
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 701-714.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2024.06.003
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Yuying1( ), ZHAO Jiaguang2, ZHOU Changhai1, ZHU Tingjun1, HUANG Jilei1, MENG Jun3, JIANG Zhihua3, ZHOU Xiaonong1, LI Shizhu1, QIAN Menbao1,*(
), ZHAO Jiaguang2, ZHOU Changhai1, ZHU Tingjun1, HUANG Jilei1, MENG Jun3, JIANG Zhihua3, ZHOU Xiaonong1, LI Shizhu1, QIAN Menbao1,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-18
Revised:2024-11-14
Online:2024-12-30
Published:2025-01-14
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHU Yuying, ZHAO Jiaguang, ZHOU Changhai, ZHU Tingjun, HUANG Jilei, MENG Jun, JIANG Zhihua, ZHOU Xiaonong, LI Shizhu, QIAN Menbao. Epidemiology and determinants of Clonorchis sinensis infection in Binyang County, Guangxi in 2022[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(6): 701-714.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2024.06.003
Table 1
Prevalence of Clonorchis sinensis infections in humans in Binyang County, Guangxi, 2022 (n = 1 007)
| 变量 Variable | 检查人数 No. examined | 粪检阳性例数 No. case with C. sinensis infection | 感染率/% (95% CI) Prevalence/% (95% CI) | EPG几何均数(95% CI) Geometric mean of EPG (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乡镇 Villages | ||||
| 宾州镇 Binzhou | 203 | 25 | 12.32 (7.76~16.87) | 219 (97~497) |
| 古辣镇 Gula | 201 | 33 | 16.42 (11.25~21.58) | 148 (91~241) |
| 黎塘镇 Litang | 203 | 12 | 5.91 (2.64~9.18) | 164 (93~288) |
| 思陇镇 Silong | 200 | 44 | 22.00 (15.84~27.38) | 113 (71~180) |
| 新圩镇 Xinxu | 200 | 42 | 21.00 (15.31~26.69) | 442 (278~702) |
| 性别 Gender | ||||
| 男性 Male | 494 | 130 | 26.32 (22.27~30.06) | 223 (169~294) |
| 女性 Female | 513 | 26 | 5.07 (3.16~6.97) | 94 (54~162) |
| 年龄/岁 Age/Year | ||||
| ≤ 14 | 252 | 5 | 1.98 (0.25~3.72) | 60 (13~270) |
| 15~29 | 54 | 5 | 9.26 (1.27~17.25) | 35 (10~124) |
| 30~44 | 147 | 30 | 20.41 (13.82~27.00) | 154 (96~249) |
| 45~59 | 255 | 62 | 24.31 (19.01~29.61) | 238 (155~364) |
| ≥ 60 | 299 | 54 | 18.06 (13.42~22.15) | 225 (146~346) |
| 民族 Ethnicity | ||||
| 汉族 Han | 872 | 143 | 16.40 (13.94~18.86) | 203 (154~266) |
| 壮族 Zhuang | 130 | 13 | 10.00 (4.77~15.23) | 152 (88~260) |
| 其他a Othersa | 5 | 0 | - | - |
| 文化程度 Education | ||||
| 文盲或半文盲 Illiteracy or semi-illiteracy | 78 | 4 | 5.13 (0.12~10.13) | 158 (24~1058) |
| 小学 Primary school | 405 | 31 | 7.65 (5.05~10.25) | 223 (124~400) |
| 初中 Junior high school | 467 | 111 | 23.77 (19.89~27.64) | 193 (142~262) |
| 高中及以上 Senior high school and above | 56 | 9 | 16.07 (6.15~26.00) | 125 (54~291) |
| 总计 Total | 1 007 | 156 | 15.49 (13.25~17.73) | 198 (153~255) |
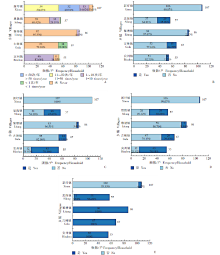
Fig. 1
Household dietary and kitchen habits across different areas in Binyang County, Guangxi, 2022 (n = 372) A: Frequency of preparing raw freshwate fish in the household; B: Purchasing raw freshwater fish from outside; C: Presenting raw freshwater fish to neighbors; D: Having experiences of receiving raw freshwater fish from neighbors; E: Using raw and cooked chopping boards separately. All values that are not shown in the figure indicate constituent ratios of 1% and less.
Table 2
Awareness of clonorchiasis knowledge among different populations in Binyang County, Guangxi, 2022 (n = 202)
| 变量 Variable | 调查人数 No. surveyed | 知晓华支睾吸虫病人数(占比/%) No. hearing of clonorchiasis (ratio/%) | 了解感染途径人数 (占比/%) No. knowing transmission (ratio/%) | 了解疾病危害人数 (占比/%) No. knowing the harm of disease (ratio/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乡镇 Villages | ||||
| 宾州镇 Binzhou | 40 | 24 (60.00) | 20 (50.00) | 4 (10.00) |
| 古辣镇 Gula | 40 | 37 (92.50) | 37 (92.50) | 36 (90.00) |
| 黎塘镇 Litang | 40 | 13 (32.50) | 11 (27.50) | 9 (22.50) |
| 思陇镇 Silong | 40 | 12 (30.00) | 9 (22.50) | 5 (12.15) |
| 新圩镇 Xinxu | 42 | 24 (57.14) | 24 (57.14) | 23 (54.76) |
| 性别 Gender | ||||
| 女性 Female | 102 | 47 (46.08) | 42 (41.18) | 31 (30.39) |
| 男性 Male | 100 | 63 (63.00) | 59 (59.00) | 46 (46.00) |
| 年龄/岁 Age/Year | ||||
| ≤ 14 | 59 | 8 (13.56) | 8 (13.56) | 7 (11.86) |
| 15~29 | 10 | 6 (60.00) | 6 (60.00) | 4 (40.00) |
| 30~44 | 26 | 21 (80.77) | 19 (73.08) | 10 (38.46) |
| 45~59 | 44 | 30 (68.18) | 28 (63.64) | 24 (54.55) |
| ≥ 60 | 63 | 45 (71.43) | 40 (63.49) | 32 (50.79) |
| 民族 Ethnicity | ||||
| 汉族 Han | 175 | 102 (58.29) | 95 (54.29) | 72 (41.14) |
| 壮族 Zhuang | 27 | 8 (29.63) | 6 (22.22) | 5 (18.52) |
| 文化程度 Education level | ||||
| 文盲或半文盲 Illiteracy or semi-illiteracy | 6 | 1 (16.67) | 1 (16.67) | 0 (0) |
| 小学 Primary school | 101 | 38 (37.62) | 33 (32.67) | 25 (24.75) |
| 初中 Junior high school | 79 | 57 (72.15) | 54 (68.35) | 42 (53.16) |
| 高中及以上 Senior high school and above | 16 | 14 (87.50) | 13 (81.25) | 10 (62.50) |
| 合计 Total | 202 | 110 (54.46) | 101 (50.00) | 77 (38.12) |
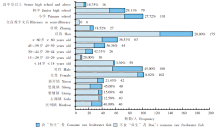
Fig. 2
Characteristic of consuming raw freshwater fish behavior among different populations in Binyang County, Guangxi, 2022 (n = 202) Note: The percentages in the figure represent the proportion of individuals consuming raw freshwater fish, and the numbers indicate the total frequency in each subgroup.
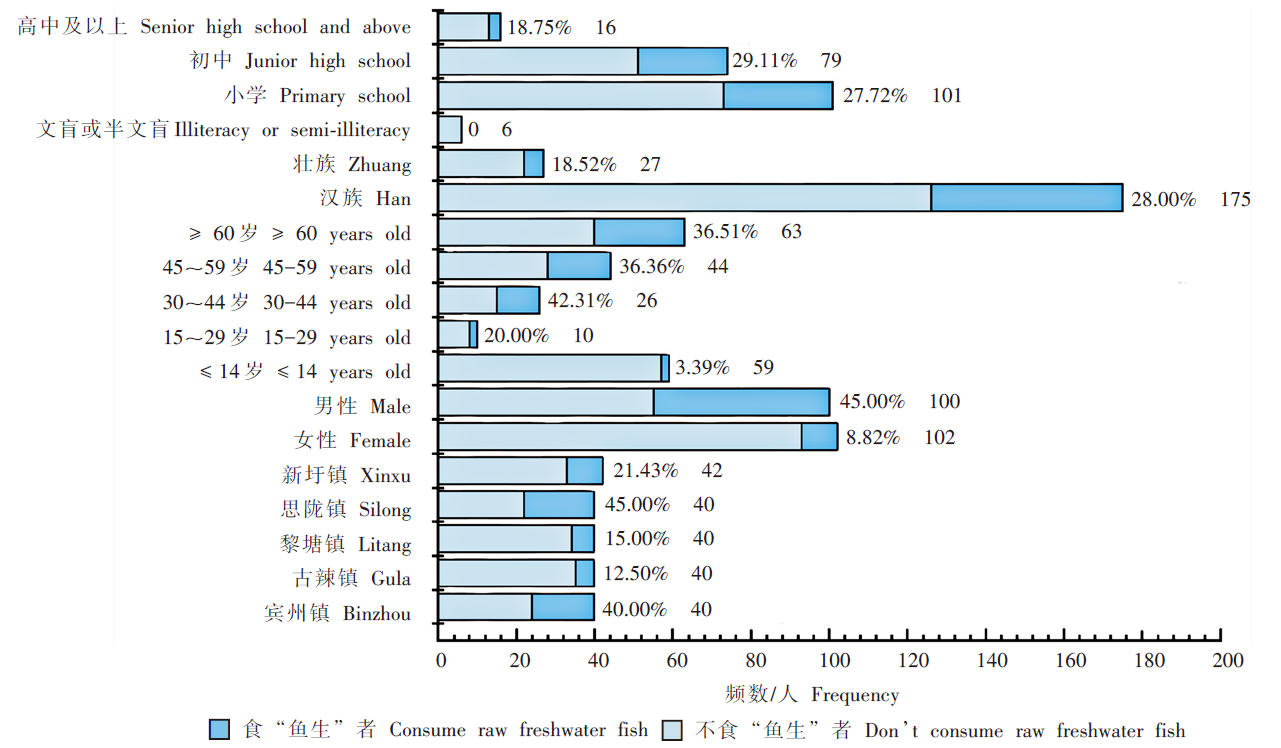
Fig. 3
Characteristic of the willingness to consume raw freshwater fish in future among different populations in Binyang County, Guangxi, 2022 (n = 202) Note: The percentages in the figure represent the proportion of individuals who are unlikely to consume raw freshwater fish in future, and the numbers indicate the total frequency in each subgroup.
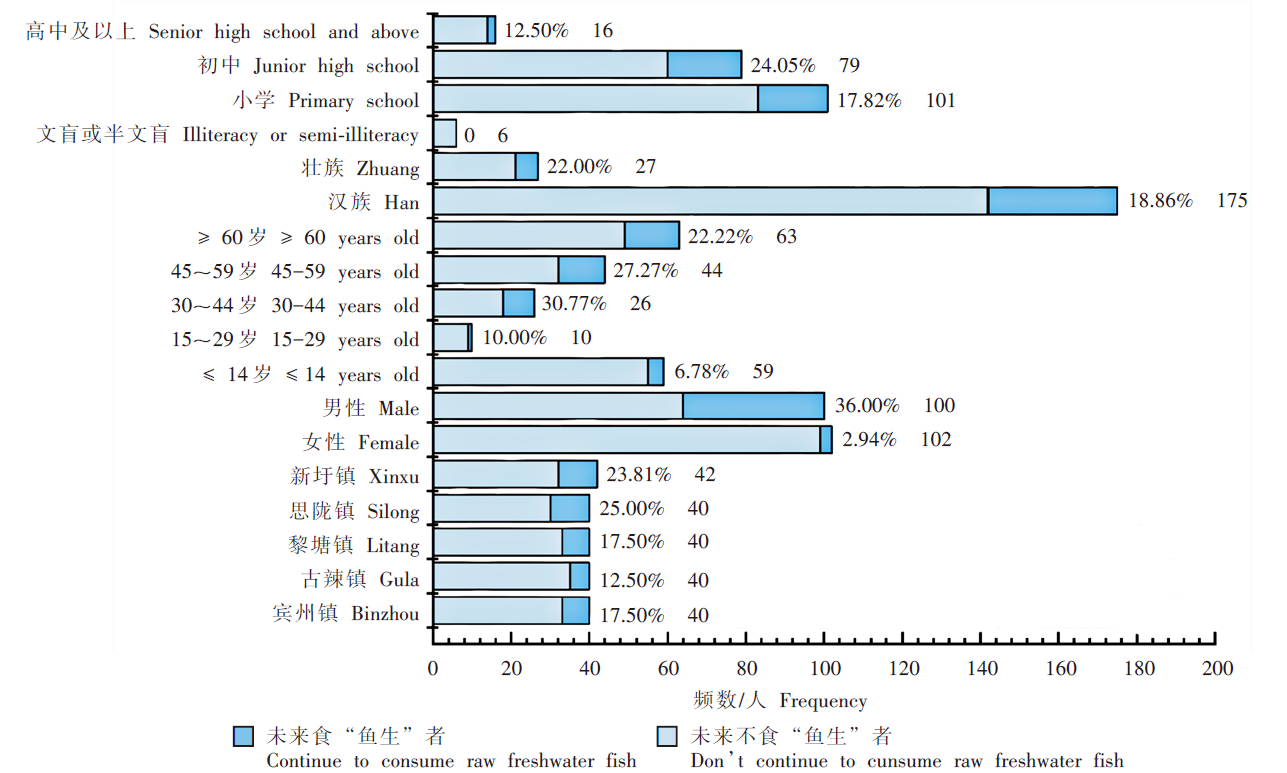
Table 3
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses of factors affecting Clonorchis sinensis infections among different populations in Binyang County, Guangxi, 2022 (n = 175)
| 变量 Variable | 调查人数 No. Surveyed | 粪检阳性例数(占比) No. case with C. sinensis infection (ratio/%) | 粗OR(95% CI) Crude OR (95% CI) | P | 调整后OR(95% CI)a Adjusted OR (95% CI)a | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乡镇 Villages | > 0.05 | |||||||
| 宾州镇 Binzhou | 29 | 11 (37.93) | - | |||||
| 古辣镇 Gula | 38 | 3 (7.89) | 0.14 (0.02~0.64) | < 0.05 | ||||
| 黎塘镇 Litang | 40 | 6 (15.00) | 0.29 (0.08~1.04) | > 0.05 | ||||
| 思陇镇 Silong | 33 | 12 (36.36) | 0.94 (0.29~2.98) | > 0.05 | ||||
| 新圩镇 Xinxu | 35 | 7 (20.00) | 0.42 (0.11~1.43) | > 0.05 | ||||
| 性别 Gender | < 0.05 | |||||||
| 女性 Female | 89 | 7 (7.87) | - | |||||
| 男性 Male | 86 | 32 (37.21) | 9.85 (3.90~30.26) | |||||
| 年龄/岁 Age/Year | < 0.05 | |||||||
| ≤ 29 | 54 | 3 (5.56) | - | |||||
| 30~44 | 24 | 9 (37.50) | 10.12 (2.67~50.58) | < 0.05 | ||||
| 45~59 | 42 | 11 (26.19) | 6.03 (1.73~28.23) | < 0.05 | ||||
| ≥ 60 | 55 | 16 (29.09) | 6.97 (2.14~31.51) | < 0.05 | ||||
| 民族 Ethnicity | > 0.05 | |||||||
| 汉族 Han | 151 | 32 (21.19) | - | |||||
| 壮族 Zhuang | 24 | 7 (29.17) | 1.58 (0.57~4.03) | |||||
| 文化程度b Education levelb | > 0.05 | |||||||
| 文盲或半文盲 Illiteracy or semi-illiteracy | 3 | 0 (0) | - | |||||
| 小学 Primary school | 79 | 13 (16.46) | - | |||||
| 初中 Junior high school | 79 | 24 (30.38) | 2.22 (1.03~4.76) | < 0.05 | ||||
| 高中及以上 Senior high school and above | 14 | 2 (14.29) | 0.85 (0.17~4.26) | > 0.05 | ||||
| 知晓华支睾吸虫病 Hearing of clonorchiasis | < 0.05 | |||||||
| 否 No | 79 | 11 (13.92) | - | |||||
| 是 Yes | 96 | 28 (29.17) | 3.21 (1.45~7.68) | |||||
| 了解感染途径 Knowing transmission route | < 0.05 | |||||||
| 否 No | 85 | 14 (16.47) | - | |||||
| 是 Yes | 90 | 25 (27.78) | 2.35 (1.11~5.22) | |||||
| 了解疾病危害 Knowing the harm of disease | > 0.05 | |||||||
| 否 No | 105 | 21 (20.00) | - | |||||
| 是 Yes | 70 | 18 (25.71) | 1.60 (0.77~3.36) | |||||
| 食“鱼生”频次 Frequency on cunsuming raw freshwater fish | < 0.05 | < 0.05 | ||||||
| 无 Never | 136 | 9 (6.62) | - | - | ||||
| 1~5次/年 1-5 times/year | 33 | 25 (75.76) | 46.12 (16.03~151.80) | < 0.05 | 30.01 (7.56~152.04) | < 0.05 | ||
| > 5次/年 > 5 times/year | 11 | 10 (90.91) | 158.14 (24.99~341.38) | < 0.05 | 81.40 (7.78~287.37) | < 0.05 | ||
| 制作“鱼生”频次 Frequency of making raw freshwater fish | < 0.05 | |||||||
| 无 Never | 92 | 14 (15.22) | - | |||||
| < 1次/年 < 1 times/year | 9 | 1 (11.11) | 0.70 (0.04~4.25) | > 0.05 | ||||
| 1~10次/年 1-10 times/year | 48 | 18 (37.50) | 3.34 (1.49~7.68) | < 0.05 | ||||
| 11~50次/年 11-50 times/year | 22 | 5 (22.73) | 1.64 (0.48~4.96) | > 0.05 | ||||
| > 50次/年 > 50 times/year | 4 | 1 (25.00) | 1.86 (0.09~15.73) | > 0.05 | ||||
| 从外面买过“鱼生” Purchased raw freshwater fish from outside | < 0.05 | |||||||
| 否 No | 145 | 28 (19.31) | - | |||||
| 是 Yes | 30 | 11 (36.67) | 3.07 (1.25~7.36) | |||||
| 向邻居赠送“鱼生” Gave raw freshwater fish to neighbors | < 0.05 | |||||||
| 否 No | 118 | 19 (16.10) | - | |||||
| 是 Yes | 57 | 20 (35.09) | 2.63 (1.24~5.60) | |||||
| 接受过赠送的“鱼生” Received raw freshwater fish as a gift | < 0.05 | < 0.05 | ||||||
| 否 No | 104 | 12 (11.54) | - | - | ||||
| 是 Yes | 71 | 27 (38.03) | 4.62 (2.16~10.39) | 15.18 (2.15~123.25) | ||||
| 生熟砧板分开使用 Use separate cutting boards for raw and cooked foods | > 0.05 | |||||||
| 否 No | 32 | 6 (18.75) | 0.77 (0.29~2.03) | |||||
| 是 Yes | 143 | 33 (23.08) | - | |||||
Table 4
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses of factors affecting consuming raw freshwater fish (n = 175)
| 变量 Variable | 调查人数 No. surveyed | 食“鱼生”人数(占比/%)No. with consuming raw freshwater fish (ratio/%) | 粗OR(95% CI) Crude OR (95% CI) | P | 调整后OR(95% CI)a Adjusted OR (95% CI)a | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乡镇 Villages | > 0.05 | |||||
| 宾州镇 Binzhou | 29 | 12 (41.38) | - | |||
| 古辣镇 Gula | 38 | 5 (13.16) | 0.22 (0.05~0.81) | < 0.05 | ||
| 黎塘镇 Litang | 40 | 6 (15.00) | 0.26 (0.07~0.89) | < 0.05 | ||
| 思陇镇 Silong | 33 | 14 (42.42) | 1.04 (0.34~3.24) | > 0.05 | ||
| 新圩镇 Xinxu | 35 | 7 (20.00) | 0.36 (0.10~1.22) | > 0.05 | ||
| 性别 Gender | < 0.05 | < 0.05 | ||||
| 女性 Female | 89 | 6 (6.74) | - | - | ||
| 男性 Male | 86 | 38 (44.19) | 10.88 (4.56~30.41) | 17.58 (6.21~61.88) | ||
| 年龄/岁b Age/Yearb | > 0.05 | |||||
| ≤ 14 | 48 | 0 (0) | - | |||
| 15~29 | 6 | 0 (0) | - | |||
| 30~44 | 24 | 10 (41.67) | 1.35 (0.44~4.01) | > 0.05 | ||
| 45~59 | 42 | 15 (35.71) | 1.05 (0.42~2.64) | > 0.05 | ||
| ≥ 60 | 55 | 19 (34.55) | - | |||
| 民族 Ethnicity | > 0.05 | |||||
| 汉族 Han | 151 | 38 (25.17) | 1.01 (0.35~3.34) | |||
| 壮族 Zhuang | 24 | 6 (25.00) | - | |||
| 文化程度c Education levelc | > 0.05 | |||||
| 文盲或半文盲 Illiteracy or semi-illiteracy | 3 | 0 (0) | - | |||
| 小学 Primary school | 79 | 19 (24.06) | 3.48 (0.42~28.76) | > 0.05 | ||
| 初中 Junior high school | 79 | 24 (30.38) | 5.18 (0.63~42.43) | > 0.05 | ||
| 高中及以上 Senior high school and above | 14 | 1 (7.14) | - | |||
| 知晓华支睾吸虫病 Hearing of clonorchiasis | < 0.05 | < 0.05 | ||||
| 否 No | 79 | 12 (15.19) | - | - | ||
| 是 Yes | 96 | 32 (33.33) | 2.80 (1.35~6.12) | 15.75 (1.40~185.99) | ||
| 了解感染途径 Knowing transmission route | < 0.05 | |||||
| 否 No | 85 | 15 (17.65) | - | |||
| 是 Yes | 90 | 29 (32.22) | 2.23 (1.11~4.66) | |||
| 了解疾病危害 Knowing the harm of disease | > 0.05 | |||||
| 否 No | 105 | 24 (22.85) | - | |||
| 是 Yes | 70 | 20 (28.57) | 1.38 (0.69~2.77) | |||
| 制作过“鱼生” Made raw freshwater fish | < 0.05 | |||||
| 否 No | 92 | 14 (15.22) | - | |||
| 是 Yes | 83 | 30 (36.14) | 3.32 (1.63~7.06) | |||
| 从外面买过“鱼生” Purchased raw freshwater fish from outside | < 0.05 | |||||
| 否 No | 145 | 30 (20.69) | - | |||
| 是 Yes | 30 | 14 (46.67) | 4.02 (1.71~9.58) | |||
| 向邻居赠送“鱼生”Gave raw freshwater fish to neighbors | < 0.05 | |||||
| 否 No | 118 | 20 (16.95) | - | |||
| 是 Yes | 57 | 24 (42.11) | 3.97 (1.94~8.29) | |||
| 接受过赠送“鱼生”Received raw freshwater fish as a gift | < 0.05 | |||||
| 否 No | 104 | 15 (14.42) | - | |||
| 是 Yes | 71 | 29 (40.85) | 4.60 (2.24~9.77) | |||
Table 5
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses of factors affecting consumption of raw fresh water fish in future (n = 169)
| 变量 Variable | 调查人数 No. surveyed | 坚持食“鱼生”人数 No. with persisting in consuming raw freshwater fish (ratio/%) | 粗OR(95% CI) Crude OR (95% CI) | P | 调整后OR(95% CI)a Adjusted OR (95% CI)a | P | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乡镇 Villages | > 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 宾州镇 Binzhou | 27 | 5 (18.52) | 0.77 (0.17~3.13) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 古辣镇 Gula | 35 | 5 (14.29) | 0.57 (0.13~2.25) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 黎塘镇 Litang | 40 | 7 (17.50) | 0.72 (0.19~2.60) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 思陇镇 Silong | 32 | 8 (25.00) | 1.12 (0.31~4.04) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 新圩镇 Xinxu | 35 | 8 (22.86) | - | |||||||||
| 性别 Gender | < 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 女性 Female | 85 | 4 (4.71) | - | |||||||||
| 男性 Male | 84 | 29 (34.52) | 10.68 (3.93~37.51) | |||||||||
| 年龄/岁 Age/Year | < 0.05 | |||||||||||
| ≤ 14 | 48 | 2 (4.17) | - | |||||||||
| 15~29 | 24 | 7 (29.17) | 9.47 (2.06~67.96) | < 0.05 | ||||||||
| 30~44 | 42 | 11 (26.19) | 8.16 (2.16~55.14) | < 0.05 | ||||||||
| 45~59 | 55 | 13 (23.64) | 7.12 (1.83~47.25) | < 0.05 | ||||||||
| 民族 Ethnicity | ||||||||||||
| 汉族 Han | 145 | 118 (81.38) | 1.46 (0.53~4.02) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 壮族 Zhuang | 24 | 18 (75.00) | - | |||||||||
| 文化程度b Education levelb | > 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 文盲或半文盲 Illiteracy or semi-illiteracy | 3 | 0 (0) | - | |||||||||
| 小学 Primary school | 79 | 12 (15.19) | - | |||||||||
| 初中 Junior high school | 75 | 19 (25.33) | 1.89 (0.14~4.66) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 高中及以上 Senior high school and above | 12 | 2 (16.67) | 1.12 (0.11~6.29) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 粪检阳性 C. sinensis infection | < 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 否 No | 132 | 11 (8.33) | - | |||||||||
| 是 Yes | 37 | 22 (59.46) | 16.13 (6.73~41.23) | |||||||||
| 知晓华支睾吸虫病 Hearing of clonorchiasis | > 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 否 No | 76 | 10 (13.16) | - | |||||||||
| 是 Yes | 93 | 23 (24.73) | 2.18 (0.96~4.90) | |||||||||
| 了解感染途径 Knowing transmission route | > 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 否 No | 82 | 11 (13.41) | - | |||||||||
| 是 Yes | 87 | 22 (25.29) | 2.19 (0.98~4.85) | |||||||||
| 了解疾病危害 Knowing the harm of disease | > 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 否 No | 102 | 19 (18.63) | - | |||||||||
| 是 Yes | 67 | 14 (20.90) | 1.15 (0.53~2.50) | |||||||||
| 食“鱼生”频次 Frequency of ingesting raw freshwater fish | < 0.05 | < 0.05 | ||||||||||
| 无 Never | 130 | 5 (3.85) | - | - | ||||||||
| 1~5次/年 1-5 times/year | 29 | 21 (72.41) | 65.63 (21.16~244.24) | < 0.05 | 3.66 (1.85~4.32) | < 0.05 | ||||||
| > 5次/年 > 5 times/year | 10 | 7 (70.00) | 58.33 (12.61~346.73) | < 0.05 | 3.55 (1.17~3.03) | < 0.05 | ||||||
| 制作“鱼生”频次 Frequency of making raw freshwater fish | > 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 无 Never | 90 | 14 (15.56) | - | |||||||||
| < 1次/年 < 1 time/year | 8 | 3 (37.50) | 3.26 (0.61~14.89) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 1~10次/年 1-10 times/year | 45 | 8 (17.78) | 1.17 (0.43~3.00) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 11~50次/年 11-50 times/year | 22 | 7 (31.82) | 2.53 (0.84~7.24) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| > 50次/年 > 50 times/year | 4 | 1 (25.00) | 1.81 (0.09~15.33) | > 0.05 | ||||||||
| 从外面买过“鱼生” Purchased raw fish from outside | > 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 否 No | 142 | 25 (17.61) | - | |||||||||
| 是 Yes | 27 | 8 (29.63) | 1.97 (0.74~4.89) | |||||||||
| 向邻居赠送“鱼生” Gave raw fish to neighbors | > 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 否 No | 116 | 21 (18.10) | - | |||||||||
| 是 Yes | 53 | 12 (22.64) | 1.32 (0.58~2.91) | |||||||||
| 接受过赠送“鱼生” Received raw fishas a gift | < 0.05 | |||||||||||
| 否 No | 103 | 15 (14.56) | - | |||||||||
| 是 Yes | 66 | 18 (27.27) | 2.20 (1.02~4.81) | |||||||||
|
| [1] | LI Tianxing, ZHANG Jiaming, XU Chenxi, WANG Zige, GUO Jingjie, LI Shan. Mechanism of a Chinese patent medicine in the treatment of liver fibrosis caused by infection of Clonorchis sinensis based on network pharmacology [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 510-515. |
| [2] | LIU Yu-ying, ZHANG Tian-tian, MA Xiao, LEI Wen, MA Bing-cun, LIU Shou. Awareness and influencing factors of knowledge on echinococcosis prevention and control among adults in Qinghai Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 723-729. |
| [3] | WANG Ke-yi, SHU Huang-fang, FANG Yue-yi, ZENG Qing-sheng, SONG Tie. Data analysis of clonorchiasis surveillance in high endemic areas of Guangdong Province in 2016—2020 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 629-634. |
| [4] | HE Zhan-ying, WANG Xiao-mei, WU Wen-ting, LI Xu, REN Hai-lin, LI Xin-yu. Surveillance and analysis of important human parasitic infections in Beijing during 2016—2020 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 557-561. |
| [5] | CHEN Zhe, YUAN Chang-hong, JIANG Wei-sheng, YANG Yu-hua, LAN Ming-xing, LIU Ke-xing, ZENG Xiao-jun, ZHU Hui-hui. Infection status of clonorchiasis sinensis and the knowledge, attitudes and practices towards the disease among human population in Xinfeng County of Jiangxi Province in 2016 and 2018 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(1): 69-75. |
| [6] | GE Jun, JIANG Wei-sheng, YUAN Chang-hong, ZHU Ting-jun, CHEN Zhe, YANG Yu-hua, LAN Ming-xing, DAI Kun-jiao, LI Dong, ZENG Xiao-jun, CHENG Ying-dan. The achievements of 3-year efforts of clonorchiasis control in the demonstration area of Xinfeng County in Jiangxi Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(5): 554-560. |
| [7] | CHEN Zhe, YE Bin, JIANG Wei-sheng, YANG Yu-hua, LAI Bo-wen, ZENG Xiao-jun, ZHOU Chang-hai. Survey on the knowledge, attitude and practice towards clonorchiasis and analysis of the influencing factors in Xinfeng County of Jiangxi Province in 2016 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(5): 567-573. |
| [8] | ZHU Ting-jun, QIAN Men-bao, CHEN Ying-dan, CHEN Zhe, GE Jun, ZENG Xiao-jun, YUAN Chang-hong, LAN Ming-xing, LI Shi-zhu. Evaluation of the effect of health education on clonorchiasis in primary schools in Xinfeng County of Jiangxi Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(5): 574-579. |
| [9] | ZHANG Yu, LU Ding, PU Chen, CHEN Lin, MAO Yong, XU Liang, LIU Yang. Application of propensity score matching method in the analysis of knowledge, attitude and practice in health education of schistosomiasis control [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(4): 513-517. |
| [10] | Xin WANG, Ben-he WANG, Shu-ya WANG, Qiang YIN, Chang-xi XU. Current endemic status of Clonorchis sinensis infection in population of Jilin Province in 2015 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(3): 291-295. |
| [11] | Men-bao QIAN, Zhi-hua JIANG, Tao GE, Xin WANG, Zhuo-hui DENG, Chang-hai ZHOU, Hui-hui ZHU, Ying-dan CHEN, Xiao-nong ZHOU. Association of raw-freshwater fish-eating practice with the infection of Clonorchis sinensis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(3): 296-301. |
| [12] | Men-bao QIAN, Zhi-hua JIANG, Xiao-qin GAN, Jia-guang ZHAO, Wei LI, Wei-jie ZHENG, Guo-li LV, Ting-jun ZHU, Xiao-nong ZHOU. Effect of health education on the awareness and control of clonorchiasis in primary school students [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(2): 202-206. |
| [13] | Xin-liu YAN, Qu-zhen GONGSANG, Wei-ping WU, Can-jun ZHENG, Chui-zhao XUE, Wei-qi CHEN, Shuai HAN, Bin LI. Survey on knowledge, attitude and behaviors toward hydatid disease among villagers and students in Tibet Autonomous Region [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2018, 36(1): 38-42. |
| [14] | Yang-jin BAIMA, Wei-ping WU, Rui-feng HE, Qu-zhen GONGSANG, Yi-xi KANGZHU, Wang-jie SUOLANG, Bin LI. Prevalence of echinococcosis in Shannan City [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2018, 36(1): 63-68. |
| [15] | Min-xia GU, Yao-jun YU, Jin-chuan ZHANG, Bin WANG, Yi-jiang YU, Cong-han REN. Current status and influencing factors of Clonorchis sinensis infection in rural areas of Ninghai County in Zhejiang Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2017, 35(6): 585-587. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||