
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2019, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 196-201.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2019.02.014
• ORGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fang-zhou CHENG( ), Chun-hua GAO, Yue-tao YANG, Jun-yun WANG*(
), Chun-hua GAO, Yue-tao YANG, Jun-yun WANG*( )
)
Received:2018-11-26
Online:2019-04-30
Published:2019-05-13
Contact:
Jun-yun WANG
E-mail:fangzhou10277@163.com;wangjy@nipd.chinacdc.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
Fang-zhou CHENG, Chun-hua GAO, Yue-tao YANG, Jun-yun WANG. Polymorphism analysis of internal transcribed spacer 1 of Leishmania isolates from different endemic areas in China[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(2): 196-201.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2019.02.014
Table 1
Reference ITS-1 sequences of Leishmania isolates from GenBank for phylogenetic analysis
| 种名Species | 世界卫生组织编码WHO code | 分离来源国Source country | 登录号Accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 杜氏利什曼原虫 L. donovani | MHOM/IN/80/DD8 | 印度 India | AJ000292 |
| MHOM/KE/75/H9 | 肯尼亚Kenya | EU326228 | |
| MHOM/ET/08/DM309-C11 | 埃塞俄比亚Ethiopia | FN182209 | |
| MHOM/ET/08/DM309-C13 | 埃塞俄比亚Ethiopia | FN182206 | |
| 婴儿利什曼原虫 L. infantum | MHOM/IR/04/IPI-UN10 | 伊朗Iran | GQ444144 |
| MHOM/UZ/2007/MUA | 乌兹别克斯坦Uzbekistan | FM164416 | |
| MHOM/UZ/2007/OBA | 乌兹别克斯坦Uzbekistan | FM164419 | |
| MHOM/BR/74/PP75 | 巴西 Brazil | EU326227 | |
| 埃塞俄比亚利什曼原虫L. aethiopica | MHOM/ET/94/1470 | 埃塞俄比亚Ethiopia | FN677344 |
| 热带利什曼原虫 L. tropica | MHOM/AF/88/KK27 | 阿富汗Afghanistan | GQ913688 |
| MHOM/SU/60/OD | 苏联 Soviet Union | EU326226 |
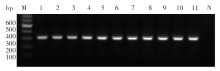
Fig. 1
PCR amplification products of ITS-1 of Leishmania isolates in ChinaM: DNA marker; 1-10: The Leishmania isolates from different endemic areas in China,KXG-Xu, KXG-Liu, KXG-927, JIASHI-1, JIASHI-5, XJ771, SC6, Cy, 801 and KS-2; 11: Reference strain, L. donovani MHOM/IN/80/DD8; N: Negative control
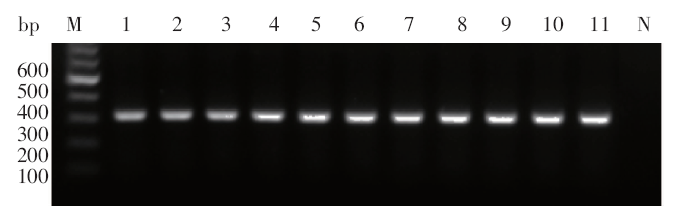
Table 2
Size of ITS-1 sequences amplified from 10 Chinese Leishmania isolates and their accession number in GenBank
| 分离株Isolate | 世界卫生组织编码 WHO code | 虫种 Species | 来源 Location | 宿主 Host | 序列长度/bp Sequence length/bp | GenBank登录号 GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KXG-Xu | MHOM/CN/1994/KXG-Xu | 婴儿利什曼原虫 L. infantum | 新疆克拉玛依 Karamay, Xinjiang | 患者 Human | 312 | MH450079a |
| KXG-Liu | MHOM/CN/1994/KXG-Liu | 婴儿利什曼原虫 L. infantum | 新疆克拉玛依 Karamay, Xinjiang | 患者 Human | 312 | MH450080a |
| KXG-927 | IMJW/CN/1992/KXG-927 | 婴儿利什曼原虫 L. infantum | 新疆克拉玛依 Karamay, Xinjiang | 白蛉 Sandfly | 312 | MH450082a |
| JIASHI-1 | MHOM/CN/2008/JIASHI-1 | 婴儿利什曼原虫 L. infantum | 新疆伽师 Jiashi, Xinjiang | 患者 Human | 313 | GQ367486b |
| JIASHI-5 | MHOM/CN/2008/JIASHI-5 | 婴儿利什曼原虫 L. infantum | 新疆伽师 Jiashi, Xinjiang | 患者 Human | 313 | MH450075a |
| XJ771 | IWUI/CN/1977/XJ771 | 婴儿利什曼原虫 L. infantum | 新疆伽师 Jiashi, Xinjiang | 白蛉 Sandfly | 313 | MH450076a |
| SC6 | MHOM/CN/1986/SC6 | 杜氏利什曼原虫 L. donovani | 四川九寨沟 Jiuzhaigou, Sichun | 患者 Huaman | 318 | MH450071a |
| Cy | MCAN/CN/2008/Cy | 杜氏利什曼原虫 L. donovani | 甘肃武都 Wudu, Gansu | 犬 Canine | 318 | MH450070a |
| 801 | MHOM/CN/1980/801 | 杜氏利什曼原虫 L. donovani | 新疆喀什 Kashi, Xinjiang | 患者 Human | 316 | GQ367489b |
| KS-2 | MHOM/CN/1996/KS-2 | 杜氏利什曼原虫 L. donovani | 新疆喀什 Kashi, Xinjiang | 患者 Human | 316 | MH450077a |
| [1] | 高春花, 管立人, 汪俊云, 等. 利什曼原虫的传播机制及传媒蛉种的研究进展[J]. 国际医学寄生虫病杂志, 2007, 34(3): 113-118. |
| [2] | Desjeux P.Leishmaniasis: current situation and new perspectives[J]. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis, 2004, 27(5): 305-318. |
| [3] | Alvar J, Vélez ID, Bern C, et al. Leishmaniasis worldwide and global estimates of its incidence[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(5): e35671. |
| [4] | Guan LR, Shen WX.Recent advances in visceral leishmaniasis in China[J]. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health, 1991, 22(3): 291-298. |
| [5] | Lu HG, Zhong L, Guan LR, et al. Separation of Chinese Leishmania isolates into five genotypes by kinetoplast and chromosomal DNA heterogeneity[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 1994, 50(6): 763-770. |
| [6] | Zhou XN, Lv S, Yang GJ, et al. Spatial epidemiology in zoonotic parasitic diseases: insights gained at the 1st International Symposium on Geospatial Health in Lijiang, China, 2007[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2009, 2: 10. |
| [7] | 管立人, 瞿靖琦, 柴君杰. 中国利什曼病的现状和对开展防治工作的若干建议[J]. 地方病通报, 2000, 15(3): 49-52. |
| [8] | Wang JY, Gao CH, Yang YT, et al. An outbreak of the desert sub-type of zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis in Jiashi, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, People’s Republic of China[J]. Parasitol Int, 2010, 59(3): 331-337. |
| [9] | Wang JY, Cui G, Chen HT, et al. Current epidemiological profile and features of visceral leishmaniasis in people’s republic of China[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2012, 5: 31. |
| [10] | 《中华传染病杂志》编辑委员会. 中国利什曼原虫感染诊断和治疗专家共识[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2017, 35(9): 513-518. |
| [11] | Guan LR, Yang YQ, Qu JQ, et al. Discovery and study of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Karamay of Xinjiang, West China[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2013, 2: 20. |
| [12] | 管立人. 我国内脏利什曼病的现状和对防治工作的展望[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2009, 27(5): 394-397. |
| [13] | Tashakori M, Mahnaz T, Kuhls K, et al. Leishmania major: genetic heterogeneity of Iranian isolates by single-strand conformation polymorphism and sequence analysis of ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer[J]. Acta Trop, 2006, 98(1): 52-58. |
| [14] | Subba Raju BV, Gurumurthy S, Kuhls K, et al. Genetic typing reveals monomorphism between antimony sensitive and resistant Leishmania donovani isolates from visceral leishmaniasis or post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis cases in India[J]. Parasitol Res, 2012, 111(4): 1559-1568. |
| [15] | Ghatee MA, Sharifi I, Kuhls K, et al. Heterogeneity of the internal transcribed spacer region in Leishmania tropica isolates from southern Iran[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2014, 144: 44-51. |
| [16] | Karamian M, Kuhls K, Hemmati M, et al. Phylogenetic structure of Leishmania tropica in the new endemic focus Birjand in East Iran in comparison to other Iranian endemic regions[J]. Acta Trop, 2016, 158: 68-76. |
| [17] | 田玉, 陈建平, 胡孝素. 山丘疫区杜氏利什曼原虫核糖体基因内转录间隔区的克隆及序列分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2004, 22(5): 294-296. |
| [18] | el Tai NO, Osman OF, el Fari M, et al. Genetic heterogeneity of ribosomal internal transcribed spacer in clinical samples of Leishmania donovani spotted on filter paper as revealed by single-strand conformation polymorphisms and sequencing[J]. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 2000, 94(5): 575-579. |
| [19] | Kuhls K, Mauricio IL, Pratlong F, et al. Analysis of ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer sequences of the Leishmania donovani complex[J]. Microbes Infect, 2005, 7(11/12): 1224-1234. |
| [20] | Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, et al. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2013, 30(12): 2725-2729. |
| [21] | Schönian G, Cupolillo E, Mauricio I.Molecular evolution and phylogeny of Leishmania[M]. Drug Resistance in Leishmania Parasites, 2013: 19-57. |
| [22] | Rioux JA, Lanotte G, Serres E, et al. Taxonomy of Leishmania. Use of isoenzymes. Suggestions for a new classification[J]. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp, 1990, 65(3): 111-125. |
| [23] | Cupolillo E, Grimaldi Júnior G, Momen H, et al. Intergenic region typing (IRT): a rapid molecular approach to the characterization and evolution of Leishmania[J]. Mol Biochem Parasitol, 1995, 73(1/2): 145-155. |
| [24] | Quispe Tintaya KW, Ying X, Dedet JP, et al. Antigen genes for molecular epidemiology of leishmaniasis: polymorphism of cysteine proteinase B and surface metalloprotease glycoprotein 63 in the Leishmania donovani complex[J]. J Infect Dis, 2004, 189(6): 1035-1043. |
| [25] | 丁丹, 高春花, 杨玥涛, 等. 我国不同流行区利什曼原虫分离株动基体小环DNA序列分析[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2013, 29(11): 1055-1059. |
| [26] | 汪俊云. 利什曼原虫DNA重复序列在虫种鉴定上的价值分析[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2005, 21(4): 304-308. |
| [27] | 张春莹, 宋兴勃, 严可宁, 等. 中国不同流行疫区利什曼原虫分离株的微卫星多态性分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2014, 41(10): 1852-1855. |
| [28] | Schönian G, Nasereddin A, Dinse N, et al. PCR diagnosis and characterization of Leishmania in local and imported clinical samples[J]. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis, 2003, 47(1): 349-358. |
| [29] | Zemanová E, Jirk<inline-graphic xlink:href="1000-7423-37-2-196/img_4.tif"/>M, Mauricio IL, et al. Genetic polymorphism within the leishmania donovani complex: correlation with geographic origin[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2004, 70(6): 613-617. |
| [30] | Zelazny AM, Fedorko DP, Li L, et al. Evaluation of 7SL RNA gene sequences for the identification of Leishmania spp.[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2005, 72(4): 415-420. |
| [31] | Berzunza-Cruz M, Cabrera N, Crippa-Rossi M, et al. Polymorphism analysis of the internal transcribed spacer and small subunit of ribosomal RNA genes of Leishmania mexicana[J]. Parasitol Res, 2002, 88(10): 918-925. |
| [32] | 管立人, 许永湘, 左新平, 等. 新疆克拉玛依皮肤利什曼病传播媒介的研究[J]. 地方病通报, 1996, 11(1): 38-41. |
| [33] | Yang BB, Guo XG, Hu XS, et al. Species discrimination and phylogenetic inference of 17 Chinese Leishmania isolates based on internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) sequences[J]. Parasitol Res, 2010, 107(5): 1049-1065. |
| [34] | Shang LM, Peng WP, Jin HT, et al. The prevalence of canine Leishmania infantum infection in Sichuan Province, southwestern China detected by real time PCR[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2011, 4(1): 173-177. |
| [35] | 张春莹, 黄玉霞, 袁余, 等. 热休克蛋白70(hsp70)基因对利什曼原虫中国分离株的系统发育分析[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2014, 30(2): 163-168. |
| [1] | WANG Xiaojun, CAI Yucheng, ZOU Xuan, LI Hui, TONG Bobo. The epidemiological characteristics of visceral leishmaniasis in Longnan City from 2005 to 2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 579-585. |
| [2] | ZHANG Li, YI Boyu, YIN Jianhai, XIA Zhigui. Epidemiological characteristics of malaria in China, 2022 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 137-141. |
| [3] | KUI Yan, XUE Chuizhao, WANG Xu, LIU Baixue, WANG Ying, WANG Liying, YANG Shijie, HAN Shuai, WU Weiping, XIAO Ning. Progress of echinococcosis control in China, 2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 142-148. |
| [4] | ZHOU Zhengbin, PAN Gaiqin, LI Yuanyuan, LIU Qin, YANG Limin, LI Zhongqiu, MA Zhitao, ZHANG Yi, LI Shizhu. Prevalence of visceral leishmaniasis in China in 2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 149-155. |
| [5] | WANG Fenfen, ZHANG Peijun, REN Mengzhi, LI Daohao. Epidemiological characteristics of visceral leishmaniasis in Yangquan City, Shanxi Province from 2006 to 2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 228-232. |
| [6] | JIA Zhenzhen, LIU Hongying, JIANG Qi, WANG Lingling, LIU Xiangjun. A case of visceral leishmaniasis misdiagnosed as a hematological disorder [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 257-259. |
| [7] | GU Yan, YU Jin, XU Cehua. Investigation on the first imported visceral leishmaniasis case in Ningxia in the past 44 years [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 260-262. |
| [8] | JIANG Tiange, ZENG Wenbo, LI Zhongqiu, ZHANG Yi. Research advances in the regulatory role of non-coding RNA in leishmaniasis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 92-97. |
| [9] | YANG Cheng-yun, HE Zhi-quan, LU De-ling, QIAN Dan, LIU Ying, LI Su-hua, ZHOU Rui-min, DENG Yan, ZHANG Hong-wei, WANG Hao, ZHAO Dong-yang, GUO Wan-shen. Epidemiological investigation on cases of visceral leishmaniasis in Henan Province in 2020 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 481-486. |
| [10] | LI Zhen, GUO Xiao-kui, WANG Yue-xiang, ZHENG Bin, ZHOU Xiao-nong. The strategy on One Health development in China based on SWOT analysis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 271-277. |
| [11] | CHEN Yuan-cai, HUANG Jian-ying, LI Jun-qiang, ZHANG Long-xian. Molecular epidemiology and subtype distribution of Cryptosporidium parvum from dairy cattle in China [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 278-284. |
| [12] | ZHANG Li, YI Bo-yu, XIA Zhi-gui, YIN Jian-hai. Epidemiological characteristics of malaria in China, 2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 135-139. |
| [13] | LUO Zhuo-wei, ZHOU Zheng-bin, GONG Yan-feng, FENG Jia-xin, LI Yuan-yuan, ZHANG Yi, LI Shi-zhu. Current status and challenges of visceral leishmaniasis in China [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 146-152. |
| [14] | ZHANG Ai-ping, LIANG Man-man, ZHU Ling-ling, SHENG Hao-yu, YANG Jiang-hua. Relapse of visceral leishmaniasis in a cured case after 64 years [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 266-268. |
| [15] | XIA Zhi-gui, FENG Jun, ZHANG Li, FENG Xin-yu, HUANG Fang, YIN Jian-hai, ZHOU Shui-sen, ZHOU Sheng, YANG Heng-lin, WANG Shan-qing, GAO Qi, TANG Lin-hua, YAN Jun. Achieving malaria elimination in China: analysis on implementation and effectiveness of the surveillance-response system [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 733-740. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||