| [6] |
Flory J, Lipska K. Metformin in 2019[J]. JAMA, 2019, 321(19): 1926-1927.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.3805 |
| [7] |
Harati R, Vandamme M, Blanchet B, et al. Drug-drug interaction between metformin and sorafenib alters antitumor effect in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Mol Pharmacol, 2021, 100(1): 32-45.
doi: 10.1124/molpharm.120.000223 pmid: 33990407 |
| [8] |
Ashrafizadeh M, Mirzaei S, Hushmandi K, et al. Therapeutic potential of AMPK signaling targeting in lung cancer: advances, challenges and future prospects[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 278: 119649.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119649 pmid: 34043989 |
| [9] |
Koroglu-Aydn P, Bayrak BB, Bugan I, et al. Histological and biochemical investigation of the renoprotective effects of metformin in diabetic and prostate cancer model[J]. Toxicol Mech Methods, 2021, 31(7): 489-500.
doi: 10.1080/15376516.2021.1919810 |
| [10] |
Alhourani AH, Tidwell TR, Bokil AA, et al. Metformin treatment response is dependent on glucose growth conditions and metabolic phenotype in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 1-10.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79139-8 |
| [11] |
Wang Z, Guo JJ, Han XQ, et al. Metformin represses the pathophysiology of AAA by suppressing the activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/autophagy pathway in ApoE(-/-) mice[J]. Cell Biosci, 2019, 9(1): 1-15.
doi: 10.1186/s13578-018-0263-x |
| [12] |
Guo LM, Cui J, Wang HR, et al. Metformin enhances anti-cancer effects of cisplatin in meningioma through AMPK-mTOR signaling pathways[J]. Mol Ther Oncolytics, 2021, 20: 119-131.
doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.11.004 |
| [13] |
Ouyang JY, Parakhia RA, Ochs RS. Metformin activates AMP kinase through inhibition of AMP deaminase[J]. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(1): 1-11.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.121806 |
| [14] |
Zheng LY, Yang W, Wu FQ, et al. Prognostic significance of AMPK activation and therapeutic effects of metformin in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(19): 5372-5380.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0203 |
| [15] | Loos JA, Dávila VA, Brehm K, et al. Metformin suppresses development of the Echinococcus multilocularis larval stage by targeting the TOR pathway[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2020, 64(9): e01808-e01827. |
| [16] |
Brehm K, Wolf M, Beland H, et al. Analysis of differential gene expression in Echinococcus multilocularis larval stages by means of spliced leader differential display[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2003, 33(11): 1145-1159.
doi: 10.1016/S0020-7519(03)00169-3 |
| [17] |
Hemer S, Brehm K. In vitro efficacy of the anticancer drug imatinib on Echinococcus multilocularis larvae[J]. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2012, 40(5): 458-462.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.07.007 |
| [18] |
Stadelmann B, Aeschbacher D, Huber C, et al. Profound activity of the anti-cancer drug bortezomib against Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes identifies the proteasome as a novel drug target for cestodes[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2014, 8(12): e3352.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003352 |
| [19] | Cheng Z, Xu Z, Tian H, et al. In vitro and efficacies of inhibitors of the EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling in the treatment of alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Antimicro Agents Chemo, 2020, 64(8): 234-236. |
| [20] |
Saraei P, Asadi I, Kakar MA, et al. The beneficial effects of metformin on cancer prevention and therapy: a comprehensive review of recent advances[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11: 3295-3313.
doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S200059 pmid: 31114366 |
| [21] |
Sanli T, Steinberg GR, Singh G, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) beyond metabolism[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2014, 15(2): 156-169.
doi: 10.4161/cbt.26726 |
| [22] |
Jia JY, Bissa B, Brecht L, et al. AMPK, a regulator of metabolism and autophagy, is activated by lysosomal damage via a novel galectin-directed ubiquitin signal transduction system[J]. Mol Cell, 2020, 77(5): 951-969.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.12.028 |
| [23] |
Zaidi S, Gandhi J, Joshi G, et al. The anticancer potential of metformin on prostate cancer[J]. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis, 2019, 22(3): 351-361.
doi: 10.1038/s41391-018-0085-2 |
| [24] |
Fan H, Yu X, Zou Z, et al. Metformin suppresses the esophageal carcinogenesis in rats treated with NMBzA through inhibiting AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2019, 40(5): 669-679.
doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy160 |
| [25] |
Lee J, Hong EM, Kim JH, et al. Metformin induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation through the AMP-activated protein kinase and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor pathways in the bile duct cancer cells[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(7): 1734-1744.
doi: 10.7150/jca.26380 |
| [26] |
Guillermo M, Mireia NS, Eric HB, et al. Self-consumption: the interplay of autophagy and apoptosis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2014, 15(2): 81-90.
doi: 10.1038/nrm3735 |
| [27] |
Wang Y, Zhang YF, Feng XM, et al. Metformin inhibits mTOR and c-Myc by decreasing YAP protein expression in OSCC cells[J]. Oncol Rep, 2021, 45(3): 1249-1260.
doi: 10.3892/or |
| [28] | Yang HC, Zhang HW, Shi KJ, et al. Autocrine osteopontin promotes the growth and metastasis of Echinococcus multilocu-laris via the EGFR signaling pathway[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2021, 39(2): 226-232. (in Chinese) |
| (杨海成, 张宏伟, 史康杰, 等. 自分泌骨桥蛋白通过EGFR信号通路促进多房棘球蚴生长和转移的研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(2): 226-232.) | |
| [29] | Tan XW, Yu XF, Jiang HQ, et al. Inhibitory effect of xanthohumol on the growth of Echinococcus multilocularis[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2021, 39(3): 304-310. (in Chinese) |
| (谭小武, 俞晓凡, 姜慧娇, 等. 黄腐酚对小鼠肝多房棘球蚴生长的抑制作用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(3): 304-310.) |
| [1] | XU Gang, MAO Yi, LI Jiang, ZHANG Hongwei, ZHANG Yongguo, WU Xiangwei, PENG Xinyu, SUN Hong, YANG Jing, CHEN Qian, ZHANG Shijie. Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode regulates its own growth through hepatic p38MAPK signaling pathway [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(4): 447-453. |
| [2] | GE Yufei, XU Gang, ZHANG Hongwei, LI Jiang, ZHANG Yongguo, SUN Hong, YANG Jing, ZHANG Shijie. Effect of all-trans tretinoic acid on the activity and growth of Echinococcus multilocularis protoscolices in vitro [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(3): 303-308. |
| [3] | DAWA Zhuoma, LIU Chuanchuan, FAN Haining. Research on the progress of programmed cell death in echinococcosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(2): 259-266. |
| [4] | KUI Yan, XUE Chuizhao, WANG Xu, LIU Baixue, WANG Ying, WANG Liying, YANG Shijie, HAN Shuai, XU Xuenian. Progress of echinococcosis control in China, 2022 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(1): 8-16. |
| [5] | ZHU Aiya, WANG Xu, WANG Jiangyou, WANG Ying, LI Yang, SONG Shan, GENG Yan, LAN Ziyao, DAI Jiarui. A child case of alveolar echinococcosis in Guizhou Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 520-523. |
| [6] | RAOWAN Tuolehong, ABUDUSALAMU Abulikemu, YANG Lingfei, CHEN Lu, LI Zhao, JIA Fang, SONG Tao. Effect evaluation and factor analysis of ultrasonic manifestations in the diagnosis of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 312-318. |
| [7] | KUI Yan, XUE Chuizhao, WANG Xu, LIU Baixue, WANG Ying, WANG Liying, YANG Shijie, HAN Shuai, WU Weiping, XIAO Ning. Progress of echinococcosis control in China, 2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 142-148. |
| [8] | MA Hui, CHONG Shigui, CHEN Gen, ZHANG Linghui, QIN Junmei, ZHAO Yumin. Research progress on the cellular signal pathways associated in alveolar echinococcosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 223-227. |
| [9] | AN Xiu-qing, WANG Miao-miao, ZHOU Hong-qian, MENG Kai, CAI Jian-ping, LIU Guang-hui, A Ji-de, YANG Jing-yu. Research progress on microvascular density in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 792-797. |
| [10] | LI Jia-ming, WANG Yi-xuan, YANG Ning-ai, MA Hui-hui, LAN Min, LIU Chun-lan, ZHAO Zhi-jun. Effects of ROP16 protein of Toxoplasma gondii on polarization and apoptosis of MH-S cells and their related mechanisms [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 579-586. |
| [11] | ZHANG Ting-ting, DU Qiu-pei, GUO Xin-jian, ZHANG Ling-qiang, WANG Zhi-xin, CHANG Zheng-song, ZHAO Qian, WANG Hai-jiu, HOU Li-zhao. Research progress on vascular invasion of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 516-523. |
| [12] | WU Liang-liang, YANG Ling-fei, SONG Tao. Ultrasound and pathological manifestations of lesions in SD rats with hepatic Echinococcus multilocularis infection established by different methods [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 549-552. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ling-hui, CHEN Gen, CHONG Shi-gui, SHEN Hui, MA Hui, ZHAO Yu-min. Research progress on the immune regulation mechanism in alveolar echinococcosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(1): 109-113. |
| [14] | LU Fei, ZHUO Xun-hui, LU Shao-hong. Research progress on the interaction between host cell autophagy and apicomplexa protozoa infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 826-831. |
| [15] | ZHOU Wen-zheng, SUN Jun-gang, ZHAO Xi-bin, CAO Li. Therapeutic effect of intensity modulated radiation therapy on secondary femur infection with Echinococcus granulosus in rats [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 443-448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||