
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 582-593.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2024.05.004
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Zhanjin1( ), CHEN Zhiheng1, LI Fuyuan1, CAI Junjie1, XUE Zhangtuo1, ZHOU Ying2, CAO Yuntai3, WANG Zhan4,*(
), CHEN Zhiheng1, LI Fuyuan1, CAI Junjie1, XUE Zhangtuo1, ZHOU Ying2, CAO Yuntai3, WANG Zhan4,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-16
Revised:2024-09-04
Online:2024-10-30
Published:2024-10-24
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Zhanjin, CHEN Zhiheng, LI Fuyuan, CAI Junjie, XUE Zhangtuo, ZHOU Ying, CAO Yuntai, WANG Zhan. Identification of lesion activities in haptic cystic echinococcosis using machine learning model based on radiomics and clinical features[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(5): 582-593.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2024.05.004
Table 1
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis of the activity of the lesions and the basic information and clinical characteristics of the HCE patients
| 临床特征 Clinical features | 无活性 Inactive (n = 272) | 有活性 Active (n = 158) | 单因素Logistic回归 Univariatelogistic regression analysis | 多因素Logistic回归 Multivariate logistic regression analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优势比(95% CI) OR(95% CI) | P | 优势比(95% CI)OR(95% CI) | P | ||||||
| 年龄/岁 Age/Year | 48.0 (40.0-57.0) | 41.5 (34.0-49.0) | 0.991(0.988~0.933) | < 0.05 | 0.992(0.990-0.995) | < 0.05 | |||
| 性别/例 Gender/case | 1.070(0.991~1.156) | > 0.05 | |||||||
| 男 Male | 123(45.2%)a | 83(52.5%)a | |||||||
| 女 Famale | 149(54.8%)a | 75(47.5%)a | |||||||
| 病灶位置/例 Lesion location/case | 0.989(0.946~1.034) | > 0.05 | |||||||
| 肝右叶 Right liver | 165(60.7%)a | 92(58.2%)a | |||||||
| 肝左叶 Left liver | 75(27.6%)a | 34(21.5%)a | |||||||
| 肝左右叶 Both liver | 32(11.8%)a | 32(20.3%)a | |||||||
| 病灶数量/例 No. lesion/case | 1.072(0.991~1.160) | > 0.05 | |||||||
| 单发 Single lesion | 171(62.9%) | 88(55.7%) | |||||||
| 多发 Multiple lesions | 101(37.1%) | 70(44.3%) | |||||||
| 病灶最大直径/cm Lesion max diameter/cm | 5.6(4.4-7.3) | 7.9(5.9-9.9) | 1.064(1.049~1.079) | < 0.05 | 1.049(1.036-1.062) | < 0.05 | |||
| 红细胞/ × 109L Red blood cells/ × 109L | 6.1(5.2-7.2) | 6.2(5.0-7.6) | 1.211(1.141~1.284) | < 0.05 | 1.297(1.219-1.379) | < 0.05 | |||
| 白细胞/ × 109L White blood cells/ × 109L | 4.6(4.2-5.0) | 5.0(4.5-5.4) | 1.018(1.000~1.037) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 血红蛋白/ × 109L Hemoglobin/ × 109L | 153.0(144.0-162.0) | 151.0(133.0-163.0) | 0.997(0.996~0.999) | < 0.05 | 0.995(0.993-0.997) | < 0.05 | |||
| 淋巴细胞/ × 109L Lymphocytes/ × 109L | 1.8(1.5-2.1) | 1.8(1.4-2.3) | 1.047(0.984~1.114) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 中性粒细胞/ × 109L Neutrophils/ × 109L | 3.3(2.7-4.0) | 3.5(2.7-4.7) | 0.911(0.807~1.029) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 单核细胞/ × 109L Monocytes/ × 109L | 0.4(0.3-0.5) | 0.4(0.3-0.4) | 1.007(0.996~1.160) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 血小板/ × 109L Platelets/ × 109L | 226.0(185.5-256.0) | 232.5(196.0-279.0) | 1.001(1.000~1.001) | < 0.05 | 1.000(0.999-1.000) | > 0.05 | |||
| 丙氨酸转氨酶/U·L-1 Alanine aminotransferase/U·L-1 | 34.0(21.0-54.0) | 27.0(18.0-44.0) | 1.000(0.999~1.000) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 总胆红素/U·L-1 Total bilirubin/μmol U·L-1 | 10.2(7.5-14.3) | 10.9(7.5-14.7) | 1.001(1.000~1.002) | < 0.05 | 1.001(1.000-1.002) | > 0.05 | |||
| 直接胆红素/U·L-1 Direct bilirubin/μmol U·L-1 | 3.4(2.6-4.6) | 4.0(2.9-5.5) | 1.001(1.000~1.003) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 间接胆红素/U·L-1 Indirect bilirubin/μmol U·L-1 | 6.6(4.2-10.2) | 6.2(4.2-8.9) | 0.996(0.999~1.000) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 总蛋白/g·L-1 Total protein/g·L-1 | 69.5(66.4-71.6) | 68.6(65.0-72.0) | 0.998(1.000~1.037) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 白蛋白/g·L-1 Albumin/g·L-1 | 40.1(37.7-43.5) | 39.6(37.1-42.1) | 0.985(0.977~0.993) | < 0.05 | 0.988(0.981-0.995) | < 0.05 | |||
| 碱性磷酸酶/U·L-1 Alkaline phosphatase/U·L-1 | 91.5(68.0-122.5) | 97.0(74.0-140.0) | 1.000(1.000~1.000) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 天冬氨酸转氨酶/U·L-1 Aspartate aminotransferase/U·L-1 | 25.0(18.0-38.5) | 24.0(20.0-35.0) | 1.000(0.999~1.001) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 凝血酶原时间/s Prothrombin time/s | 11.1(10.5-11.8) | 10.9(10.4-11.7) | 1.018(0.987~1.050) | > 0.05 | |||||
| 国际标准化比率 International normalized ratio | 0.9(0.9-1.0) | 0.9(0.9-1.0) | 1.414(0.978~1.114) | > 0.05 | |||||
| D-二聚体/µg·L-1 D-Dimer/µg·L-1 | 0.7(0.5-0.9) | 0.6(0.4-0.9) | 1.010(0.985~1.035) | > 0.05 | |||||
Table 2
The final selected 51 radiomics features
| 类型 Type | 影像特征 Radiomics features |
|---|---|
| 灰度共生矩阵(n = 9) Gray level co-occurrence matrix (n = 9) | gradient_glcm_InverseVariance、lbp_3D_m1_glcm_ClusterShade、lbp_3D_m2_glcm_ClusterShade、wavelet_HLH_glcm_Correlation、wavelet_HLL_glcm_Correlation、wavelet_LHL_glcm_Correlation、wavelet_LHL_glcm_Imc2、wavelet_LLH_glcm_Imc2、wavelet_LLL_glcm_MaximumProbability |
| 形状特征(n = 2) Shape features (n = 2) | original_shape_MinorAxisLength、original_shape_Sphericity |
| 灰度运行长度矩阵(n = 6) Gray level run length matrix(n = 6) | exponential_glrlm_GrayLevelNonUniformity、exponential_glrlm_RunVariance、lbp_3D_k_glrlm_RunVariance、lbp_3D_m1_glrlm_ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis、lbp_3D_m2_glrlm_RunVariance、wavelet_HHH_glrlm_ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis |
| 灰度区域大小矩阵(n = 16) Gray level size zone matrix (n = 16) | exponential_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformity、exponential_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized、exponential_glszm_ZoneEntropy、lbp_3D_k_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized、lbp_3D_k_glszm_GrayLevelVariance、lbp_3D_k_glszm_SmallAreaEmphasis、lbp_3D_k_glszm_SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis、lbp_3D_k_glszm_ZoneEntropy、lbp_3D_m1_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized、lbp_3D_m1_glszm_SmallAreaEmphasis、lbp_3D_m2_glszm_GrayLevelVariance、lbp_3D_m2_glszm_SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis、 log_sigma_2_0_mm_3D_glszm_LargeAreaHighGrayLevelEmphasis、original_glszm_SmallAreaHighGrayLevelEmphasis、wavelet_HHL_glszm_SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis、wavelet_LLH_glszm_SmallAreaLowGrayLevelEmphasis |
| 灰度依赖矩阵(n = 6) Gray level dependence matrix (n = 6) | lbp_3D_k_gldm_DependenceEntropy、lbp_3D_k_gldm_DependenceVariance、lbp_3D_m1_gldm_SmallDependenceEmphasis、wavelet_HHL_gldm_LargeDependenceLowGrayLevelEmphasis、wavelet_LHH_gldm_LargeDependenceHighGrayLevelEmphasis、wavelet_LHL_gldm_LargeDependenceHighGrayLevelEmphasis |
| 邻域灰度差矩阵(n = 6)Neighborhood gray-tone difference matrix (n = 2) | lbp_3D_m2_ngtdm_Complexity、log_sigma_2_0_mm_3D_ngtdm_Busyness、wavelet_HHH_ngtdm_Busyness、wavelet_LHH_ngtdm_Busyness、wavelet_LLH_ngtdm_Complexity、wavelet_LLL_ngtdm_Complexity |
| 一阶统计特征(n = 6) First-order statistics features (n = 6) | lbp_3D_k_firstorder_Minimum、lbp_3D_m1_glszm_GrayLevelNonUniformityNormalized、lbp_3D_m2_glszm_GrayLevelVariance、wavelet_HLH_firstorder_Median、wavelet_LLH_firstorder_Skewness、wavelet_LLL_firstorder_10Percentile |
Table 3
Final parameters of the 7 models
| 模型 Model | 参数 Parameter |
|---|---|
| 逻辑回归 LR | LogisticRegression (penalty = ‘l1’, solver = ‘saga’, max_iter = 1, random_state = 0) |
| 支持向量机 SVM | SVC (kernel = ‘linear’, C = 0.1, probability = True, random_state = 0) |
| K-近邻 KNN | KNeighborsClassifier (algorithm = ‘kd_tree’, n_neighbors = 5) |
| 随机森林 RandomForest | RandomForestClassifier (n_estimators = 10, max_depth = 3, min_samples_split = 4, random_state = 0) |
| 极限梯度提升 XGBoost | XGBClassifier (n_estimators = 10, objective = ‘binary:logistic’, max_depth = 3, min_child_weight = 2, use_label_encoder = False, eval_metric = ‘error’) |
| 轻量梯度提升 LightGBM | LGBMClassifier (n_estimators = 10, max_depth = 3, min_child_weight = 0.5) |
| 极端随机树 ExtraTrees | ExtraTreesClassifier (n_estimators = 10, max_depth = 3, min_samples_split = 2, random_state = 0) |
Fig. 3
ROC curves of the machine learning model A: ROC curves of 7 machine learning algorithms during 5-fold cross-validation on the training set; B: ROC curves of these 7 algorithms on an external validation set; C: ROC curves for clinical model, radiomics model and combined model constructed using the XGBoost algorithm; D: ROC curves for clinical model, radiomics model and combined model constructed using the XGBoost algorithm.
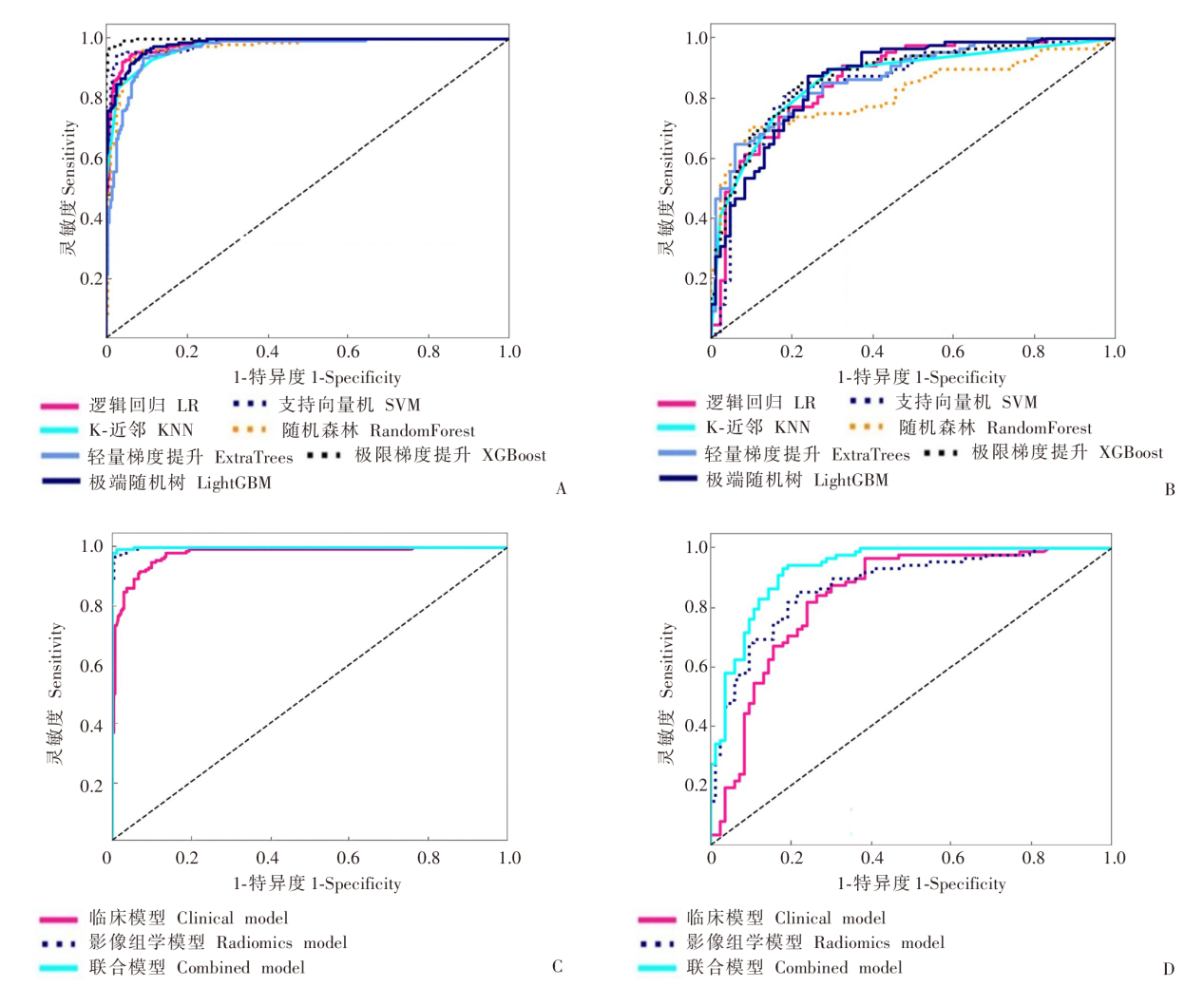
Table 4
Performance of 7 machine learning models in training sets and validation sets
| 模型 Model | 队列 Cohort | 准确率 Accuracy | 曲线下面积AUC | 95%置信区间 95%CI | 灵敏度 Sensitivity | 特异度 Specificity | 阳性预测值 PPV | 阴性预测值 NPV | F1值 F1 | 阈值 Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 逻辑回归 LR | 训练集 Train set | 0.940 | 0.983 | 0.974~0.993 | 0.943 | 0.937 | 0.898 | 0.966 | 0.920 | 0.374 |
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.789 | 0.867 | 0.813~0.922 | 0.898 | 0.675 | 0.745 | 0.862 | 0.814 | 0.021 | |
| 支持向量机SVM | 训练集 Train set | 0.963 | 0.984 | 0.974~0.994 | 0.943 | 0.974 | 0.955 | 0.967 | 0.949 | 0.464 |
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.807 | 0.852 | 0.792~0.912 | 0.795 | 0.819 | 0.824 | 0.791 | 0.809 | 0.225 | |
| K-近邻 KNN | 训练集 Train set | 0.921 | 0.975 | 0.965~0.986 | 0.835 | 0.971 | 0.943 | 0.910 | 0.886 | 0.500 |
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.789 | 0.864 | 0.810~0.917 | 0.739 | 0.843 | 0.833 | 0.753 | 0.783 | 0.250 | |
| 随机森林 RandomForest | 训练集 Train set | 0.926 | 0.971 | 0.956~0.986 | 0.956 | 0.908 | 0.858 | 0.972 | 0.904 | 0.418 |
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.795 | 0.816 | 0.751~0.882 | 0.693 | 0.904 | 0.884 | 0.735 | 0.777 | 0.460 | |
| 极限梯度提升 XGBoost | 训练集 Train set | 0.981 | 0.998 | 0.997~1.000 | 0.968 | 0.989 | 0.981 | 0.982 | 0.975 | 0.483 |
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.813 | 0.874 | 0.822~0.927 | 0.841 | 0.783 | 0.804 | 0.823 | 0.822 | 0.190 | |
| 轻量梯度提升LightGBM | 训练集 Train set | 0.921 | 0.984 | 0.976~0.992 | 0.956 | 0.901 | 0.848 | 0.972 | 0.899 | 0.346 |
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.813 | 0.868 | 0.815~0.922 | 0.863 | 0.759 | 0.792 | 0.840 | 0.812 | 0.282 | |
| 极端随机树 ExtraTrees | 训练集 Train set | 0.916 | 0.964 | 0.948~0.980 | 0.930 | 0.908 | 0.855 | 0.957 | 0.891 | 0.420 |
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.784 | 0.870 | 0.818~0.922 | 0.636 | 0.940 | 0.918 | 0.709 | 0.752 | 0.467 |
Table 5
AUC and accuracy of clinical models, radiomics models and combined models for 7 classifiers
| 模型 Model | 队列 Cohort | 临床模型 Clinical Models | 影像模型 Radiomics Models | 联合模型 Combined Models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 曲线下面积 AUC | 准确率 Accuracy | 曲线下面积 AUC | 准确率 Accuracy | 曲线下面积 AUC | 准确率 Accuracy | ||||
| 逻辑回归 LR | 训练集 Train set | 0.905 | 0.896 | 0.983 | 0.940 | 0.993 | 0.986 | ||
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.812 | 0.813 | 0.867 | 0.789 | 0.886 | 0.836 | |||
| 支持向量机 SVM | 训练集 Train set | 0.923 | 0.904 | 0.963 | 0.984 | 0.987 | 0.991 | ||
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.814 | 0.819 | 0.807 | 0.852 | 0.826 | 0.863 | |||
| K-近邻 KNN | 训练集 Train set | 0.861 | 0.854 | 0.975 | 0.921 | 0.979 | 0.977 | ||
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.764 | 0.783 | 0.864 | 0.789 | 0.889 | 0.816 | |||
| 随机森林 RandomForest | 训练集 Train set | 0.951 | 0.921 | 0.971 | 0.926 | 0.988 | 0.957 | ||
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.798 | 0.762 | 0.816 | 0.795 | 0.835 | 0.826 | |||
| 极度梯度提升 XGBoost | 训练集 Train set | 0.977 | 0.916 | 0.998 | 0.981 | 1.000 | 0.988 | ||
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.839 | 0.789 | 0.874 | 0.813 | 0.931 | 0.871 | |||
| 轻量梯度提升 LightGBM | 训练集 Train set | 0.895 | 0.862 | 0.984 | 0.921 | 0.992 | 0.975 | ||
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.789 | 0.819 | 0.868 | 0.813 | 0.921 | 0.854 | |||
| 极端梯度树 ExtraTrees | 训练集 Train set | 0.912 | 0.919 | 0.964 | 0.916 | 0.978 | 0.964 | ||
| 验证集 Validation set | 0.834 | 0.824 | 0.870 | 0.784 | 0.905 | 0.865 | |||
Table 6
Performance of the clinical model, radiomics model and combined model in training sets and validation sets
| 模型 Model | 队列 Cohort | 准确率 Accuracy | 曲线下面积AUC | 95%置信区间 95% CI | 灵敏度 Sensitivity | 特异度 Specificity | 阳性预测值 PPV | 阴性预测值 NPV | F1值 F1 | 阈值 Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 临床模型 Clinical model | 训练集 Train set | 0.916 | 0.977 | 0.964~0.990 | 0.943 | 0.901 | 0.847 | 0.965 | 0.892 | 0.384 |
| 影像模型 Radiomics model | 训练集 Train set | 0.981 | 0.998 | 0.997~1.000 | 0.968 | 0.989 | 0.981 | 0.982 | 0.975 | 0.483 |
| 联合模型 Combined model | 训练集 Train set | 0.988 | 1.000 | 0.999~1.000 | 0.987 | 0.989 | 0.981 | 0.993 | 0.984 | 0.323 |
| 临床模型 Clinical model | 验证集 Validation set | 0.789 | 0.839 | 0.776~0.901 | 0.955 | 0.614 | 0.724 | 0.927 | 0.824 | 0.164 |
| 影像模型 Radiomics model | 验证集 Validation set | 0.813 | 0.874 | 0.822~0.927 | 0.841 | 0.783 | 0.804 | 0.823 | 0.822 | 0.190 |
| 联合模型 Combined model | 验证集 Validation set | 0.871 | 0.931 | 0.894~0.968 | 0.920 | 0.819 | 0.844 | 0.907 | 0.880 | 0.409 |
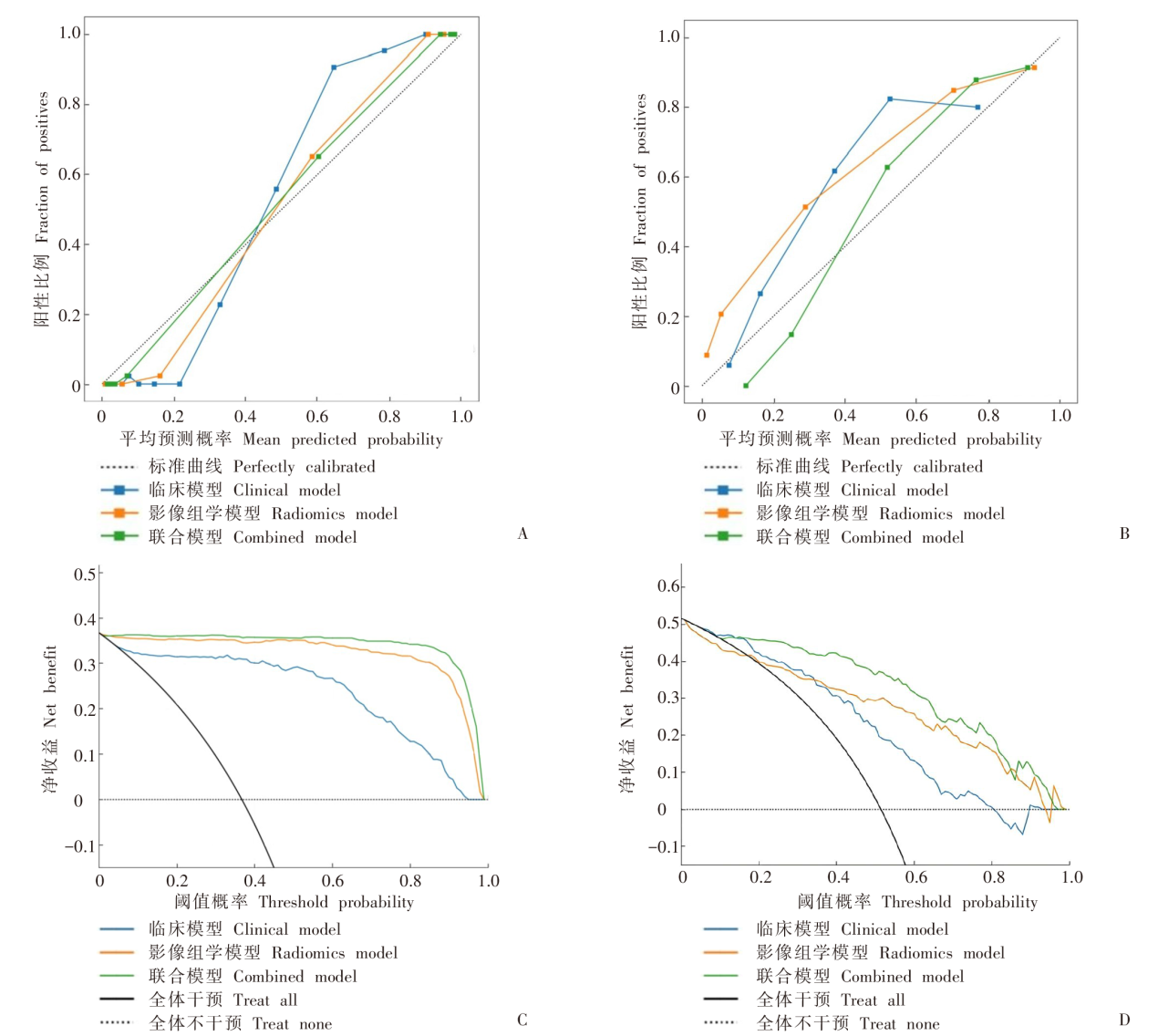
Fig. 4
Calibration curves and DCA curves for the clinical model, radiomics model and combined model A, B: The calibration curves for the clinical model, radiomics model and combined model in the training and external validation sets, respectively; C, D: The DCA curves for the clinical model, radiomics model and combined model in the training and external validation sets, respectively.
|
| [1] | XIE Qiao, LI Jun, DONG Lifeng. Clinical and endoscopic characteristics of 10 cases of amoebic colitis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2024, 42(4): 496-501. |
| [2] | HOU Jiao, WEN Hao, WANG Ming-kun, JIANG Tie-min, FANG Bin-bin, LI Jing, ZHANG Chuan-shan, WANG Hui. Analysis of the influencing factors of lesion activity in hepatic cystic echinococcosis patients [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 309-314. |
| [3] | ZHU Ling-hong, ZHU Lu-min, WANG Bo, YANG Zhi-yong, ZHANG Jing-ni, JI Li, CAI Qi-gang, HAN Xiu-min. Analysis of clinical features of echinococcosis cases [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(1): 61-68. |
| [4] | NING Xiao-ling*, MA Qin. Clinical Features Analysis of Demodectic Blephartis Observed in 40 Patients [J]. , 2016, 34(2): 19-182-封三. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||