
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2019, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 399-405.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2019.04.005
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ying DONG1,*( ), Shu-ping LIU1,2, Yan-chun XU1, Yan LIU1, Yan DENG1, Meng-ni CHEN1
), Shu-ping LIU1,2, Yan-chun XU1, Yan LIU1, Yan DENG1, Meng-ni CHEN1
Received:2019-01-28
Online:2019-08-30
Published:2019-09-05
Contact:
Ying DONG
E-mail:luxidongying@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
Ying DONG, Shu-ping LIU, Yan-chun XU, Yan LIU, Yan DENG, Meng-ni CHEN. Mutations and predicted structure change of G6PD isolated from a patient with primaquine-induced hemolysis in Yunnan Province[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(4): 399-405.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2019.04.005
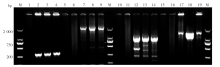
Fig. 1
PCR products of G6PD exon fragments amplified from the blood sample of a P. vivax infected patient with primaquine-induced hemolysis M: DNA marker; 1, 5, 10, 15: The 1st round PCR blank control (no template); 6, 11, 16: The 2nd round PCR blank control; 2-4: The PCR products of G6PD exon2; 7-9: The PCR products of G6PD exon3-7; 12-14: The PCR products of G6PD exon8-9; 17-19: The PCR products of G6PD exon10-13
Table 1
Model parameters of predicted 3D structure of G6PD identified from a hemolysis patient infected with P. vivax
| 氨基酸序列 | 二聚体Dimers | 四聚体Tetramers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acid sequence | 入模氨基酸范围Amino acid position | GMQE | QMEAN | 一致性/% Identity/% | 入模氨基酸范围Amino acid position | GMQE | QMEAN | 一致性/% Identity/% | |
| 参比模型Reference model | 6e07.1.A | 1qki.1.A | |||||||
| NC_000023.11 | 28-513 | 0.97 | -0.64 | 99.22 | 12-493 | 0.98 | -1.49 | 99.36 | |
| X55448.1 | 28-513 | 0.97 | -0.65 | 98.83 | 12-493 | 0.98 | -2.17 | 98.56 | |
| homo2608 | 28-513 | 0.97 | -0.66 | 99.42 | 12-493 | 0.98 | -2.26 | 99.19 | |
| [1] | Flannery EL, Chatterjee AK, Winzeler EA.Antimalarial drug discovery-approaches and progress towards new medicines[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2017, 15(9): 572. |
| [2] | WHO Malaria Policy Advisory Committee and Secretaria. Malaria policy advisory committee to the WHO: conclusions and recommendations of september 2012 meeting[J]. Malar J, 2012, 11: 424. |
| [3] | Assefa A, Ali A, Deressa W, et al. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency in Ethiopia: absence of common African and Mediterranean allelic variants in a nationwide study[J]. Malar J, 2018, 17: 388. |
| [4] | Ashley EA, Recht J, White NJ.Primaquine: the risks and the benefits[J]. Malar J, 2014, 13: 418. |
| [5] | Gonçalves BP, Tiono AB, Ouédraogo A, et al. Single low dose primaquine to reduce gametocyte carriage and Plasmodium falciparum transmission after artemether-lumefantrinein children with asymptomatic infection: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. BMC Med, 2016, 14: 40. |
| [6] | Domingo GJ, Satyagraha AW, Anvikar A, et al. G6PD testing in support of treatment and elimination of malaria: recommendations for evaluation of G6PD tests[J]. Malar J, 2013, 12: 391. |
| [7] | White NJ, Qiao LG, Qi G, et al. Rationale for recommending a lower dose of primaquine as a Plasmodium falciparum gametocytocide in populations where G6PD deficiency is common[J]. Malar J, 2012, 11: 418. |
| [8] | Kim S, Nguon C, Guillard B, et al. Performance of the CareStartTM G6PD deficiency screening test, a point-of-care diagnostic for pimaquine therapy screening[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(12): e28357. |
| [9] | Von Fricken ME, Weppelmann TA, Eaton WT, et al. Performance of the CareStart glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) rapid diagnostic test in Gressier[J]. Haiti Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2014, 91(1): 77-80. |
| [10] | Adu-Gyasi D, Asante KP, Newton S, et al. Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of CareStart G6PD deficiency rapid diagnostic test (RDT) in a malaria endemic area in Ghana, Africa[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0125796. |
| [11] | Howes RE, Dewi M, Piel FB, et al. Spatial distribution of G6PD deficiency variants across malaria-endemic regions[J]. Malar J, 2013, 12: 418. |
| [12] | Howes RE, Battle KE, Satyagraha AW, et al. G6PD deficiency: global distribution, genetic variants and primaquine therapy[J]. Adv Parasitol, 2013, 81: 133-201. |
| [13] | Howes RE, Piel FB, Patil AP, et al. G6PD deficiency prevalence and estimates of affected populations in malaria endemic countries: a geostatistical model-based map[J]. PLoS Med, 2012, 9(11): e1001339. |
| [14] | Tang TK, Huang CS, Huang MJ, et al. Diverse point mutations result in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) polymor-phism in Taiwan[J]. Blood, 1992, 79(8): 2135-2140. |
| [15] | Louicharoen C, Patin E, Paul R, et al. Positively selected G6PD-Mahidol mutation reduces Plasmodium vivax density in southeast Asians[J]. Science, 2009, 326(5959): 1546-1549. |
| [16] | Kuwahata M, Wijesinghe R, Ho MF, et al. Population screening for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiencies in Isabel Province, Solomon Islands, using a modified enzyme assay on filter paper dried bloodspots[J]. Malar J, 2010, 9: 223. |
| [17] | Vulliamy T, Luzzatto L, Hirono A, et al. Hematologically important mutation: glucosc-6-phosphate dehydrogenase[J]. Blood Cell Molecules Dis, 1997, 23(15): 302-313. |
| [18] | Filosa S, Fico A, Paglialunga F, et al. Failure to increase glucose consumption through the pentose-phosphate pathway results in the death of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene-deleted mouse embryonic stem cells subjected to oxidative stress[J]. Biochem J, 2003, 370(3): 935-943. |
| [19] | Carter N, Pamba A, Duparc S, et al. Frequency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in malaria patients from six African countries enrolled in two randomized anti-malarial clinical trials[J]. Malar J, 2011, 10: 241. |
| [20] | Ginsburg H, Atamna H, Shalmiev G, et al. Resistance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency to malaria: effects of fava bean hydroxypyrimidine glucosides on Plasmodium falciparum growth in culture and on the phagocytosis of infected cells[J]. Parasitology, 1996, 113(1): 7-18. |
| [21] | Guindo A, Fairhurst RM, Doumbo OK, et al. X-linked G6PD deficiency protects hemizygous males but not heterozygous females against severe malaria[J]. PLoS Med, 2007, 4(3): e66. |
| [22] | Goo YK, Ji SY, Shin HI, et al. First evaluation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency in vivax malaria endemic regions in the republic of Korea[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(5): e97390. |
| [23] | 李华宪, 张再兴, 周新文, 等. 云南省1999-2001年疟疾流行态势分析[J]. 中国寄生虫病防治杂志, 2003, 16(2): 89-92. |
| [24] | 董莹, 孙艾明, 陈梦妮, 等. 云南省输入性及本地感染间日疟原虫裂殖子表面蛋白1基因5区序列的多态性分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2017, 35(1): 1-7. |
| [25] | 张丽, 丰俊, 张少森, 等. 2017年全国消除疟疾进展及疫情特征分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018, 36(3): 201-209. |
| [26] | 中华人民共和国卫生部. 中华人民共和国卫生行业标准(WS259-2015): 疟疾诊断标准[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2015: 2-3. |
| [27] | 朱垚吉, 邓艳, 毛祥华, 等. 不同感染来源疟原虫株的18S sRNA基因同源性分析[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2014, 9(4): 331-334. |
| [28] | Howes RE, Chan ER, Rakotomanga TA, et al. Prevalence and genetic variants of G6PD deficiency among two Malagasy populations living in Plasmodium vivax-endemic areas[J]. Malar J, 2017, 16: 139. |
| [29] | Kießling N, Brintrup J, Zeynudin A, et al. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity measured by spectrophotometry and associated genetic variants from the Oromiya zone, Ethiopia[J]. Malar J, 2018, 17: 358. |
| [30] | Minucci A, Moradkhani K, Hwang MJ, et al. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) mutations database: review of the “old” and update of the new mutations[J]. Blood Cell Mol Dis, 2012, 48(3): 154-165. |
| [31] | Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome[J]. Nature, 2001, 409(6822): 860-921. |
| [32] | Dombrowski JG, Souza RM, Curry J, et al. G6PD deficiency alleles in a malaria-endemic region in the western Brazilian Amazon[J]. Malar J, 2017, 16: 253. |
| [33] | Beutler E.Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: a historical perspective[J]. Blood, 2008, 111(1): 16-24. |
| [34] | Shah SS, Macharia A, Makale J, et al. Genetic determinants of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity in Kenya[J]. BMC Med Genet, 2014, 15: 93. |
| [35] | Gómez-Manzo S, errón-Hernández J, de la Mora-de la Mora I, et al. TCloning, expression, purification and characterization of His-tagged human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a simplified method for protein yield[J]. Protein J, 2013, 32(7): 585-592. |
| [36] | Jiang W, Yu G, Liu P, et al. Structure and function of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient variants in Chinese population[J]. Hum Genet, 2006, 119(5): 463-478. |
| [37] | Li Q, Yang F, Liu R, et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency at the China-Myanmar border[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0134593. |
| [38] | 潘小莉, 庄丹燕, 陈怡博, 等. 宁波地区273例G6PD缺乏症基因突变类型分析[J]. 中国优生与遗传杂志, 2017, 25(5): 37-39. |
| [39] | Levy HR.Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenases[J]. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol, 1979, 48: 97-192. |
| [40] | Au SW, Gover S, Lam VM, et al. Human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: the crystal structure reveals a structural NADP+ molecule and provides insights into enzyme deficiency[J]. Structure, 2000, 8(3): 293-303. |
| [41] | Au SW, Naylor CE, Gover S, et al. Solution of the structure of tetrameric human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by molecular replacement[J]. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 1999, 55(4): 826-834. |
| [42] | Cohen P, Rosemeyer MA.Subunit interactions of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from human erythrocytes[J]. Eur J Biochem, 1969, 8(1): 8-15. |
| [1] | DING Hongyun, DONG Ying, XU Yanchun, DENG Yan, LIU Yan, WU Jing, CHEN Mengni, ZHANG Canglin. Polymorphism analysis of multidrug resistance protein 1 gene in imported Plasmodium vivax in Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 404-411. |
| [2] | LI Benfu, WANG Zhengqing, XU Qian, ZI Jinrong, YAN Xinliu, PENG Jia, LI Jianxiong, CAI Xuan, WU Fangwei, YANG Yaming. Sequence analysis of mitochondrial co1 and nd1 genes in Echinococcus granulosus in Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 306-311. |
| [3] | WANG Guan-xi, LI Ya-shu, LI Yue-yue, CAO Yuan-yuan, YANG Meng-meng, ZHANG Mei-hua, WU Jing-yao, LIANG Cheng, LI Ju-lin, ZHOU Hua-yun, TANG Jian-xia, ZHU Guo-ding. Resistance to deltamethrin and knockdown resistance mutation in Aedes albopictus from Jiangsu Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 468-474. |
| [4] | PU Li-hua, ZHANG Xing-ze, GUAN Shao-jun, CHENG Wen-jie, ZOU Feng-cai, MAO Hua-ming, YANG Jian-fa. Blastocystis sp. infection in dairy cattle in Yunnan Province and its gene subtype analysis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 809-815. |
| [5] | CAI Xuan, YANG Ya-ming, LI Ben-fu, YAN Xin-liu, PENG Jia, ZI Jin-rong, WU Fang-wei. Investigation on the prevalence of human parasitic infections in the ecoregion of southern part of Yunnan-Guangxi-Guangdong neighboring area, Yunnan Province in 2015 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 848-852. |
| [6] | ZI Jin-rong, WANG Li-bo, YANG Ya-ming, LI Ben-fu, YAN Xin-liu, PENG Jia, CAI Xuan, WANG Zheng-qing, DU Zun-wei, WU Fang-wei. Current status of Ascaris lumbricoides infection in populations in Yunan Province, 2015 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 273-277. |
| [7] | WU Fang-wei, WANG Li-bo, LI Ben-fu, YAN Xin-liu, ZI Jin-rong, PENG Jia, CAI Xuan, BAO Xue-ying, YANG Ya-ming. Survey on current status of human hookworm infection in Yunnan Province in 2015 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 781-784. |
| [8] | Shu-ping LIU, Ying DONG, Yan-chun XU, Yan LIU, Yan DENG, Cang-lin ZHANG, Meng-ni CHEN. The mutation polymorphism of G6PD gene coding region in vivax malaria patients in Yunnan Province, China [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(2): 146-151. |
| [9] | Rui YANG, Yu-ting ZHENG, Xiao-yu YANG, Li-min DONG, Zu-rui LIN, Yao-wu ZHOU, Xu-can ZENG, Hong-bin LI, Jin-yong JIANG. Investigation on malaria vectors in Jinghong, a border area in Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(4): 406-410. |
| [10] | Cang-lin ZHANG, Xue-ying BAO, Jia PENG, Jin-rong ZI, Zhen RAN, Na LU, Ya-ming YANG. Species identification of Pomacea snails in southwest Yunan Province based on COⅠgene polymorphism [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(1): 75-81. |
| [11] | DONG Ying1, DENG Yan1, XU Yan-chun1, CHEN Meng-ni1, MAO Xiang-hua1, . Analysis of gene sequence polymorphisms and prediction of antigen epitopes of merozoite surface protein-3 in Plasmodium falciparum from different infection sources [J]. , 2018, 36(3): 3-210-217. |
| [12] | Cheng-yun YANG, Su-hua LI, Ya-lan ZHANG, Rui-min ZHOU, Ying LIU, Dan QIAN, Yu-ling ZHAO, Bian-li XU, Hong-wei ZHANG, Yan DENG. Analysis of mutations of Plasmodium falciparum multidrug resistance gene 1 and K13 gene in imported Plasmodium falciparum in Henan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2018, 36(2): 97-102. |
| [13] | Ying DONG, Yan DENG, Meng-ni CHEN, Yan-chun XU, Xiang-hua MAO, Jian WANG, Ai-ming SUN, Jing-bo XUE. Analysis of genes associated with antifolate drug resistance in Plasmodium vivax from different infection sources [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2018, 36(2): 103-111. |
| [14] | Jin-yong JIANG, Hui-ying CHEN, Hong-ning ZHOU, Ya-jun MA. Analysis of knowdown resistance gene mutation in Culex tritaeniorhynchus resistant to DDT and deltamethrin in Yunnan Province, China [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2017, 35(6): 536-540. |
| [15] | ZENG Xu-can, ZHOU Zi-you, ZHOU Xing-wu, LI Jian-xiong, LUO Chun-hai, . SWOT analysis of malaria elimination program in Yunnan Province [J]. , 2017, 35(4): 18-392-395. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||