
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 68-74.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2023.01.010
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yaoguang( ), JIANG Li*(
), JIANG Li*( ), WANG Zhenyu, ZHU Min, ZHU Qian, MA Xiaojiang, YU Qing, Chen Jian
), WANG Zhenyu, ZHU Min, ZHU Qian, MA Xiaojiang, YU Qing, Chen Jian
Received:2022-06-10
Revised:2022-10-11
Online:2023-02-28
Published:2023-02-27
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHANG Yaoguang, JIANG Li, WANG Zhenyu, ZHU Min, ZHU Qian, MA Xiaojiang, YU Qing, Chen Jian. Analysis of the causes of misdiagnosis of seven imported malaria cases in Shanghai from 2020 to 2021[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 68-74.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2023.01.010
Table 1
Results reported by the district CDCs of Shanghai, 2020—2021
| 区 Districts | 样品数 Total samples | 阳性样品数 Positive samples | 阴性样品数 Negative samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 恶性疟原虫 P. falciparum | 间日疟原虫 P. vivax | 卵形疟原虫 P. ovale | 三日疟原虫 P. malariae | |||
| 浦东 Pudong | 23 | 18 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| 闵行 Minhang | 21 | 20 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 嘉定 Jiading | 12 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 松江 Songjiang | 10 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 宝山 Baoshan | 8 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 青浦 Qingpu | 8 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 杨浦 Yangpu | 5 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 金山 Jinshan | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 静安 Jingan | 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 虹口 Hongkou | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 黄浦 Huangpu | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 长宁 Changning | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 奉贤 Fengxian | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 普陀 Putuo | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 崇明 Chongming | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 徐汇 Xuhui | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 合计 Total | 112 | 93 | 6 | 7 | 2 | 4 |
Table 2
The basic situation of seven imported malaria cases and the results of the municipal rechecking of the district CDCs
| 病例编号 Case code | 性别 Gender | 年龄 Age | 外出国家 Country visited | 归国时间 Return time | 此次发病时间 Onset time | 区级报告结果 Reported results of district CDC | 市级复核结果 Rechecked results of municipal CDC | 病例最终 确认结果 Ultimate outcome | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 镜检 Microscopic detection | PCR | 镜检 Microscopic detection | PCR | ||||||||
| 病例1 Case 1 | 男Male | 30 | 几内亚Guinea | 2020.8.7 | 2020.8.8 | (-) | - | Pf | Pf | Pf | |
| 病例2 Case 2 | 男Male | 64 | 几内亚Guinea | 2020.8.25 | 2020.8.27 | Pf | Pf | (-) | Pf | Pf | |
| 病例3 Case 3 | 男Male | 32 | 刚果布Congo | 2021.6.18 | 2021.7.6 | Po | (-) | Pm | Pm | Pm | |
| 病例4 Case 4 | 男Male | 31 | 几内亚Guinea | 2021.8.10 | 2021.8.17 | (-) | Pf | Pf | Pf | Pf | |
| 病例5 Case 5 | 男Male | 35 | 几内亚Guinea | 2021.9.16 | 2021.9.30 | (+) | (-) | Pm | Pm | Pm | |
| 病例6 Case 6 | 男Male | 53 | 几内亚Guinea | 2021.12.7 | 2021.12.9 | Pv | (-) | Po | Po | Po | |
| 病例7 Case 7 | 男Male | 37 | 几内亚Guinea | 2021.12.7 | 2021.12.10 | Pv | (-) | Po | Po | Po | |
Table 3
The condition of microscopic examination and quality of blood smears of seven imported malaria cases
| 病例编号 Case code | 疟原虫特征 The feature of Plasmodium | 血涂片质量 Quality of blood smears | 原虫密度计数(个/μL) Parasite counting (Parasite/μL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 病例1 Case 1 | 查见恶性疟环状体,核小而致密,胞质较稀疏 The ring form stage of P. falciparum was found, with small and dense nucleus and sparse cytoplasm | 无厚血膜 No thick blood membrane | 904a |
| 病例2 Case 2 | 未查见疟原虫,血片中可见豪焦小体 Parasites were not found, and Howell - Jolly bodies were found in blood smear | 良好 Fine | - |
| 病例3 Case 3 | 查见三日疟配子体和未成熟裂殖体,被寄生红细胞略缩小 The gametophytes and immature schizonites of P. malariae were found, and the parasitized red blood cells were slightly reduced in size | 良好 Fine | 1 486 |
| 病例4 Case 4 | 大部分疟原虫未能着色,仅查见疟原虫粉色细胞核,胞浆不可见 Most of the parasites failed to be stained, only the pink nucleus was found, and the cytoplasm was not visible | 染色过淡 Too light dyeing | 235 |
| 病例5 Case 5 | 查见三日疟小滋养体,原虫形态不典型,被寄生红细胞略缩小;厚血膜中查见“菊花状”裂殖体 It was found that the small trophozoites of P. malariae, the patterns were not typical, and the parasitized red blood cells were slightly reduced. “Chrysanthemum shaped”schizonites were found in thick blood membrane | 良好 Fine | 114 |
| 病例6 Case 6 | 查见卵形疟大滋养体,被寄生红细胞正常或略涨大,边缘呈彗星状、伞矢状拖尾 P. oval large trophozoites were found, and the parasitized red blood cells were normal or slightly enlarged, with comet-like and umbrella-sagittal | 良好 Fine | 2 182 |
| 病例7 Case 7 | 查见卵形疟大滋养体,被寄生红细胞正常或略涨大,边缘呈彗星状、伞矢状拖尾 P. oval large trophozoites were found, and the parasitized red blood cells were normal or slightly enlarged, with comet-like and umbrella-sagittal | 良好 Fine | 6 807 |
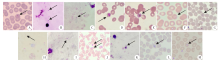
Fig. 2
Morphology of Plasmodium in blood smears of the seven imported malaria cases(Giemsa staining,× 1 000) A: P. falciparum ring form stage in thin blood smear of case 1; B: P. falciparum ring form stage in thick blood smear of case 1 (made by SCDC); C: Howell-Jolly body in thick blood smear of case 2; D: P. malariae gametocyte stage in thin blood smear of case 3; E: P. malariae immature schizont stage in thin blood smear of case 3; F: Suspected P. falciparum ring form stage in thin blood smear of case 4; G: P. falciparum ring form stage in re-staining thin blood smear of case 4; H: Suspected P. falciparum ring form stage in thick blood smear of case 4; I: P. falciparum ring form stage in re-staining thick blood smear of case 4; J: P. malariae small trophozoite stage in thin blood smear of case 5; K: P. malariae mature schizont stage in thick blood smear of case 5; L: P. ovale large trophozoite stage in thin blood smear of case 6; M: P. ovale large trophozoite stage in thin blood smear of case 7.
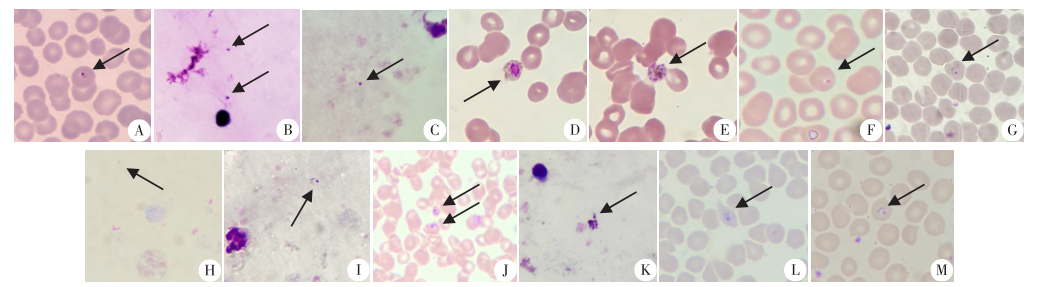
Table 4
DNA concentration and purity of imported malaria cases 3, 5, 6 and 7 from district and municipal CDC groups
| 病例编号 Case code | DNA浓度/ng·μl-1 DNA concentration/ng·μl-1 | A260/A280 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 市疾控 Municipal CDC | 区疾控 District CDC | 市疾控 Municipal CDC | 区疾控 District CDC | ||
| 病例3 Case 3 | 42.48 | 515.68 | 1.78 | 1.00 | |
| 病例5 Case 5 | 24.70 | 568.18 | 1.69 | 1.22 | |
| 病例6 Case 6 | 7.11 | 706.97 | 1.77 | 1.69 | |
| 病例7 Case 7 | 14.38 | 673.44 | 1.70 | 1.50 | |
|
| [1] | TANG Qi, LV Chao, WANG Xi, GUO Suying, XU Xiaojuan, ZHU Hai, LI Yinlong, LIN Weina, ZHOU Xinjie, FENG Ting, XU Jing, QIN Zhiqiang. Efficiency evaluation of three assays for detection of Schistosoma japonicum infections in wild mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(2): 186-191. |
| [2] | ZHANG Zhaoyu, JI Xingyu, WEN Lihai, WANG Caohaowei, JI Haitao, CHEN Huijie. Epidemiological characteristics of imported malaria in Shenyang, Liaoning Province from 2013 to 2022 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(4): 525-528. |
| [3] | GAN Liqin, LI Yuan, LIU Wuyi, LIANG Xiangsheng, HUANG Dana, GAO Shitong. Analysis of the epidemic characteristics of imported malaria in Longgang District, Shenzhen City, 2018-2023 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(4): 533-536. |
| [4] | HE Yisha, XIE Chaoyong, WANG Yu, LI Yanjing. The analysis of the epidemiological characteristics and the diagnosis of imported malaria before and after the COVID-19 pandemic in Nanjing City [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(2): 267-271. |
| [5] | YANG Shuo, XIA Shang, YAN Shuning, XUE Jingbo, SHI Benyun, HAO Yuwan, LI Mengru, LIANG Jiarui, XIA Zhigui, ZHENG Bin. Analysis on the sources of imported malaria risk in China based on international trade relations [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(6): 744-748. |
| [6] | LIU Jiancheng, XU Yan, WANG Longjiang, KONG Xiangli, WANG Yongbin, LI Yuejin. Surveillance on imported malaria in Linyi City of Shandong Province from 2015 to 2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 249-252. |
| [7] | JI Peng-hui, JIANG Tian-tian, HE Zhi-quan, ZHOU Rui-min, LI Su-hua, YANG Cheng-yun, QIAN Dan, LIU Ying, WANG Hao, ZHANG Hong-wei. Analysis on epidemiological characteristics of imported quartan malaria in Henan Province from 2011 to 2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 801-805. |
| [8] | SHI Guang-zhong, ZHANG Hai-ting, WANG Shuo, HE Hai-bo, CHEN Xia, MAMATJAN Umar, YU Lin, AYIXIAMU Keyoumu, ZHAO Jiang-shan. An imported case of ovale malaria in Xinjiang during the epidemic period of COVID-19 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 689-691. |
| [9] | LIU Su-zhen, JI Feng-ying, SHI Li-mei. Investigation of imported malaria cases at a COVID-19 isolation point in Qingdao [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 261-265. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xuan, RUAN Wei, WANG Xiao-xiao, CHEN Hua-liang, LU Qiao-yi, ZHANG Jia-qi, YU Ke-gen, YAO Li-nong. Epidemiological characteristics of imported severe malaria cases in Zhejiang Province from 2012—2020 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 466-472. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yao-guang, JIANG Li, WANG Zhen-yu, ZHU Min, ZHU Qian, MA Xiao-Jiang, WU Huan-yu. Laboratory diagnosis of two misdiagnosed imported Plasmodium ovale malaria cases in Shanghai [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 553-556. |
| [12] | ZHANG Yao-guang, JIANG Li, WANG Zhen-yu, ZHU Min, ZHU Qian, MA Xiao-jiang, WU Huan-yu. Analysis of malaria detection capability of laboratories in the districts of Shanghai during 2017—2019 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(3): 337-342. |
| [13] | CHEN Zhu-yun, OUYANG Rong, XIE Han-guo, LIN Yao-ying, XIAO Li-zhen, ZHANG Shan-ying. Epidemic status of imported malaria at different stages of malaria elimination in Fujian Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 702-708. |
| [14] | YANG He-xian, LI Jia-quan. Epidemic characteristics of imported malaria during 2013-2019 in Baoshan City, Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(5): 660-663. |
| [15] | LI Mei, XIA Zhi-gui, YIN Jian-hai, YAN He. Consideration and recommendations for malaria blood testing during the COVID-19 pandemic [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(4): 464-468. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||