

中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 259-266.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2024.02.018
收稿日期:2023-12-07
修回日期:2024-01-28
出版日期:2024-04-30
发布日期:2024-04-25
通讯作者:
* 樊海宁(1970—),男,博士,主任医师,从事肝胆胰外科临床与基础研究。E-mail:作者简介:达哇卓玛(1993—),女,博士研究生,主治医师,从事地方病临床与基础研究工作。E-mail:dawazhuoma5031@163.com
基金资助:
DAWA Zhuoma1,2( ), LIU Chuanchuan2,3, FAN Haining2,3,*(
), LIU Chuanchuan2,3, FAN Haining2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-12-07
Revised:2024-01-28
Online:2024-04-30
Published:2024-04-25
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:摘要:
棘球蚴病是由细粒棘球绦虫和多房棘球绦虫的中绦期幼虫感染引起的人兽共患病,人类作为易感中间宿主通过偶然食入了虫卵被幼虫感染。细胞程序性死亡在棘球绦虫生长发育过程中普遍存在,与其生长发育、组织修复和疾病产生有关。细胞程序性死亡包括在发育和组织稳态中的经典凋亡以及在外源性和内源性微环境中发生的其他形式如焦亡、自噬、铁死亡等。本文对多种程序性细胞死亡途径在棘球蚴病发生发展中的作用以及药物干预研究作一综述,以期为棘球蚴病预防和治疗中寻找潜在靶标提供理论资料。
中图分类号:
达哇卓玛, 刘川川, 樊海宁. 细胞程序性死亡在棘球蚴病中的研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2024, 42(2): 259-266.
DAWA Zhuoma, LIU Chuanchuan, FAN Haining. Research on the progress of programmed cell death in echinococcosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases, 2024, 42(2): 259-266.
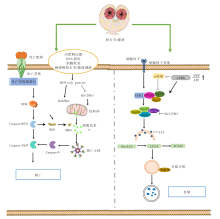
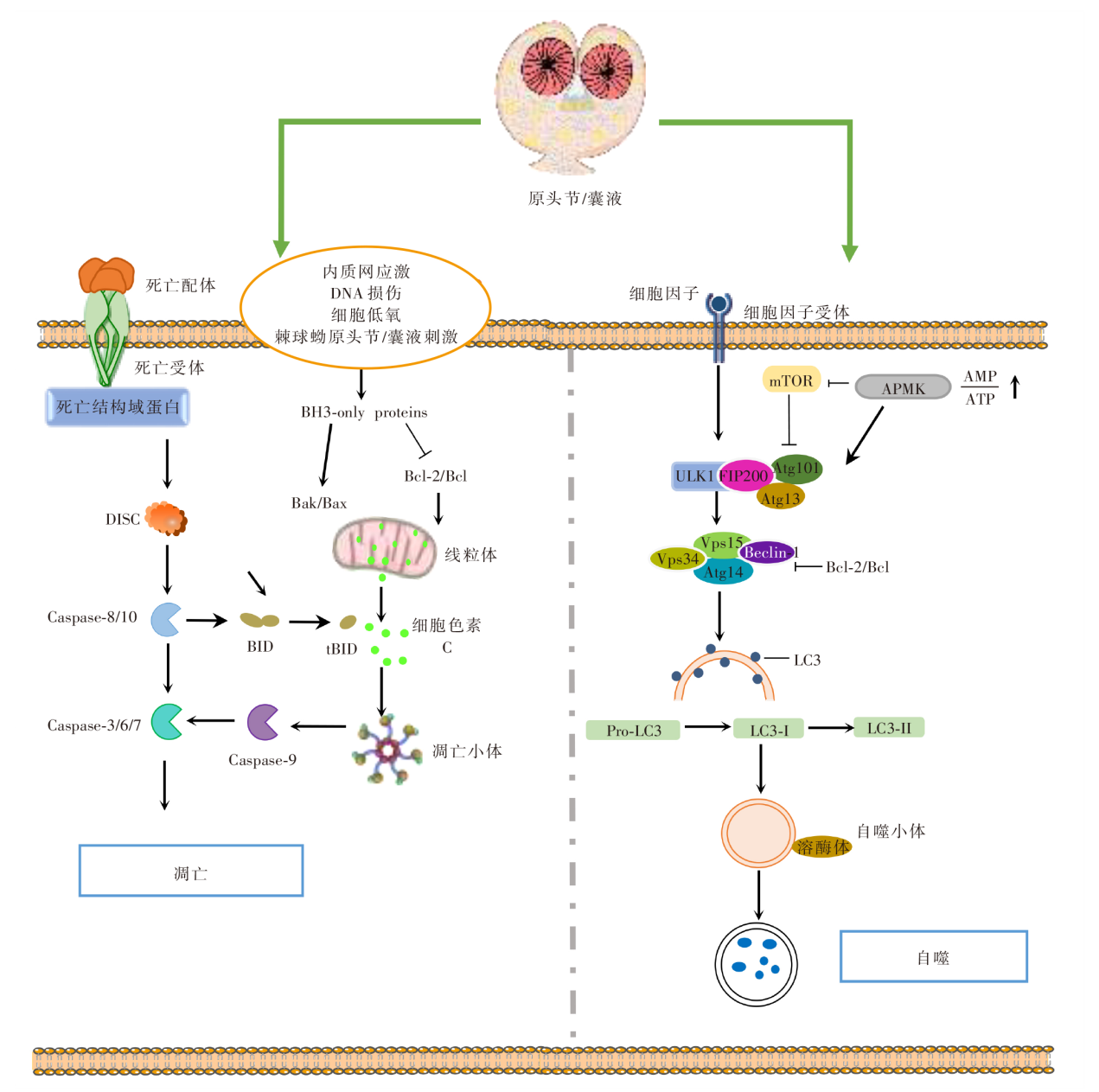
图2
凋亡与自噬作用机制图 DISC:死亡诱导信号复合物;Bcl-2:B淋巴细胞瘤-2;BH3-only proteins:Bcl-2同源结构域蛋白;Caspase:含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶;Bak/Bax:B淋巴细胞瘤关联X蛋白/B淋巴细胞瘤2拮抗因子;BID:BH3结构域凋亡诱导蛋白;tBID;活性截断型BID;mTOR:哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白;AMPK:磷酸化腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶;AMP:腺嘌呤核苷酸;ATP:三磷酸腺苷;ULK1:自噬启动蛋白;FIP200:FAK家族相互作用蛋白200;Atg13:自噬相关蛋白13;Vps4:液泡分选蛋白4;Beclin-1:苄氯素-1;LC3:微管相关蛋白轻链3;Pro-LC3:LC3前体。
| [1] |
Stojkovic M, Junghanss T. Cystic and alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2013, 114: 327-334.
doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53490-3.00026-1 pmid: 23829922 |
| [2] | Wen H, Vuitton L, Tuxun T, et al. Echinococcosis: advances in the 21st century[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2019, 32(2): e00075-18. |
| [3] | Lymbery AJ. Phylogenetic pattern, evolutionary processes and species delimitation in the Genus Echinococcus[J]. Adv Parasitol, 2017, 95: 111-145. |
| [4] | Lin XY, Ouyang SY, Zhi CX, et al. Focus on ferroptosis, pyroptosis, apoptosis and autophagy of vascular endothelial cells to the strategic targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2022, 715: 109098. |
| [5] | Obeng E. Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and its signals: a review[J]. Rev Brasleira De Biol, 2021, 81(4): 1133-1143. |
| [6] | Nössing C, Ryan KM. 50 years on and still very much alive: ‘Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics’[J]. Br J Cancer. 2023, 128(3): 426-431. |
| [7] | Bedoui S, Herold MJ, Strasser A. Emerging connectivity of programmed cell death pathways and its physiological implications[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(11): 678-695. |
| [8] |
Spotin A, Majdi MMA, Sankian M, et al. The study of apoptotic bifunctional effects in relationship between host and parasite in cystic echinococcosis: a new approach to suppression and survival of hydatid cyst[J]. Parasitol Res, 2012, 110(5): 1979-1984.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-011-2726-4 pmid: 22167369 |
| [9] | Mamuti W, Sako Y, Nakao M, et al. Recent advances in characterization of Echinococcus antigen B[J]. Parasitol Int, 2006, 55 Suppl: S57-S62. |
| [10] |
Paredes R, Jiménez V, Cabrera G, et al. Apoptosis as a possible mechanism of infertility in Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cysts[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2007, 100(5): 1200-1209.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.21108 pmid: 17031852 |
| [11] |
Cheng Z, Zhu S, Wang L, et al. Identification and characterisation of Emp53, the homologue of human tumor suppressor p53, from Echinococcus multilocularis: its role in apoptosis and the oxidative stress response[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2015, 45(8): 517-526.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2015.02.010 pmid: 25858091 |
| [12] | Wang N, Zhan JF, Guo C, et al. Molecular characterisation and functions of Fis1 and PDCD6 genes from Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(9): 2669. |
| [13] |
Giri BR, Roy B. Cysticercus fasciolaris infection induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in rat liver: a strategy for host-parasite cross talk[J]. Parasitol Res, 2016, 115(7): 2617-2624.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-016-5008-3 pmid: 26987645 |
| [14] | Zhan JF, Song HY, Wang N, et al. Molecular and functional characterization of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAP, BIRP) in Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Front Microbiol, 2020, 11: 729. |
| [15] |
Mokhtari AM, Sankian M, Eftekharzadeh MI, et al. Apoptosis of human lymphocytes after exposure to hydatid fluid[J]. Iran J Parasitol, 2011, 6(2): 9-16.
pmid: 22347282 |
| [16] | Nono JK, Pletinckx K, Lutz MB, et al. Excretory/secretory-products of Echinococcus multilocularis larvae induce apoptosis and tolerogenic properties in dendritic cells in vitro[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2012, 6(2): e1516. |
| [17] | Li JJ, Tang GY, Qin WJ, et al. Toxic effects of arsenic trioxide on Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces through ROS production, and Ca2+-ER stress-dependent apoptosis[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2018, 50(6): 579-585. |
| [18] | Ahmadpour E, Spotin A, Moghimi A, et al. Tumor suppressor p73 induces apoptosis of murine peritoneal cell after exposure to hydatid cyst antigens; a possibly survival mechanism of cystic echinococcosis in vivo mice model[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(10): e0292434. |
| [19] | Xu K, Yin FJ, Zhang YG, et al. Effect of polylocular Echinococcus multilocularis cyst fluid on apoptosis and autophagy of mouse hepatocytes[J]. Acad J Chin PLA Med Sch, 2022, 43(1): 81-86, 94. (in Chinese) |
| (徐凯, 尹凤娇, 张耀刚, 等. 多房棘球蚴囊液对小鼠肝细胞凋亡与自噬影响的研究[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2022, 43(1): 81-86, 94.) | |
| [20] | Hu HH, Kang JF, Chen R, et al. Drug-induced apoptosis of Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces[J]. Parasitol Res, 2011, 109(2): 453-459. |
| [21] | Naseri M, Akbarzadeh A, Spotin A, et al. Scolicidal and apoptotic activities of albendazole sulfoxide and albendazole sulfoxide-loaded PLGA-PEG as a novel nanopolymeric particle against Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces[J]. Parasitol Res, 2016, 115(12): 4595-4603. |
| [22] |
Shahnazi M, Azadmehr A, Jondabeh MD, et al. Evaluating the effect of Myrtus communis on programmed cell death in hydatid cyst protoscolices[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Med, 2017, 10(11): 1072-1076.
doi: S1995-7645(17)31254-3 pmid: 29203104 |
| [23] | Moghadaszadeh M, Khayyati M, Spotin A, et al. Scolicidal and apoptotic activities of 5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone as a potent agent against Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2021, 14(7): 623. |
| [24] | Ma RJ, Qin WJ, Xie YM, et al. Dihydroartemisinin induces ER stress-dependent apoptosis of Echinococcus protoscoleces in vitro[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2020, 52(10): 1140-1147. |
| [25] | Dikic I, Elazar Z. Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018, 19(6): 349-364. |
| [26] | Brier LW, Ge L, Stjepanovic G, et al. Regulation of LC3 lipidation by the autophagy-specific class Ⅲ phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase complex[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2019, 30(9): 1098-1107. |
| [27] |
Yang ZF, Klionsky DJ. Mammalian autophagy: core molecular machinery and signaling regulation[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2010, 22(2): 124-131.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.11.014 pmid: 20034776 |
| [28] |
Wang NB, Zhang QX, Luo LY, et al. β-asarone inhibited cell growth and promoted autophagy via P53/Bcl-2/Bclin-1 and P53/AMPK/mTOR pathways in Human Glioma U251 cells[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(3): 2434-2443.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.26118 pmid: 28776671 |
| [29] | Fan SJ, Yue LY, Wan W, et al. Inhibition of autophagy by a small molecule through covalent modification of the LC3 protein[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2021, 60(50): 26105-26114. |
| [30] | Parola M, Pinzani M. Liver fibrosis: pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2019(65): 37-55. |
| [31] |
Hernández-Gea V, Ghiassi-Nejad Z, Rozenfeld R, et al. Autophagy releases lipid that promotes fibrogenesis by activated hepatic stellate cells in mice and in human tissues[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 142(4): 938-946.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.044 pmid: 22240484 |
| [32] | Shmarakov IO, Jiang HG, Liu J, et al. Hepatic stellate cell activation: a source for bioactive lipids[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids, 2019, 1864(5): 629-642. |
| [33] | Wang BY, Yang H, Fan YY, et al. 3-methyladenine ameliorates liver fibrosis through autophagy regulated by the NF-κB signaling pathways on hepatic stellate cell[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(64): 107603-107611. |
| [34] |
Gao JH, Wei B, de Assuncao TM, et al. Hepatic stellate cell autophagy inhibits extracellular vesicle release to attenuate liver fibrosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73(5): 1144-1154.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.044 pmid: 32389810 |
| [35] | Wei XL, Xu Q, Rexiti FL, et al. Dynamic changes of DC and T cell subsets in mice during Echinococcus multilocularis infection[J]. Cent Eur J Immunol, 2014, 39(1): 19-24. |
| [36] | Ma XJ, Shang M, Yin QC, et al. Maturation of dendritic cells in peripheral blood of patients with alveolar echinococcosis[J]. China Trop Med, 2019, 19(2): 111-115. (in Chinese) |
|
(马晓静, 尚梅, 尹启超, 等. 泡型肝包虫患者外周血树突状细胞成熟度[J]. 中国热带医学, 2019, 19(2): 111-115.)
doi: 10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2019.02.03 |
|
| [37] | Gao XY, Zhang GH, Huang L. Modulation of human melanoma cell proliferation and apoptosis by hydatid cyst fluid of Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2018, 11: 1447-1456. |
| [38] | Deng J, Huang DL, Zhang YG. Effect of Echinococcus multilocularis infections on mitochondrial functions of macrophages[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2021, 33(5): 470-475. (in Chinese) |
| (邓珺, 黄登亮, 张耀刚, 等. 多房棘球蚴感染对巨噬细胞线粒体功能的影响[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2021, 33(5): 470-475.) | |
| [39] | Jin GQ, Zhang ZH, Feng HJ, et al. Beneficial effect of Pink1/Parkin pathway-mediated mitophagy on preventing cellular damage brought on by Echinococcus multilocularis in AML12 cells[J]. Asian J Surg, 2024, 47(1): 571-573. |
| [40] |
Lodder J, Denaës T, Chobert MN, et al. Macrophage autophagy protects against liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Autophagy, 2015, 11(8): 1280-1292.
doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1058473 pmid: 26061908 |
| [41] | Loos JA, Caparros PA, Nicolao MC, et al. Identification and pharmacological induction of autophagy in the larval stages of Echinococcus granulosus: an active catabolic process in calcareous corpuscles[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2014, 44(7): 415-427. |
| [42] | Nicolao MC, Loos JA, Rodrigues RC, et al. Bortezomib initiates endoplasmic reticulum stress, elicits autophagy and death in Echinococcus granulosus larval stage[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(8): e0181528. |
| [43] | Loos JA, Nicolao MC, Cumino AC. Metformin promotes autophagy in Echinococcus granulosus larval stage[J]. Mol Biochem Parasitol, 2018, 224: 61-70. |
| [44] | Loos JA, Dávila VA, Rodrígues CR, et al. Metformin exhibits preventive and therapeutic efficacy against experimental cystic echinococcosis[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2017, 11(2): e0005370. |
| [45] | Loos JA, Negro P, Cumino AC. In vitro anti-echinococcal activity of octreotide: additive effect of metformin linked to autophagy[J]. Acta Trop, 2020, 203: 105312. |
| [46] |
Shi JJ, Gao WQ, Shao F. Pyroptosis: gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2017, 42(4): 245-254.
doi: S0968-0004(16)30182-7 pmid: 27932073 |
| [47] | Shi JJ, Zhao Y, Wang YP, et al. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7521): 187-192. |
| [48] | Casaravilla C, Pittini Á, Rückerl D, et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by particles from the Echinococcus granulosus laminated layer[J]. Infect Immun, 2020, 88(9): e00190-e00120. |
| [49] | Chen CS, Zhang YG, Wang HJ, et al. Effect and mechanism of reactive oxygen species-mediated NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome activation in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2023, 29(14): 2153-2171. |
| [50] | Wang T. Expression and significance of GSDMD/Caspase-1, Caspase-4 and Caspase-5 in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[D]. Xining: Qinghai University, 2019: 8-13. (in Chinese) |
| (王涛. GSDMD/Caspase-1、Caspase-4、Caspase-5等焦亡相关因子在肝泡型包虫病的表达及其意义[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2019: 8-13). | |
| [51] | Nie R, Li WD, Ye GB, et al. Research progress on the role of pyroptosis inhuman parasitic diseases[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2022, 40(6): 780-785, 791. (in Chinese) |
|
(乜茹, 李文登, 冶赓博, 等. 细胞焦亡在人体寄生虫病中的研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(6): 780-785, 791.)
doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.06.014 |
|
| [52] | Liu J, Kang R, Tang DL. Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis[J]. FEBS J, 2022, 289(22): 7038-7050. |
| [53] |
Tang DL, Chen X, Kang R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications[J]. Cell Res, 2021, 31(2): 107-125.
doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1 pmid: 33268902 |
| [54] | Aslam H, Bi S, Irshadullah M. Analysis of antioxidant enzymes and oxidative stress markers in the liver of naturally infected Indian water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) with cystic echinococcosis[J]. J Parasit Dis, 2023, 47(2): 340-348. |
| [55] | Heidarpour M, Mohri M, Borji H, et al. Oxidant/antioxidant status in cattle with liver cystic echinococcosis[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2013, 195(1/2): 131-135. |
| [1] | 王春生, 乌尔格力, 西利扎提·库来西, 李玉倩, 先依旦·阿布拉, 苏比·泰来提, 蒲雪莉, 王佳玲, 李孟, 房志远, 叶建荣. 细粒棘球蚴囊液致敏过程中IL-1β受体阻滞剂对肺损伤的治疗作用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2024, 42(2): 199-203. |
| [2] | 李涛, 李子华, 张翠影, 赵巍. 人源细粒棘球蚴囊壁与囊液中宿主蛋白的鉴定与分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2023, 41(6): 677-682. |
| [3] | 吴晓莹, 胡媛, 曹建平. 细粒棘球绦虫多肽-壳聚糖季铵盐纳米颗粒的制备[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2023, 41(3): 300-305. |
| [4] | 李奔福, 王正青, 徐倩, 字金荣, 严信留, 彭佳, 李建雄, 蔡璇, 吴方伟, 杨亚明. 云南省细粒棘球绦虫线粒体co1和nd1基因序列分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2023, 41(3): 306-311. |
| [5] | 焦红杰, 齐文静, 郭刚, 包建玲, 吴川川, 宋传龙, 李军, 张文宝, 严媚. 细粒棘球蚴抗原B对小鼠巨噬细胞RAW264.7的极化作用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2023, 41(1): 23-28. |
| [6] | 乜茹, 李文登, 冶赓博, 尹凤娇, 庞明泉, 王志鑫, 樊海宁. 细胞焦亡在人体寄生虫病中的研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(6): 780-785. |
| [7] | 李佳铭, 王艺璇, 杨宁爱, 马慧慧, 兰敏, 刘春兰, 赵志军. 刚地弓形虫ROP16蛋白对MH-S细胞极化和凋亡的影响及其相关机制[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(5): 579-586. |
| [8] | 仲顺虎, 孙玥, 郭小腊, 郑亚东, 陈轶霞. 多房棘球蚴感染小鼠脾淋巴细胞中差异表达miRNA的鉴定及其生物信息学分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(3): 288-294. |
| [9] | 卓怡呈, 杨海成, 刘程豪, 张宝财, 多小勇, 张示杰. 骨桥蛋白表达水平对多房棘球蚴原头节生长发育的影响[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(3): 299-304. |
| [10] | 孙叶挺, 江楠, 姜岩岩, 李腾, 蒋小凤, 曹建平, 沈玉娟. 细粒棘球蚴原头节源外泌体体外刺激髓源抑制性细胞极化的研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(2): 175-180. |
| [11] | 邵晗, 李思源, 李军. 二甲双胍对多房棘球蚴囊泡和原头节自噬及凋亡的影响[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(1): 43-49. |
| [12] | 鲁飞, 卓洵辉, 陆绍红. 顶复门原虫感染与宿主细胞自噬相互作用的研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(6): 826-831. |
| [13] | 史琦琪, 刘丛珊, 霍乐乐, 魏玉芬, 姜斌, 殷梦, 薛剑, 陶奕, 张皓冰. 氨基醇类化合物HT24对多房棘球蚴原头节微管蛋白表达水平的影响[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(4): 437-443. |
| [14] | 周文正, 孙俊刚, 赵喜滨, 曹力. 三维适形调强放疗对大鼠继发性股骨细粒棘球蚴感染的疗效研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(4): 443-448. |
| [15] | 侯永恒, 吕芳丽. 弓形虫感染与宿主细胞自噬的相互作用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(4): 537-542. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||