

中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 767-775.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2024.06.012
收稿日期:2024-06-22
修回日期:2024-08-28
出版日期:2024-12-30
发布日期:2025-01-14
通讯作者:
高金亮(1976—),男,博士,教授,从事蜱源活性蛋白研究。E-mail:作者简介:贺晓菲(1994—),女,硕士研究生,从事蜱源抗凝蛋白研究。E-mail:xfaslhxf@163.com
基金资助:
HE Xiaofei1,2( ), GAO Jinliang1,2,*(
), GAO Jinliang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-22
Revised:2024-08-28
Online:2024-12-30
Published:2025-01-14
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:摘要:
蜱是一种人兽共患的体表吸血寄生虫,其在吸血过程中会触发机体的凝血系统。为逃避宿主防御机制,蜱会分泌多种抗凝血蛋白来调节宿主凝血系统,以维持血液的持续流动。这些抗凝血蛋白多为蛋白酶抑制剂,可与宿主的凝血因子及血小板活性相关分子相互作用,从而有效调节宿主的血液凝固过程。目前已发现大量具有抗凝血活性的蜱源蛋白分子,这些蛋白分子的结构多样,且与宿主体内的目标分子具有较高的特异性和较强的亲和力。基于这些蜱源抗凝分子开发的抗凝药物有望兼具高效抗凝作用和较低的出血风险。本文综述了部分蜱源抗凝血分子的研究进展,讨论了它们的作用机制及潜在的临床应用价值,旨在为新型抗凝药物的研发提供参考。
中图分类号:
贺晓菲, 高金亮. 蜱源抗凝血蛋白及其在医学领域的潜在价值[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2024, 42(6): 767-775.
HE Xiaofei, GAO Jinliang. Tick-derived anticoagulant proteins and their potential value in the medical field[J]. Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases, 2024, 42(6): 767-775.
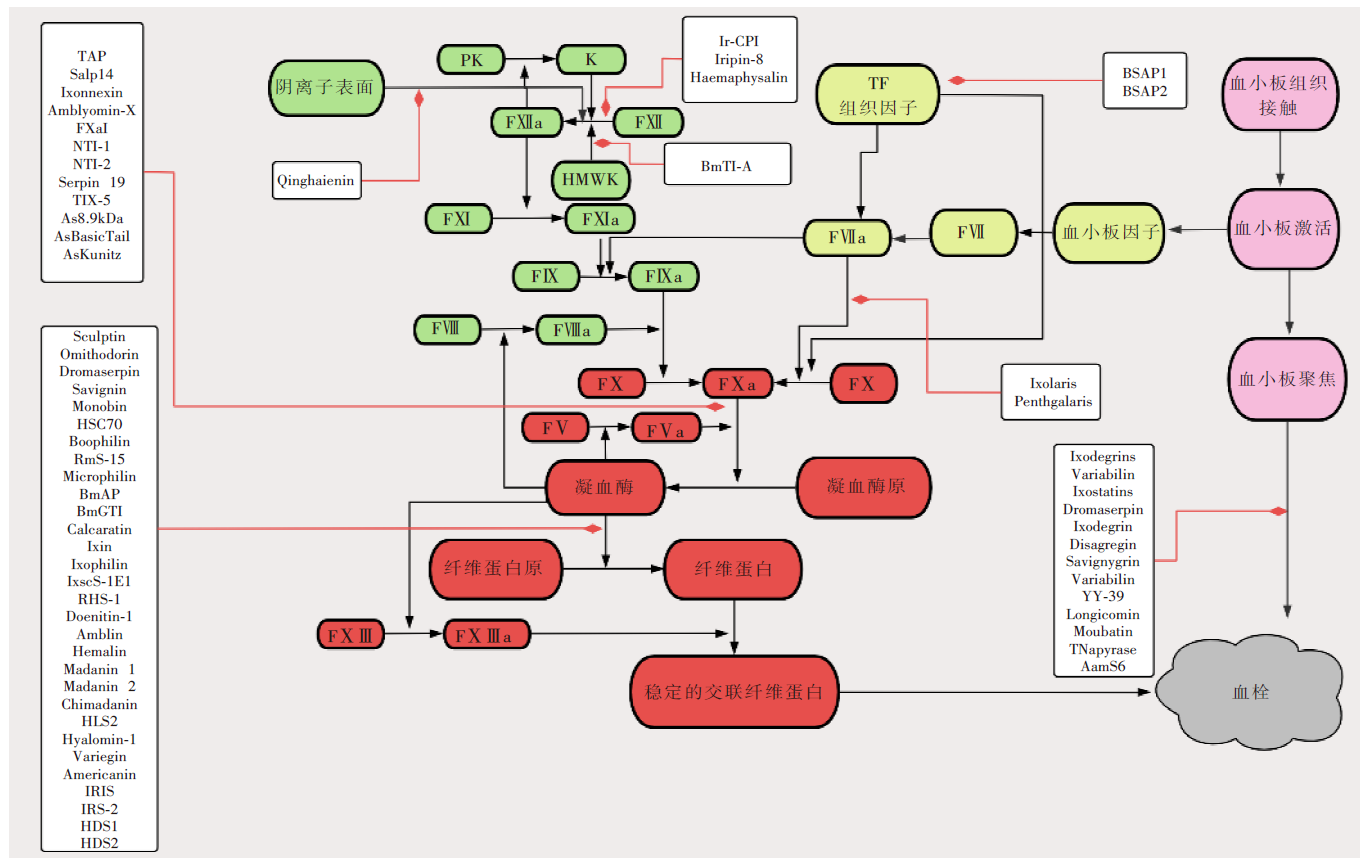
图1
脊椎动物凝血与蜱源蛋白酶抑制剂的抗凝机制示意图 注:绿色区域为内源性凝血途径;黄色区域为外源性凝血途径;红色区域为共同凝血途径;粉色区域为血小板发挥功能区;白色方框为各种蜱源蛋白酶抑制剂及其作用靶点。HMWK:高分子量激肽原;PK:前激肽释放酶;K:激肽释放酶;TF:组织因子;FⅤ:凝血因子Ⅴ;FⅦ:凝血因子Ⅶ;FⅧ:凝血因子Ⅷ;FⅨ:凝血因子Ⅸ;FⅩ:凝血因子Ⅹ;FⅪ:凝血因子Ⅺ;FⅫ:凝血因子Ⅻ;FⅩⅢ:凝血因子ⅩⅢ;FⅤa:凝血因子Ⅴa;FⅦa:凝血因子Ⅶa;FⅧa:凝血因子Ⅷa;FⅨ:凝血因子Ⅸa;FⅩ:凝血因子Ⅹa;FⅪa:凝血因子Ⅺa;FⅫa:凝血因子Ⅻa;FⅩⅢa:凝血因子ⅩⅢa。本图根据参考文献[15]制作。
| [1] | Chen Z, Liu JZ. Recent progress in tick taxonomy and a global list of tick species[J]. Chin J Appl Entomol, 2020, 57(5): 1009-1045. (in Chinese) |
| (陈泽, 刘敬泽. 蜱分类学研究进展[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2020, 57(5): 1009-1045.) | |
| [2] | Du YF, Zhou JL. Advance in inhibitory molecules of cysteine protease of ticks[J]. Prog Vet Med, 2016, 37(12): 95-99. (in Chinese) |
| (杜艳芳, 周金林. 蜱半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制分子研究进展[J]. 动物医学进展, 2016, 37(12): 95-99.) | |
| [3] | Yu ZJ, Yang XL, Chen J, et al. An overview on the physiological and ecological adaptation mechanisms of the overwinter ticks[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2014, 32(5): 385-387, 392. (in Chinese) |
| (于志军, 杨小龙, 陈洁, 等. 蜱类越冬生理生态适应机制概述[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2014, 32(5): 385-387, 392.) | |
| [4] | Sonenshine DE, Roe RM. Ticks, people and animals[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 2014: 3-16. |
| [5] | Anderson JF, Magnarelli LA. Biology of ticks[J]. Infect Dis Clin North Am, 2008, 22(2): 195-215. |
| [6] | Edgington TS, Dickinson CD, Ruf W. The structural basis of function of the TF. VIIa complex in the cellular initiation of coagulation[J]. Thromb Haemost, 1997, 78(1): 401-405. |
| [7] | Ma XT, Yuan ZJ. Discovery of coagulation factors and coagulation theory[J]. J Postgrad Med, 1986, 9(1): 31-34. (in Chinese) |
| (马献图, 袁自江. 凝血诸因子的发现及凝血学说[J]. 医师进修杂志, 1986, 9(1): 31-34.) | |
| [8] | Renné T, Schmaier AH, Nickel KF, et al. In vivo roles of factor Ⅻ[J]. Blood, 2012, 120(22): 4296-4303. |
| [9] |
Emsley J, McEwan PA, Gailani D. Structure and function of factor Ⅺ[J]. Blood, 2010, 115(13): 2569-2577.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-199182 pmid: 20110423 |
| [10] |
Smith SA, Choi SH, Collins JN, et al. Inhibition of polyphosphate as a novel strategy for preventing thrombosis and inflammation[J]. Blood, 2012, 120(26): 5103-5110.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-444935 pmid: 22968458 |
| [11] |
Mann KG, Butenas S, Brummel K. The dynamics of thrombin formation[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2003, 23(1): 17-25.
doi: 10.1161/01.atv.0000046238.23903.fc pmid: 12524220 |
| [12] | Nuttall PA. Wonders of tick saliva[J]. Ticks Tick Borne Dis, 2019, 10(2): 470-481. |
| [13] |
Parizi LF, Ali A, Tirloni L, et al. Peptidase inhibitors in tick physiology[J]. Med Vet Entomol, 2018, 32(2): 129-144.
doi: 10.1111/mve.12276 pmid: 29111611 |
| [14] | Jmel MA, Aounallah H, Bensaoud C, et al. Insights into the role of tick salivary protease inhibitors during ectoparasite-host crosstalk[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(2): 892. |
| [15] |
Schön MP. The tick and I: parasite-host interactions between ticks and humans[J]. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges, 2022, 20(6): 818-853.
doi: 10.1111/ddg.14821 pmid: 35674196 |
| [16] | Blisnick AA, Foulon T, Bonnet SI. Serine protease inhibitors in ticks: an overview of their role in tick biology and tick-borne pathogen transmission[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7: 199. |
| [17] | Chmelař J, Kotál J, Langhansová H, et al. Protease inhibitors in tick saliva: the role of serpins and cystatins in tick-host-pathogen interaction[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2017, 7: 216. |
| [18] |
Weitz JI, Chan NC. Are ticks the answer to medical device-associated clotting?[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2019, 74(17): 2190-2192.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.08.1027 |
| [19] | Decrem Y, Rath G, Blasioli V, et al. Ir-CPI, a coagulation contact phase inhibitor from the tick Ixodes ricinus, inhibits thrombus formation without impairing hemostasis[J]. J Exp Med, 2009, 206(11): 2381-2395. |
| [20] |
Pireaux V, Tassignon J, Demoulin S, et al. Anticoagulation with an inhibitor of factors XIa and XIIa during cardiopulmonary bypass[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2019, 74(17): 2178-2189.
doi: S0735-1097(19)37465-0 pmid: 31648711 |
| [21] | Kato N, Iwanaga S, Okayama T, et al. Identification and characterization of the plasma kallikrein-kinin system inhibitor, haemaphysalin, from hard tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2005, 93(2): 359-367. |
| [22] |
Tanaka AS, Andreotti R, Gomes A, et al. A double headed serine proteinase inhibitor—human plasma kallikrein and elastase inhibitor—from Boophilus microplus larvae[J]. Immunopharmacology, 1999, 45(1-3):171-177.
pmid: 10615008 |
| [23] | Kotál J, Polderdijk SGI, Langhansová H, et al. Ixodes ricinus salivary serpin Iripin-8 inhibits the intrinsic pathway of coagulation and complement[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9480. |
| [24] | Gao JL, She ZF, Gao DB, et al. Application of a tick-derived anticoagulant protein Qinghaienin and its encoding gene in anticoagulant: CN116410303B[P]. 2023-09-12( 引用时间). (in Chinese) |
| (高金亮, 折占飞, 高东兵, 等. 一种蜱的抗凝血蛋白Qinghaienin及其编码基因在抗凝血中的应用: CN116410303B[P]. 2023-09-12( 引用时间).) | |
| [25] |
Monteiro RQ, Rezaie AR, Ribeiro JM, et al. Ixolaris: a factor Xa heparin-binding exosite inhibitor[J]. Biochem J, 2005, 387(Pt 3): 871-877.
doi: 10.1042/BJ20041738 pmid: 15617517 |
| [26] |
Monteiro RQ, Rezaie AR, Bae JS, et al. Ixolaris binding to factor X reveals a precursor state of factor Xa heparin-binding exosite[J]. Protein Sci, 2008, 17(1): 146-153.
doi: 10.1110/ps.073016308 pmid: 18042685 |
| [27] |
de Paula VS, Sgourakis NG, Francischetti IMB, et al. NMR structure determination of Ixolaris and factor X(a) interaction reveals a noncanonical mechanism of Kunitz inhibition[J]. Blood, 2019, 134(8): 699-708.
doi: 10.1182/blood.2018889493 pmid: 31133602 |
| [28] | Francischetti IM, Mather TN, Ribeiro JM. Penthalaris, a novel recombinant five-Kunitz tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) from the salivary gland of the tick vector of Lyme disease, Ixodes scapularis[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2004, 91(5): 886-898. |
| [29] | Ehebauer MT, Mans BJ, Gaspar AR, et al. Identification of extrinsic blood coagulation pathway inhibitors from the tick Ornithodoros savignyi (Acari ∶ Argasidae)[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2002, 101(2/3): 138-148. |
| [30] | Chlastáková A, Kotál J, Beránková Z, et al. Iripin-3, a new salivary protein isolated from Ixodes ricinus ticks, displays immunomodulatory and anti-hemostatic properties in vitro[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 626200. |
| [31] |
Neeper MP, Waxman L, Smith DE, et al. Characterization of recombinant tick anticoagulant peptide. a highly selective inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa[J]. J Biol Chem, 1990, 265(29): 17746-17752.
pmid: 2211658 |
| [32] |
Francischetti IM, Meng ZJ, Mans BJ, et al. An insight into the salivary transcriptome and proteome of the soft tick and vector of epizootic bovine abortion, Ornithodoros coriaceus[J]. J Proteomics, 2008, 71(5): 493-512.
doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2008.07.006 pmid: 18725333 |
| [33] |
Das S, Banerjee G, DePonte K, et al. Salp25D, an Ixodes scapularis antioxidant, is 1 of 14 immunodominant antigens in engorged tick salivary glands[J]. J Infect Dis, 2001, 184(8): 1056-1064.
pmid: 11574922 |
| [34] |
Narasimhan S, Koski RA, Beaulieu B, et al. A novel family of anticoagulants from the saliva of Ixodes scapularis[J]. Insect Mol Biol, 2002, 11(6): 641-650.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2583.2002.00375.x pmid: 12421422 |
| [35] | Denisov SS, Ippel JH, Castoldi E, et al. Molecular basis of anticoagulant and anticomplement activity of the tick salivary protein Salp14 and its homologs[J]. J Biol Chem, 2021, 297(1): 100865. |
| [36] | Assumpção TC, Mizurini DM, Ma DY, et al. Ixonnexin from tick saliva promotes fibrinolysis by interacting with plasminogen and tissue-type plasminogen activator, and prevents arterial thrombosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 4806. |
| [37] |
Batista IF, Ramos OH, Ventura JS, et al. A new Factor Xa inhibitor from Amblyomma cajennense with a unique domain composition[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2010, 493(2): 151-156.
doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2009.10.009 pmid: 19853573 |
| [38] |
Branco VG, Iqbal A, Alvarez-Flores MP, et al. Amblyomin-X having a Kunitz-type homologous domain, is a noncompetitive inhibitor of FⅩa and induces anticoagulation in vitro and in vivo[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2016, 1864(10): 1428-1435.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.07.011 pmid: 27479486 |
| [39] |
Gaspar AR, Joubert AM, Crause JC, et al. Isolation and characterization of an anticoagulant from the salivary glands of the tick, Ornithodoros savignyi (Acari ∶ Argasidae)[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 1996, 20(10): 583-598.
doi: 10.1007/BF00052809 pmid: 8952072 |
| [40] |
Ibrahim MA, Ghazy AH, Maharem T, et al. Isolation and properties of two forms of thrombin inhibitor from the nymphs of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii (Acari ∶ Ixodidae)[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2001, 25(8): 675-698.
pmid: 12171275 |
| [41] |
Joubert AM, Crause JC, Gaspar AR, et al. Isolation and characterization of an anticoagulant present in the salivary glands of the bont-legged tick, Hyalomma truncatum[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 1995, 19(2): 79-92.
pmid: 7656731 |
| [42] | Kim TK, Tirloni L, Radulovic Z, et al. Conserved Amblyomma americanum tick Serpin19, an inhibitor of blood clotting factors Xa and XIa, trypsin and plasmin, has anti-haemostatic functions[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2015, 45(9/10): 613-627. |
| [43] | Schuijt TJ, Narasimhan S, Daffre S, et al. Identification and characterization of Ixodes scapularis antigens that elicit tick immunity using yeast surface display[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(1): e15926. |
| [44] |
Schuijt TJ, Bakhtiari K, Daffre S, et al. Factor Xa activation of factor V is of paramount importance in initiating the coagulation system: lessons from a tick salivary protein[J]. Circulation, 2013, 128(3): 254-266.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.003191 pmid: 23817575 |
| [45] | Costa GCA, Ribeiro ICT, Melo-Junior O, et al. Amblyomma sculptum salivary protease inhibitors as potential anti-tick vaccines[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 611104. |
| [46] | Iqbal A, Goldfeder MB, Marques-Porto R, et al. Revisiting antithrombotic therapeutics; sculptin, a novel specific, competitive, reversible, scissile and tight binding inhibitor of thrombin[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 1431. |
| [47] |
van de Locht A, Stubbs MT, Bode W, et al. The ornithodorin-thrombin crystal structure, a key to the TAP enigma?[J]. EMBO J, 1996, 15(22): 6011-6017.
pmid: 8947023 |
| [48] | Aounallah H, Fessel MR, Goldfeder MB, et al. rDromaserpin: A novel anti-hemostatic serpin, from the salivary glands of the hard tick Hyalomma dromedarii[J]. Toxins (Basel), 2021, 13(12): 913. |
| [49] |
Nienaber J, Gaspar AR, Neitz AW. Savignin, a potent thrombin inhibitor isolated from the salivary glands of the tick Ornithodoros savignyi (Acari ∶ Argasidae)[J]. Exp Parasitol, 1999, 93(2): 82-91.
doi: 10.1006/expr.1999.4448 pmid: 10502470 |
| [50] | Mans BJ, Andersen JF, Schwan TG, et al. Characterization of anti-hemostatic factors in the argasid, Argas monolakensis: implications for the evolution of blood-feeding in the soft tick family[J]. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2008, 38(1): 22-41. |
| [51] | He XM, Liu L, Cheng TY. HSC70 from Haemaphysalis flava (Acari ∶ Ixodidae) exerts anticoagulation activity in vitro[J]. Ticks Tick Borne Dis, 2019, 10(1): 170-175. |
| [52] | Liu L, Tang H, Duan DY, et al. Characterization of AV422 from Haemaphysalis flava ticks in vitro[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2021, 84(4): 809-823. |
| [53] | Assumpção TC, Ma DY, Mizurini DM, et al. In vitro mode of action and anti-thrombotic activity of boophilin, a multifunctional kunitz protease inhibitor from the midgut of a tick vector of babesiosis, Rhipicephalus microplus[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2016, 10(1): e0004298. |
| [54] | Xu T, Lew-Tabor A, Rodriguez-Valle M. Effective inhibition of thrombin by Rhipicephalus microplus serpin-15 (RmS-15) obtained in the yeast Pichia pastoris[J]. Ticks Tick Borne Dis, 2016, 7(1): 180-187. |
| [55] |
Ciprandi A, de Oliveira SK, Masuda A, et al. Boophilus microplus: its saliva contains microphilin, a small thrombin inhibitor[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2006, 114(1): 40-46.
doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2006.02.010 pmid: 16600217 |
| [56] |
Horn F, Dos Santos PC, Termignoni C. Boophilus microplus anticoagulant protein: an antithrombin inhibitor isolated from the cattle tick saliva[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2000, 384(1): 68-73.
pmid: 11147837 |
| [57] | Ricci CG, Pinto AF, Berger M, et al. A thrombin inhibitor from the gut of Boophilus microplus ticks[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2007, 42(4): 291-300. |
| [58] |
Motoyashiki T, Tu AT, Azimov DA, et al. Isolation of anticoagulant from the venom of tick, Boophilus calcaratus, from Uzbekistan[J]. Thromb Res, 2003, 110(4): 235-241.
pmid: 14512088 |
| [59] |
Hoffmann A, Walsmann P, Riesener G, et al. Isolation and characterization of a thrombin inhibitor from the tick Ixodes ricinus[J]. Pharmazie, 1991, 46(3): 209-212.
pmid: 1881945 |
| [60] | Narasimhan S, Perez O, Mootien S, et al. Characterization of Ixophilin, a thrombin inhibitor from the gut of Ixodes scapularis[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e68012. |
| [61] | Ibelli AM, Kim TK, Hill CC, et al. A blood meal-induced Ixodes scapularis tick saliva serpin inhibits trypsin and thrombin, and interferes with platelet aggregation and blood clotting[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2014, 44(6): 369-379. |
| [62] | Yu YF, Cao J, Zhou YZ, et al. Isolation and characterization of two novel serpins from the tick Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides[J]. Ticks Tick Borne Dis, 2013, 4(4): 297-303. |
| [63] | Lu JL, Wang K, Gao ZH, et al. Doenitin-1: a novel Kunitz family protein with versatile functions during feeding and reproduction of the tick Haemaphysalis doenitzi[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2022, 9: 872244. |
| [64] | Lai R, Takeuchi H, Jonczy J, et al. A thrombin inhibitor from the ixodid tick, Amblyomma hebraeum[J]. Gene, 2004, 342(2): 243-249. |
| [65] |
Liao M, Zhou JL, Gong HY, et al. Hemalin, a thrombin inhibitor isolated from a midgut cDNA library from the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis[J]. J Insect Physiol, 2009, 55(2): 164-173.
doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2008.11.004 pmid: 19061894 |
| [66] |
Iwanaga S, Okada M, Isawa H, et al. Identification and characterization of novel salivary thrombin inhibitors from the Ixodidae tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis[J]. Eur J Biochem, 2003, 270(9): 1926-1934.
doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03560.x pmid: 12709051 |
| [67] | Figueiredo AC, de Sanctis D, Pereira PJB. The tick-derived anticoagulant madanin is processed by thrombin and factor Xa[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e71866. |
| [68] |
Nakajima C, Imamura S, Konnai S, et al. A novel gene encoding a thrombin inhibitory protein in a cDNA library from Haemaphysalis longicornis salivary gland[J]. J Vet Med Sci, 2006, 68(5): 447-452.
pmid: 16757887 |
| [69] |
Imamura S, da Silva Vaz Junior I, Sugino M, et al. A serine protease inhibitor (serpin) from Haemaphysalis longicornis as an anti-tick vaccine[J]. Vaccine, 2005, 23(10): 1301-1311.
doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.08.041 pmid: 15652673 |
| [70] | Jablonka W, Kotsyfakis M, Mizurini DM, et al. Identification and mechanistic analysis of a novel tick-derived inhibitor of thrombin[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(8): e0133991. |
| [71] |
Koh CY, Kazimirova M, Trimnell A, et al. Variegin, a novel fast and tight binding thrombin inhibitor from the tropical bont tick[J]. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282(40): 29101-29113.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705600200 pmid: 17684009 |
| [72] | Koh CY, Kumar S, Kazimirova M, et al. Crystal structure of thrombin in complex with S-variegin: insights of a novel mechanism of inhibition and design of tunable thrombin inhibitors[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(10): e26367. |
| [73] | Iyer JK, Koh CY, Kazimirova M, et al. Avathrin: a novel thrombin inhibitor derived from a multicopy precursor in the salivary glands of the ixodid tick, Amblyomma variegatum[J]. FASEB J, 2017, 31(7): 2981-2995. |
| [74] |
Zhu K, Bowman AS, Brigham DL, et al. Isolation and characterization of americanin, a specific inhibitor of thrombin, from the salivary glands of the lone star tick Amblyomma americanum (L.)[J]. Exp Parasitol, 1997, 87(1): 30-38.
doi: 10.1006/expr.1997.4175 pmid: 9287955 |
| [75] |
Chmelar J, Oliveira CJ, Rezacova P, et al. A tick salivary protein targets cathepsin G and chymase and inhibits host inflammation and platelet aggregation[J]. Blood, 2011, 117(2): 736-744.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-293241 pmid: 20940421 |
| [76] | Prevot PP, Adam B, Boudjeltia KZ, et al. Anti-hemostatic effects of a serpin from the saliva of the tick Ixodes ricinus[J]. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(36): 26361-26369. |
| [77] | Du WJ, Gao ZH, Wang K, et al. Expression and function assessment of two serpin-type serine protease inhibitors from Haemaphysalis doenitzi[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2020, 132: 1-9. |
| [78] | Gao X, Shi L, Zhou YZ, et al. Characterization of the anticoagulant protein Rhipilin-1 from the Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides tick[J]. J Insect Physiol, 2011, 57(2): 339-343. |
| [79] | Cao J, Shi L, Zhou YZ, et al. Characterization of a new Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor from the hard tick Rhipicephalus hemaphysaloides[J]. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol, 2013, 84(2): 104-113. |
| [80] | Zhang HS, Qiao RQ, Gong HY, et al. Identification and anticoagulant activity of a novel Kunitz-type protein HA11 from the salivary gland of the tick Hyalomma asiaticum[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2017, 71(1): 71-85. |
| [81] |
Ceraul SM, Dreher-Lesnick SM, Mulenga A, et al. Functional characterization and novel rickettsiostatic effects of a Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor from the tick Dermacentor variabilis[J]. Infect Immun, 2008, 76(11): 5429-5435.
doi: 10.1128/IAI.00866-08 pmid: 18779339 |
| [82] | Feng TT, Tong H, Zhang QQ, et al. Targeting Haemaphysalis longicornis serpin to prevent tick feeding and pathogen transmission[J]. Insect Sci, 2024, 31(3): 694-706. |
| [83] |
Mulenga A, Kim TK, Ibelli AM. Deorphanization and target validation of cross-tick species conserved novel Amblyomma americanum tick saliva protein[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2013, 43(6): 439-451.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2012.12.012 pmid: 23428900 |
| [84] |
Štibrániová I, Bartíková P, Holíková V, et al. Deciphering biological processes at the tick-host interface opens new strategies for treatment of human diseases[J]. Front Physiol, 2019, 10: 830.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00830 pmid: 31333488 |
| [85] | van den Kerkhof DL, Nagy M, Wichapong K, et al. Inhibition of platelet adhesion, thrombus formation, and fibrin formation by a potent αⅡbβ3 integrin inhibitor from ticks[J]. Res Pract Thromb Haemost, 2021, 5(1): 231-242. |
| [86] |
Mans BJ, Louw AI, Neitz AW. Savignygrin, a platelet aggregation inhibitor from the soft tick Ornithodoros savignyi, presents the RGD integrin recognition motif on the Kunitz-BPTI fold[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(24): 21371-21378.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112060200 pmid: 11932256 |
| [87] |
Wang X, Coons LB, Taylor DB, et al. Variabilin, a novel RGD-containing antagonist of glycoprotein Ⅱb-Ⅲa and platelet aggregation inhibitor from the hard tick Dermacentor variabilis[J]. J Biol Chem, 1996, 271(30): 17785-17790.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.30.17785 pmid: 8663513 |
| [88] |
Tang J, Fang YQ, Han YJ, et al. YY-39, a tick anti-thrombosis peptide containing RGD domain[J]. Peptides, 2015, 68: 99-104.
doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.08.008 pmid: 25152502 |
| [89] | Cheng YG, Wu HY, Li DC. An inhibitor selective for collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation from the salivary glands of hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis and its mechanism of action[J]. Sci China Ser C Life Sci, 1999, 42(5): 457-464. |
| [90] |
Waxman L, Connolly TM. Isolation of an inhibitor selective for collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation from the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata[J]. J Biol Chem, 1993, 268(8): 5445-5449.
pmid: 8449906 |
| [91] | Masoud HMM, Helmy MS, Darwish DA, et al. Apyrase with anti-platelet aggregation activity from the nymph of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2020, 80(3): 349-361. |
| [92] |
Mulenga A, Kim T, Ibelli AM. Amblyomma americanum tick saliva serine protease inhibitor 6 is a cross-class inhibitor of serine proteases and papain-like cysteine proteases that delays plasma clotting and inhibits platelet aggregation[J]. Insect Mol Biol, 2013, 22(3): 306-319.
doi: 10.1111/imb.12024 pmid: 23521000 |
| [93] | The writing committee of the report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China. Report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2022: an updated summary[J]. Chin J Interv Cardiol, 2023, 31(7): 485-508. (in Chinese) |
| (中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022》概要[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2023, 31(7): 485-508.) | |
| [94] |
Wootton DM, Ku DN. Fluid mechanics of vascular systems, diseases, and thrombosis[J]. Annu Rev Biomed Eng, 1999, 1: 299-329.
pmid: 11701491 |
| [95] | Banik N, Yang SB, Kang TB, et al. Heparin and its derivatives: challenges and advances in therapeutic biomolecules[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(19): 10524. |
| [96] | Anzabi Zadeh S, Street WN, Thomas BW. Optimizing warfarin dosing using deep reinforcement learning[J]. J Biomed Inform, 2023, 137: 104267. |
| [97] | Karcioglu O, Zengin S, Ozkaya B, et al. Direct (new) oral anticoagulants (DOACs): drawbacks, bleeding and reversal[J]. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem, 2022, 20(2): 103-113. |
| [98] |
Turk B. Targeting proteases: successes, failures and future prospects[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2006, 5(9): 785-799.
doi: 10.1038/nrd2092 pmid: 16955069 |
| [99] |
Chmelar J, Calvo E, Pedra JH, et al. Tick salivary secretion as a source of antihemostatics[J]. J Proteomics, 2012, 75(13): 3842-3854.
doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2012.04.026 pmid: 22564820 |
| [100] |
Bordon KCF, Cologna CT, Fornari-Baldo EC, et al. From animal poisons and venoms to medicines: achievements, challenges and perspectives in drug discovery[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 1132.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01132 pmid: 32848750 |
| [101] |
Chmelař J, Kotál J, Kovaříková A, et al. The use of tick salivary proteins as novel therapeutics[J]. Front Physiol, 2019, 10: 812.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00812 pmid: 31297067 |
| [102] | Lobba ARM, Alvarez-Flores MP, Fessel MR, et al. A kunitz-type inhibitor from tick salivary glands: a promising novel antitumor drug candidate[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2022, 9: 936107. |
| [103] |
Grover SP, Mackman N. Intrinsic pathway of coagulation and thrombosis[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2019, 39(3): 331-338.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.312130 pmid: 30700128 |
| [104] | Jiang S, Zheng YZ, Kong Y, et al. Research of antibodies targeting coagulation factor Ⅻ and coagulation factor Ⅺ[J]. Pharm Biotechnol, 2022, 29(4): 401-407. (in Chinese) |
| (蒋帅, 郑益政, 孔毅, 等. 靶向凝血因子Ⅻ和凝血因子Ⅺ的抗体研究进展[J]. 药物生物技术, 2022, 29(4): 401-407.) | |
| [105] | Huang YX, Wang Y, Shen MY. Research progress on the safety of anticoagulants for venous thrombosis[J]. Chin J Geriatr Care, 2022, 20(2): 98-101. (in Chinese) |
| (黄韵璇, 王颖, 沈梦媛. 静脉血栓抗凝治疗药物安全性的研究进展[J]. 中国老年保健医学, 2022, 20(2): 98-101.) |
| [1] | 朱昊天, 周勇志, 曹杰, 王亚楠, 张厚双, 徐前明, 周金林. 长角血蜱天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶8基因的鉴定及其抵抗田鼠巴贝虫感染作用的研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2024, 42(4): 433-438. |
| [2] | 张钰, 张科, 刘佳伟, 王安琪, 团勇, 张东, 闫利平, 李凯. 普氏野马分布区域亚洲璃眼蜱的宏基因组分析与病原体评估[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2024, 42(4): 439-446. |
| [3] | 孙连阳, 崔浩, 董晓楠, 康佳美, 丁玉林, 习娟, 杨洋, 贺志雄, 刘永宏, 赵丽. 内蒙古全沟硬蜱的鉴定、人工饲养及生活史观察[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2024, 42(3): 345-353. |
| [4] | 李逢时, 赵姗姗, 谭文波, 吾热力哈孜·哈孜汗, 谷新利, 王素文, 刘钢, 王远志. 新疆红狐体表犬硬蜱的分子生物学和雄蜱形态学研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2023, 41(6): 739-743. |
| [5] | 纪鹏慧, 蒋甜甜, 贺志权, 王丹, 岳思宁, 李素华, 杨成运, 王昊, 张红卫, 周瑞敏. 河南省信阳地区家畜寄生蜱感染巴贝虫的分子流行病学调查[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2023, 41(5): 567-572. |
| [6] | 费思伟, 赵翰卿, 尹静娴, 孙芷珊, 郭晓奎, KASSEGNE Kokouvi, 周晓农. 基于文献计量分析的蜱及蜱传疾病研究领域发展趋势[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2023, 41(5): 609-618. |
| [7] | 刘岳青, 马林源, 陈开廷, 高金亮, 王鹏. 蜱源Kunitz型丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制分子的结构与功能研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2023, 41(5): 625-630. |
| [8] | 刘雅芳, 陈彬, 芦新焱, 李光华, 杜春红, 姜丹丹, 杨兴. 云南微小扇头蜱线粒体基因组全序列测定与分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(5): 677-681. |
| [9] | 宋瑞其, 翟雪洁, 李才善, 葛婷, 甘露, 张梦圆, 樊新丽, 李永畅, 张杨, 巴音查汗. 亚洲璃眼蜱和小亚璃眼蜱新疆地理株各发育阶段生物学特性的比较分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(3): 369-378. |
| [10] | 张霞, 颜凤, 牟小会, 林紫敏, 聂映, 程金芝, 商正玲, 吴家红. 埃及伊蚊黄蛋白c基因的克隆、表达及其体外抗凝血作用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(2): 153-158. |
| [11] | 旷策嫣, 周金林. 蜱的化学感觉系统与驱避剂的研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(1): 104-108. |
| [12] | 何文文, 伍军, 呼尔查, 阿力木江, 史倩云, 诺明达来, 甘露, 郝蕴伟, 巴音查汗. 基于最大熵模型的新疆银盾革蜱和边缘革蜱生境适应性评价[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(1): 68-75. |
| [13] | 周淑姮, 曾志伟, 刘维俊, 王加熊, 徐国英, 肖方震. 闽东地区野生动物寄生蜱感染梨形虫状况的调查及基因型分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(1): 76-83. |
| [14] | 吕立红, 张金成, 胡永红. 蜱类保护性抗原研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(4): 542-547. |
| [15] | 乌兰图雅, 殷旭红, 崔云虹, 刘丹, 王亭富, 苗雨润, 阿木日汗, 曹民治, 赵志伟, 邢方超, 鲁建英, 高娃. 内蒙古中西部草原蜱媒病原体多样性及基因型分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(1): 27-35. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||