
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 385-394.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2025.03.013
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Chenxi1( ), GUO Xianguo1,*(
), GUO Xianguo1,*( )(
)( ), LV Yan1, YIN Pengwu1, SONG Wenyu1, PENG Peiying2, XIANG Rong1, CHEN Yanling1,3, LI Bei1
), LV Yan1, YIN Pengwu1, SONG Wenyu1, PENG Peiying2, XIANG Rong1, CHEN Yanling1,3, LI Bei1
Received:2024-10-28
Revised:2025-03-13
Online:2025-06-30
Published:2025-06-18
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:CLC Number:
LIU Chenxi, GUO Xianguo, LV Yan, YIN Pengwu, SONG Wenyu, PENG Peiying, XIANG Rong, CHEN Yanling, LI Bei. Investigation of chigger mites on the surface of murines and other small mammals in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(3): 385-394.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2025.03.013
Table 1
Taxonomic status and constituent ratio of four dominant murine species in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province
| 优势鼠种 Dominant rodent species | 分类地位(科、属) Taxonomic status (Family, Genus) | 数量/只 Number | 构成比/% Cr/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高山姬鼠 A. chevrieri | 鼠科、姬鼠属 Muridae, Apodemus | 233 | 30.0 |
| 大绒鼠 E. miletus | 仓鼠科、绒鼠属 Cricetidae, Eothenomys | 133 | 17.1 |
| 西南绒鼠 E. custos | 仓鼠科、绒鼠属 Cricetidae, Eothenomys | 91 | 11.7 |
| 北社鼠 N. confucianus | 鼠科、白腹鼠属 Muridae, Niviventer | 83 | 10.7 |
| 合计 Total | 540 | 69.4 |
Table 2
Taxonomic checklist of 132 species of chigger mites (Acari:Trombiculidae) in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province
| 恙螨中文名称 Chinese name of chigger mites | 拉丁名 Latin name of chigger mites | 恙螨中文名称 Chinese name of chigger mites | 拉丁名 Latin name of chigger mites | 恙螨中文名称 Chinese name of chigger mites | 拉丁名 Latin name of chigger mites |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 恙螨亚科 | Trombiculinae | 岩栖纤恙螨b | L. rupestre | 钳齿恙螨属 | Cheladonta |
| 纤恙螨属 | Leptotrombidium | 竹栖纤恙螨 | L. bambicola | 密齿钳齿恙螨 | C. micheneri |
| 中华纤恙螨 | L. sinicum | 鼠蝠纤恙螨 | L. myotis | 囊棒恙螨属 | Ascoschoengastia |
| 小板纤恙螨a | L. scutellare | 临淮岗纤恙螨b | L. linhuaikongense | 梭形囊棒恙螨 | A. spindalis |
| 绒鼠纤恙螨 | L. eothenomydis | 福建纤恙螨 | L. fujianense | 民和囊棒恙螨 | A. minheensis |
| 新猬纤恙螨 | L. neotebraci | 海岛纤恙螨a | L. insulare | 四方囊棒恙螨 | A. sifanga |
| 寒冬纤恙螨 | L. hiemalis | 云南纤恙螨 | L. yunnanense | 拉氏囊棒恙螨 | A. latyshevi |
| 乡野纤恙螨b | L. rusticum | 普通纤恙螨 | L. gemiticulum | 云南囊棒恙螨 | A. yunnanensis |
| 树鼩纤恙螨 | L. shuqui | 棕鼠平纤恙螨 | L. rufocanum | 李氏囊棒恙螨 | A. leechi |
| 王氏纤恙螨 | L. wangi | 林姬纤恙螨 | L. mlinji | 山林囊棒恙螨 | A. montana |
| 密点纤恙螨 | L. densipunctatum | 湟川纤恙螨 | L. huangchuanense | 褐鼠囊棒恙螨 | A. rattinorvegici |
| 永胜纤恙螨 | L. yongshengense | 巴颜纤恙螨 | L. bayanense | 爬虫恙螨属 | Herpetacarus |
| 于氏纤恙螨b | L. yui | 横板纤恙螨 | L. hengdun | 芒棒爬虫恙螨 | H. aristoclavus |
| 地里纤恙螨a | L. deliense | 雨林纤恙螨 | L. yulini | 针毛爬虫恙螨 | H. spinosetosus |
| 英帕纤恙螨b | L. imphalum | 庐山纤恙螨 | L. lushanense | 细棒爬虫恙螨 | H. tenuiclavus |
| 贡山纤恙螨 | L. gongshanense | 麂纤恙螨 | L. muntiaci | 枪棒爬虫恙螨 | H. hastoclavus |
| 钉毛纤恙螨 | L. spicanisetum | 大海纤恙螨 | L. dahai | 背展恙螨亚科 | Gahrliepiinae |
| 吉首纤恙螨a | L. sialkotense (L. jishoum) | 疏羽纤恙螨 | L. shuyui | 无前恙螨属 | Walchia |
| 已纤恙螨 | L. zeta | 山蝠纤恙螨 | L. nyctali | 四川无前恙螨 | W. szechuanica |
| 错那纤恙螨 | L. cuonae | 叶片恙螨属 | Trombiculindus | 太平洋无前恙螨b | W. pacifica |
| 扁板纤恙螨 | L. deplanoscutum | 狭毛叶片恙螨 | T. stenosetosus | 葛洪无前恙螨 | W. kor |
| 川西纤恙螨 | L. chuanxi | 棘列叶片恙螨 | T. jilie | 无结无前恙螨 | W. enode |
| 社鼠纤恙螨 | L. sheshui | 高山叶片恙螨 | T. alpinus | 藏南无前恙螨 | W. zangnanica |
| 曲靖纤恙螨 | L. qujingense | 签叶叶片恙螨 | T. qianye | 川无前恙螨 | W. chuanica |
| 金马纤恙螨 | L. jinmai | 云南叶片恙螨 | T. yunnanus | 西沙无前恙螨 | W. xishaensis |
| 长中纤恙螨 | L. longimedium | 楔形叶片恙螨 | T. cuneatus | 攸氏无前恙螨 | W. ewingi |
| 红纤恙螨b | L. akamushi | 竹叶片恙螨 | T. bambusoides | 棒六恙螨属 | Schoengastiella |
| 高山纤恙螨 | L. alpinum | 怒江叶片恙螨 | T. nujiange | 林谷棒六恙螨b | S. ligula |
| 异毛纤恙螨 | L. allosetum | 齿列叶片恙螨 | T. chilie | 背展恙螨属 | Gahrliepia |
| 中鼩纤恙螨 | L. sinotupaium | 新恙螨属 | Neotrombicula | 长足背展恙螨 | G. longipedalis |
| 徐氏纤恙螨 | L. hsui | 德钦新恙螨 | N. deqinensis | 丛林背展恙螨 | G. silvatica |
| 昆明纤恙螨 | L. kunmingense | 日本新恙螨 | N. japonica | 射点背展恙螨 | G. radiopunctata |
| 粗毛纤恙螨 | L. robustisetum | 通天河新恙螨 | N. tongtianhensis | 宽板背展恙螨 | G. latiscutata |
| 碧罗雪山纤恙螨 | L. biluoxueshanense | 旱獭新恙螨 | N. marmotae | 德钦背展恙螨 | G. deqinensis |
| 沧江纤恙螨 | L. cangjiangense | 微恙螨属 | Microtrombicula | 浙江背展恙螨 | G. chekiangensis |
| 川村纤恙螨 | L. kawamurai | 越毛微恙螨 | M. vitosa | 云南背展恙螨 | G. yunnanensis |
| 东洛纤恙螨 | L. dognluoense | 合轮恙螨属 | Helenicula | 田姬背展恙螨 | G. agrariusia |
| 江苏纤恙螨 | L. kiangsuense | 柯氏合轮恙螨 | H. kohlsi | 迷易背展恙螨 | G. miyi |
| 居中纤恙螨b | L. intermedium | 阿坝合轮恙螨 | H. abaensis | 大板背展恙螨 | G. megascuta |
| 陇川纤恙螨 | L. longchuanense | 宫川合轮恙螨 | H. miyagawai | 麻板背展恙螨 | G. madun |
| 高姬纤恙螨 | L. apodevrieri | 沟毛合轮恙螨 | H. aulacochaeta | 多毛背展恙螨 | G. myriosetosa |
| 北里纤恙螨 | L. kitasatoi | 云南合轮恙螨 | H. yunnanensis | 舌板背展恙螨 | G. linguipelta |
| 中甸纤恙螨 | L. zhongdianense | 奥氏合轮恙螨 | H. olsufjevi | 列恙螨亚科 | Leeuwenhoekiinae |
| 碧山纤恙螨 | L. bishanense | 西盟合轮恙螨b | H. simena | 甲梯恙螨属 | Chatia |
| 云岭纤恙螨 | L. yunlingense | 徐氏合轮恙螨 | H. hsui | 尖螯甲梯恙螨 | C. acrichela |
| 鹅颈山纤恙螨 | L. ejingshanense | 伯劳合轮恙螨 | H. lanius | 高山甲梯恙螨 | C. alpine |
| 保鼠纤恙螨 | L. baoshui | 珠恙螨属 | Doloisia | 螯齿恙螨属 | Odontacarus |
| 尾毛纤恙螨 | L. caudatum | 莫卡珠恙螨 | D. moica | 西山螯齿恙螨 | O. xishana |
| 林地纤恙螨 | L. saltuosum | 六胸毛珠恙螨 | D. hexasternosetosa | 巨螯齿恙螨b | O. majesticus |
| 六毛纤恙螨 | L. sexsetum | 泰山珠恙螨 | D. taishanensis |
Table 3
Statistical analysis of 14 genera of chigger mites on small mammals in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province
| 科 Family | 亚科 Subfamily | 属 Genus | 种数 No. species | 种构成比 Cr of species/% | 个体数 No. individual | 个体数量构成比 Cr of individual/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 恙螨科 Trombiculidae | 恙螨亚科 Trombiculinae | 纤恙螨属 Leptotrombidium | 67 | 50.8 | 15 296 | 75.3 |
| 叶片恙螨属 Trombiculindus | 9 | 6.8 | 672 | 3.3 | ||
| 新恙螨属 Neotrombicula | 4 | 3.0 | 197 | 1.0 | ||
| 微恙螨属 Microtrombicula | 1 | 0.8 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 合轮恙螨属 Helenicula | 9 | 6.8 | 978 | 4.8 | ||
| 珠恙螨属 Doloisia | 3 | 2.3 | 8 | 0 | ||
| 囊棒恙螨属 Ascoschoengastia | 8 | 6.1 | 591 | 2.9 | ||
| 爬虫恙螨属 Herpetacarus | 4 | 3.0 | 114 | 0.6 | ||
| 钳齿恙螨属 Cheladonta | 1 | 0.8 | 58 | 0.3 | ||
| 小计 Subtotal | 106 | 80.3 | 17 915 | 88.2 | ||
| 背展恙螨亚科 Gahrliepiinae | 无前恙螨属 Walchia | 8 | 6.1 | 1 921 | 9.5 | |
| 背展恙螨属 Gahrliepia | 13 | 9.9 | 361 | 1.8 | ||
| 棒六恙螨属 Schoengastiella | 1 | 0.8 | 81 | 0.4 | ||
| 小计 Subtotal | 22 | 16.7 | 2 363 | 11.6 | ||
| 列恙螨科 Leeuwenhoekiidae | 列恙螨亚科 Leeuwenhoekiinae | 螯齿恙螨属 Odontacarus | 2 | 1.5 | 23 | 0.1 |
| 甲梯恙螨属 Chatia | 2 | 1.5 | 12 | 0.1 | ||
| 小计 Subtotal | 4 | 3.0 | 35 | 0.2 | ||
| 合计 Total | 132 | 100 | 20 313 | 100 |
Table 4
Constituent ratio of five dominant species of chigger mites in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province
| 优势恙螨 Dominant chigger species | 数量/只 Number | 构成比/% Cr/% |
|---|---|---|
| 密点纤恙螨 L. densipunctatum | 3 445 | 17.0 |
| 永胜纤恙螨 L. yongshengense | 3 101 | 15.3 |
| 竹栖纤恙螨 L. bambicola | 2 010 | 9.9 |
| 攸氏无前恙螨 W. ewingi | 1 181 | 5.8 |
| 江苏纤恙螨 L. kiangsuense | 900 | 4.4 |
| 合计 Total | 10 637 | 52.4 |
Table 5
Constituent ratio of five main vector chigger mites in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province
| 主要媒介恙螨 Main vector chigger species | 数量/只 Number | 构成比/% Cr/% |
|---|---|---|
| 英帕纤恙螨 L. imphalum | 814 | 4.0 |
| 西盟合轮恙螨 H. simena | 486 | 2.4 |
| 岩栖纤恙螨 L. rupestre | 315 | 1.6 |
| 小板纤恙螨 L. scutellare | 181 | 0.9 |
| 地里纤恙螨 L. deliense | 125 | 0.6 |
| 合计 Total | 1 921 | 9.5 |
Table 6
Infection and community indicators of chigger mites in regions with different altitudes in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province
| 海拔梯度 Altitude gradients/m | 恙螨个体数及构成比No. and Cr of chigger individual | 感染指标Infection index | 群落指标Community index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Cr /% | PM /% | MA | MI | H’ | D | S | E | |||
| 1 000~1 999 | 13 832 | 68.1 | 84.8 | 58.61 | 69.16 | 2.53 | 0.87 | 57 | 0.63 | ||
| 2 000~2 999 | 5 254 | 25.9 | 62.9 | 16.27 | 25.88 | 3.39 | 0.94 | 104 | 0.73 | ||
| 3 000~3 999 | 1 227 | 6.0 | 47.5 | 5.6 | 11.8 | 2.49 | 0.85 | 50 | 0.64 | ||
| 合计Total | 20 313 | 100 | 65.2 | 26.11 | 40.07 | 3.2 | 0.92 | 32 | 0.65 | ||
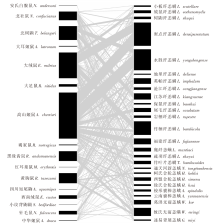
Fig. 3
Bilateral network diagram of mutual relationships between hosts (small mammals) and chigger mites in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province Note:The width of the black patch represents the number of a certain hosts (small mammals) and a certain chiggers, while the gray line or band represents the bilateral relationship between the hosts (small mammals) and the chiggers.

|
| [1] | LI Zhi, MENG Ru, HAN Yuan, YUAN Qing, HUANG Ying, DUO Hong, FU Yong. Genetic evolutionary characteristics for piroplasm infection in equines in Qinghai Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(3): 335-339. |
| [2] | SHEN Guosong, MENG Weidong. Analysis of Trichomonas vaginalis infections among women based on 2016-2023 data from multiple hospitals in Huzhou region [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(3): 340-344. |
| [3] | DAI Jiarui, ZHU Aiya, LI Yang, LI Anmei, GENG Yan, YUAN Maoyang, GAN Xintian. Prevalence of soil-transmitted nematode infections in national surveillance sites of Guizhou Province from 2020 to 2023 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(3): 358-363. |
| [4] | GUAN Yuwei, XIANG Yulong, ZHOU Jingzhu, LUO Xiaolong, KONG Xuexue, ZHANG Yan, HU Yong, LIANG Wenqin. Investigation of bacterial community diversity in parasitic ticks from three autonomous prefectures in Guizhou Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(3): 370-376. |
| [5] | YANG Yawen, HONG Yujie, QIAN Gege, LING Min, WANG Zixuan, YU Hui, SUN Huaiyu, TAO Xianglin, LI Minjie, SUN Entao. Macrogenomic next-generation sequencing of microbial community diversity and functional genes in Dermatophagoides farinae [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(3): 395-402. |
| [6] | SHI Chengyu, CHANG Yunjing, LV Fangli. Impact of chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection on host neuropsychiatric and behavioral well-being [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(3): 429-435. |
| [7] | LI Bowen, WANG Junhao, ZENG Xi, XU Kaya. A adolescent case of recurrent single cerebral hemorrhage caused by cerebrothoracic paragonimiasis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(3): 446-448. |
| [8] | HU Shengbao, HUANG Haitao, XIAO Fuhao, DU Ziyou, GUO Dongli, CAI Lajia. A case with Clonorchis sinensis infection in Golmud City, Qinghai Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(3): 449-451. |
| [9] | LI Benfu, XIAO Dan, LU Chunhua, SHI Shuai, YAN Xinliu, ZI Jinrong, PENG Jia, LI Jianxiong, WANG Zhengqing, XU Qian, WU Fangwei, YANG Yaming. Analysis of the infection factors Echinococcus granulosus in dogs in Shangri-La City, Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(2): 281-285. |
| [10] | ZHU Yong, XU Jingru, YAN Shuning, LI Ling, JIANG Yuanya, WANG Lan, LIU Daiqiang. Prevalence and risk factors of hookworm infections among agricultural planters in Rongchang District, Chongqing Municipality [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(2): 290-295. |
| [11] | TANG Juan, XU Lu, PANG Jie. A case of Trichomonas tenax infection complicated with asymptomatic pulmonary infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(2): 295-297. |
| [12] | HUANG Lihua, WU Jun, LI Zhengjin, LUO Jiao, GU Wei. Fasciola hepatica infection complicated by hepatic tuberculosis: a case report [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(2): 304-306. |
| [13] | LI Qingyu, JIN Yong, MA Weiqiong, HUANG Zhiyong. A case of central nervous system and pulmonary infection caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(2): 307-310. |
| [14] | ZHANG Xiaocheng, SHEN Yujuan, HU Yuan, JIANG Yanyan, LIU Hua, CAO Jianping. Establishment and influencing factors of experimental animal models for intestinal protozoa infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(1): 135-139. |
| [15] | WANG Lu’er, ZHENG Yuhua, JI Chunhua, XUE Shuqin. Epidemiological investigation and disposal of 5 visceral leishmaniasis cases in Gaoping County, Shanxi Province from 2022 to 2023 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2025, 43(1): 143-146. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||