
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 460-467.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.04.007
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
LV Wen-xiang( ), CHENG Peng, PENG Hui, WANG Hai-yang, LIU Hong-mei, WANG Hai-fang, GUO Xiu-xia, GONG Mao-qing, LIU Li-juan*(
), CHENG Peng, PENG Hui, WANG Hai-yang, LIU Hong-mei, WANG Hai-fang, GUO Xiu-xia, GONG Mao-qing, LIU Li-juan*( )
)
Received:2021-11-02
Revised:2022-03-13
Online:2022-08-30
Published:2022-09-07
Contact:
LIU Li-juan
E-mail:lwxiang1996@163.com;jj8liu@sina.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LV Wen-xiang, CHENG Peng, PENG Hui, WANG Hai-yang, LIU Hong-mei, WANG Hai-fang, GUO Xiu-xia, GONG Mao-qing, LIU Li-juan. Diversity analysis of intestinal bacterial flora of Culex pipiens pallens at different developmental stages[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 460-467.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.04.007
Table 1
Basic charactoristics of 16S rRNA gene sequencing of intestinal bacteria in different developmental stages of Culex pipiens pallens
| 样品Sample | 原始标签数No. raw tag | 有效标签数 No. effective tag | 平均片段长度/bp Average length/bp | 不同分类水平物种数量 Statistics of the number of classify distribution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 门Phyla | 纲Class | 目Order | 科Family | 属Genus | ||||
| Ⅳ龄幼虫The fourth instar larva | ||||||||
| L1 | 67 114 | 58 096 | 415.40 | 11 | 19 | 55 | 90 | 162 |
| L2 | 72 466 | 64 056 | 415.25 | 12 | 21 | 58 | 93 | 171 |
| L3 | 71 951 | 62 972 | 414.63 | 15 | 25 | 72 | 105 | 187 |
| 蛹Pupa | ||||||||
| P1 | 73 525 | 63 673 | 415.01 | 12 | 23 | 61 | 95 | 164 |
| P2 | 69 258 | 60 714 | 415.03 | 14 | 23 | 58 | 89 | 160 |
| P3 | 69 857 | 60 684 | 414.74 | 16 | 27 | 64 | 102 | 179 |
| 雌成蚊 Female mosquito | ||||||||
| A1 | 67 119 | 59 037 | 412.94 | 11 | 19 | 55 | 81 | 141 |
| A2 | 74 434 | 66 009 | 414.13 | 12 | 23 | 60 | 93 | 162 |
| A3 | 70 069 | 62 294 | 414.62 | 13 | 25 | 60 | 94 | 166 |
| 总计Total | 22 | 45 | 112 | 178 | 329 | |||
Table 2
Alpha diversity index of intestinal bacteria in different developmental stages of Culex pipiens pallens
| 样品 Sample | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 香农指数Shannon index | 辛普森指数Simpson index | 覆盖度Good’s coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅳ龄幼虫The fourth instar larva | 1 035.17 ± 41.71a | 6.05 ± 0.16a | 0.95 ± 0.00a | 0.99 |
| 蛹Pupa | 1 038.76 ± 31.56a | 6.58 ± 0.04a | 0.95 ± 0.00a | 0.99 |
| 雌成蚊Female mosquito | 963.24 ± 71.00a | 5.93 ± 0.05b | 0.93 ± 0.01b | 0.99 |
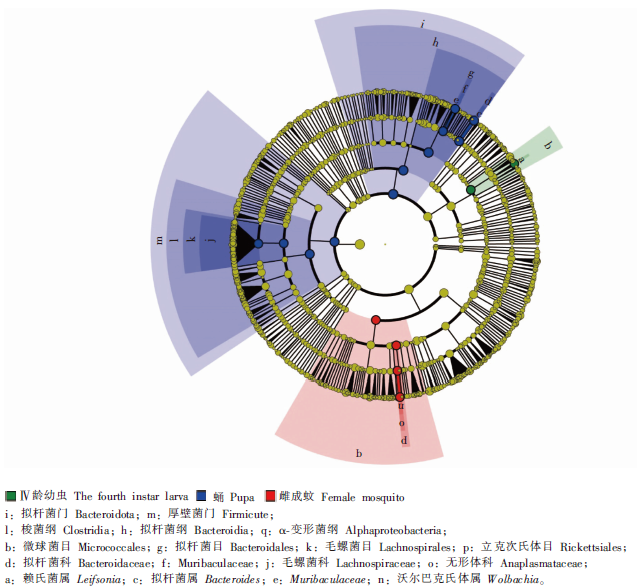
Fig. 4
Position of different flora or species of intestinal bacteria in different developmental stages of Culex pipiens pallens in the phylogenetic tree The circles from the outer to the inner represent phylum, class, order, family, and genus, respectively. Different coloured nodes in the branches represent the microflora that play an important role in the corresponding groups, whereas yellow nodes indicate bacterial groups that are nonsignificant in all groups.
| [1] |
Engel P, Moran NA. The gut microbiota of insects-diversity in structure and function[J]. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2013, 37(5): 699-735.
doi: 10.1111/1574-6976.12025 |
| [2] | Hu ZY, Xia Q. Advances in the histology study, function and application of insect intestinal flora[J]. Biotechnol Bull, 2021, 37(1): 102-112. (in Chinese) |
|
( 胡紫媛, 夏嫱. 昆虫肠道菌群组学研究及功能和应用进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(1): 102-112.)
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2020-0859 |
|
| [3] |
Yun JH, Roh SW, Whon TW, et al. Insect gut bacterial diversity determined by environmental habitat, diet, developmental stage, and phylogeny of host[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2014, 80(17): 5254-5264.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.01226-14 |
| [4] | Wang WW, He C, Cui J, et al. Comparative analysis of the composition of intestinal bacterial communities in Dastarcus helophoroides fed different diets[J]. J Insect Sci, 2014, 14: 111. |
| [5] |
Coon KL, Brown MR, Strand MR. Mosquitoes host communities of bacteria that are essential for development but vary greatly between local habitats[J]. Mol Ecol, 2016, 25(22): 5806-5826.
doi: 10.1111/mec.13877 |
| [6] |
Gimonneau G, Tchioffo MT, Abate L, et al. Composition of Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae microbiota from larval to adult stages[J]. Infect Genet Evol, 2014, 28: 715-724.
doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2014.09.029 pmid: 25283802 |
| [7] | Feng LZ, Liu WD. Studies on the morphological differences of the adults of Chinese Culex pipiens var. pallens and Culex fatigans[J]. Acta Entomol Sin, 1954(2): 103-114, 196. (in Chinese) |
| ( 冯兰洲, 刘维德. 中国尖音库蚊淡色变种与乏倦库蚊成虫在形态上的区别的研究[J]. 昆虫学报, 1954(2): 103-114, 196.) | |
| [8] | Yan DM, Wang WZ, Wang XS, et al. Investigation of mosquitoes and mosquito-borne viruses in some regions of Guizhou Province, China, 2019[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32(4): 422-427. (in Chinese) |
| ( 闫冬明, 王文周, 王雪霜, 等. 贵州省部分地区2019年蚊虫及蚊媒病毒调查研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32(4): 422-427.) | |
| [9] | Nan XW, Xie XX, Yu HM, et al. An investigation of the vector mosquitoes and arboviruses during a Japanese encephalitis epidemic in Baotou of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China, 2018[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2020, 31(6): 652-656. (in Chinese) |
| ( 南晓伟, 解新霞, 于红敏, 等. 内蒙古包头市2018年一起流行性乙型脑炎疫情的媒介蚊虫及感染虫媒病毒调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31(6): 652-656.) | |
| [10] |
Liu LJ, Zhang BG, Cheng P, et al. Overwintering of Culex pipiens pallens (Diptera : Culicidae) in Shandong, China[J]. J Entomol Sci, 2016, 51(4): 314-320.
doi: 10.18474/JES15-38.1 |
| [11] |
Wang Y, Gilbreath TM 3rd, Kukutla P, et al. Dynamic gut microbiome across life history of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae in Kenya[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(9): e24767.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024767 |
| [12] |
Wang XM, Liu T, Wu Y, et al. Bacterial microbiota assemblage in Aedes albopictus mosquitoes and its impacts on larval development[J]. Mol Ecol, 2018, 27(14): 2972-2985.
doi: 10.1111/mec.14732 |
| [13] |
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(15): 2114-2120.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170 |
| [14] |
Reyon D, Tsai SQ, Khayter C, et al. FLASH assembly of TALENs for high-throughput genome editing[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2012, 30(5): 460-465.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.2170 |
| [15] |
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, et al. VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics[J]. PeerJ, 2016, 4: e2584.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.2584 |
| [16] |
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data[J]. Nat Methods, 2010, 7(5): 335-336.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303 pmid: 20383131 |
| [17] |
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, et al. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2007, 73(16): 5261-5267.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-07 |
| [18] |
Yadav KK, Datta S, Naglot A, et al. Diversity of cultivable midgut microbiota at different stages of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus from Tezpur, India[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(12): e0167409.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167409 |
| [19] |
Tandina F, Almeras L, Koné AK, et al. Use of MALDI-TOF MS and culturomics to identify mosquitoes and their midgut microbiota[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2016, 9(1): 495.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1776-y |
| [20] | Liu XG, Yang YJ, Liao QJ, et al. Analysis of the bacterial community structure and diversity in the intestine of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera : Pyralidae)[J]. Acta Entomol Sin, 2016, 59(9): 965-976. (in Chinese) |
| ( 刘小改, 杨亚军, 廖秋菊, 等. 稻纵卷叶螟肠道细菌群落结构与多样性分析[J]. 昆虫学报, 2016, 59(9): 965-976.) | |
| [21] | Ya YK, Xia M, Li J, et al. Diversity analysis of intestinal flora in the third and fourth-instar larvae of Solenopsis invicta[J]. J Environ Entomol, 2021, 43(2): 420-429. (in Chinese) |
| ( 押玉柯, 夏敏, 李军, 等. 红火蚁三龄、四龄幼虫肠道菌菌群多样性分析[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2021, 43(2): 420-429.) | |
| [22] | Liu J, Chen D, Zhuang GF, et al. Isolation and identification of cultivable symbiotic bacteria from the intestinal tract of Musca domestica during development[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2017, 35(2): 120-124. (in Chinese) |
| ( 刘婧, 陈丹, 庄桂芬, 等. 家蝇发育过程中肠道可培养共生细菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2017, 35(2): 120-124.) | |
| [23] |
Chen HJ, Hao DJ, Wei ZQ, et al. Bacterial communities associated with the pine wilt disease insect vector Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera : Cerambycidae) during the larvae and pupae stages[J]. Insects, 2020, 11(6): 376.
doi: 10.3390/insects11060376 |
| [24] |
Ma SL, Yang Y, Jack CJ, et al. Effects of Tropilaelaps mercedesae on midgut bacterial diversity of Apis mellifera[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2019, 79(2): 169-186.
doi: 10.1007/s10493-019-00424-x |
| [25] |
Zhang ZQ, Jiao S, Li XH, et al. Bacterial and fungal gut communities of Agrilus mali at different developmental stages and fed different diets[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 15634.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34127-x |
| [26] | Vera-Ponce de León A, Jahnes BC, Duan J, et al. Cultivable, host-specific bacteroidetes symbionts exhibit diverse polysaccharolytic strategies[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2020, 86(8): e00091-20. |
| [27] |
Sibai M, Altunta ş E, Yldrm B, et al. Microbiome and longevity: high abundance of longevity-linked Muribaculaceae in the gut of the long-living rodent Spalax leucodon[J]. OMICS, 2020, 24(10): 592-601.
doi: 10.1089/omi.2020.0116 |
| [28] |
Dickson LB, Jiolle D, Minard G, et al. Carryover effects of larval exposure to different environmental bacteria drive adult trait variation in a mosquito vector[J]. Sci Adv, 2017, 3(8): e1700585.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700585 |
| [29] |
Minard G, Mavingui P, Moro CV. Diversity and function of bacterial microbiota in the mosquito holobiont[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2013, 6: 146.
doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-146 |
| [30] |
Kittayapong P, Baisley KJ, Sharpe RG, et al. Maternal transmission efficiency of Wolbachia superinfections in Aedes albopictus populations in Thailand[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2002, 66(1): 103-107.
doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2002.66.103 |
| [31] | Wu JR, Zhang QJ, Xiao YJ. Research on Wolbachia technique for control of mosquito-borne diseases[J]. Biol Teach, 2017, 42(7): 13-14. (in Chinese) |
| ( 吴姣榕, 张秋金, 肖义军. 沃尔巴克氏体技术控制蚊媒病研究概述[J]. 生物学教学, 2017, 42(7): 13-14.) | |
| [32] | Yang C, Xi ZY, Hu ZY. Blocking transmission of mosquito-borne diseases through population suppression using Wolbachia[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2020, 31(1): 113-116. (in Chinese) |
| ( 杨翠, 奚志勇, 胡志勇. 应用沃尔巴克氏体通过种群压制阻断蚊媒病传播的研究进展[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31(1): 113-116.) | |
| [33] |
Pan XL, Pike A, Joshi D, et al. The bacterium Wolbachia exploits host innate immunity to establish a symbiotic relationship with the dengue vector mosquito Aedes aegypti[J]. ISME J, 2018, 12(1): 277-288.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2017.174 |
| [34] |
González-Serrano F, Pérez-Cobas AE, Rosas T, et al. The gut microbiota composition of the moth Brithys crini reflects insect metamorphosis[J]. Microb Ecol, 2020, 79(4): 960-970.
doi: 10.1007/s00248-019-01460-1 pmid: 31796995 |
| [1] | CAO Deping, WU Defang, PANG Mingquan, PENG Xiaohong, LI Dayu, FAN Haining. Difference analysis of the gut microbiome in patients with echinococcosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 103-107. |
| [2] | SHANG Jing-ye, ZHANG Guang-jia, YU Wen-jie, HE Wei, LIAO Sha, LI Rui-rui, HUANG Yan, LIU Yang, ZHONG Bo. Advances in researches on the genetic diversity of Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(5): 637-641. |
| [3] | JIN Hang-yi, ZHANG Ling-ling, ZHU Su-juan, XU Wei-min, CHEN Jun-fang, RUAN Wei, YAO Li-nong, CHEN Hua-liang. Analysis of genetic polymorphisms of merozoite surface protein-1 and circumsporozoite protein of Plasmodium vivax [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 323-331. |
| [4] | Jie ZHOU, Chun-xiao LI, Ce-jie LAN, Jian GAO, Qin-mei LIU, Ai-juan SUN, Tong-yan ZHAO. Comparative analysis of antennal olfactory gene expression between Culex pipiens pallens and Culex pipiens molestus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(4): 453-457. |
| [5] | Cang-lin ZHANG, Xue-ying BAO, Jia PENG, Jin-rong ZI, Zhen RAN, Na LU, Ya-ming YANG. Species identification of Pomacea snails in southwest Yunan Province based on COⅠgene polymorphism [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(1): 75-81. |
| [6] | CHEN Tian-mu, ZHOU Hong-ning, LUO Chun-hai, ZENG Xu-can, GUO Xiang-rui, LIN Zu-rui, TU Hong, WANG Xue-zhong, ZHANG Shao-sen, ZHOU Shui-sen. Composition of anopheline larvae in the China-Myanmar border region in Yingjiang County of Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2018, 36(2): 112-118. |
| [7] | Xiao-ming WANG, Kun WU, Xiao-guang CHEN, Gui-yun YAN. Research advances on diversity and function of mosquito-bacteria symbiosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2017, 35(3): 305-312. |
| [8] | Qiu-an HU, Shan LV, Yun-hai GUO, He-xiang LIU, Yi ZHANG. Genetic diversity of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Nan’ao Island of Guangdong Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2017, 35(2): 130-135. |
| [9] | YIN Fang-yuan1,2, LI Fa-cai1,2, ZHAO Jun-long1, HU Min1 *. Research Progress on Genetic Diversity in Animal Parasitic Nematodes [J]. , 2015, 33(5): 12-387-392. |
| [10] | WANG Hui-yong*,LI Bei-li,ZHANG Yan-xing,ZHA Dao-de,TU Long-xia. Composition and Seasonal Fluctuation of Acaroid Mite Communities in Warehousing Environment of Northern Anhui Province [J]. , 2014, 32(2): 21-165-166,封三. |
| [11] | WU Song-quan1 *,WANG Guang-li1,ZHOU Wu1,ZHONG Shi-gen2. Cloning and Expression of Transferrin Protein from Culex pipiens pallens and a Study of its Antimicrobial Activity [J]. , 2014, 32(1): 8-38-41. |
| [12] | SU Jing1,XU Bin2 *,LIU Xiu-feng1,YIN Ming-bo1,HU Wei1, 2. Genetic Variations of the Elastase Gene among Eight Populations of Schistosoma japonicum [J]. , 2013, 31(4): 4-264-269. |
| [13] | LIShi-gen. Drug Resistance Evolution of Dichlorvos-Resistant and Cypermethrin-Resistant Strains of Culex pipiens pallens [J]. , 2009, 27(4): 18-312. |
| [14] | DONGWen-ge;GUOXian-guo*;MENXing-yuan;QIANTi-jun;WUDian. Diversity of Ectoparasites on Niviventer confucianus in the Surrounding Areas of Erhai Lake [J]. , 2009, 27(3): 12-244. |
| [15] | ZHANGYu-jiang;CAOHan-li;DAIXiang;Azaz;JIANGWei;Abulikm;LIBing;Abulimt;LEIGang;Rezwan;LIANGXin-hai;LIUHong-bin;YUXin;FENGChong-hui. Classification and Diversity of Tick Community in Tarim Basin [J]. , 2006, 24(6): 2-409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||