
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 622-628.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.05.009
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Xian-shi( ), JI Wen-xiang, XIONG Chun-rong, ZHOU Yong-hua, XU Yong-liang, TONG De-sheng(
), JI Wen-xiang, XIONG Chun-rong, ZHOU Yong-hua, XU Yong-liang, TONG De-sheng( )
)
Received:2022-03-15
Revised:2022-06-22
Online:2022-10-30
Published:2022-10-27
Contact:
TONG De-sheng
E-mail:txsvik@163.com;tds419@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TANG Xian-shi, JI Wen-xiang, XIONG Chun-rong, ZHOU Yong-hua, XU Yong-liang, TONG De-sheng. Study on anxiety-like behavior of mice with late-stage infection of Schistosoma japonicum[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 622-628.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.05.009
Table 1
The results of open field tests in mice with late-stage infection of S. japonicum
| 指标 Index | 感染组 Infection group | 未感染组 Uninfection group | 转基因组 Transgenic group |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总路程/mm Total distance/mm | 33 476.8 ± 71 190.44 | 12 719.55 ± 6 451.56 | 21 710.23 ± 11 544.04c |
| 中央区路程/mm Travelling distance in the central zone/mm | 4 637.04 ± 10 362.40 | 1 569.83 ± 1 337.72 | 3 016.18 ± 2 335.31c |
| 中央路程百分比/% Percentage of travelling distance in the centrol zone/% | 12.34 ± 4.37 | 11.00 ± 5.54 | 12.81 ± 5.25 |
| 活动次数/次 Number of locomotor activity/times | 123.68 ± 50.23b | 119.14 ± 48.37 | 147.90 ± 41.17c |
| 活动时间/s Duration of locomotor activity/s | 346.77 ± 181.03a | 273.53 ± 113.64 | 378.42 ± 128.24c |
| 中央时间百分比/% Time percentage spent in centrol zone/% | 54.83 ± 49.67 | 52.43 ± 68.37 | 60.71 ± 50.88 |
| 平均速度/mm·s-1 Mean speed/mm·s-1 | 37.15 ± 79.01 | 14.11 ± 7.16 | 24.09 ± 12.81c |
| 中央平均速度/mm·s-1 Mean speed in the centrol zone/mm·s-1 | 79.29 ± 88.68 | 61.11 ± 57.44 | 71.14 ± 43.51 |
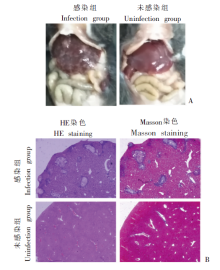
Fig. 1
Observation of the morphology and histology of the liver in mice with late-stage infection of S. japonicum A: Liver appearance, the liver of the mice in the infection group was dark and hard, with white granules unevenly distributed on the surface, accompanied by splenomegaly; the liver of uninfected mice was light, uniform, soft and smooth. B: Liver tissue section, the egg granuloma structure was formed in the liver tissue of mice in the infection group, the adjacent liver cells were denatured and necrotic, and the liver sinuses were significantly expanded and distorted; Normal liver structure in the uninfected group (HE staining and Masson staining).
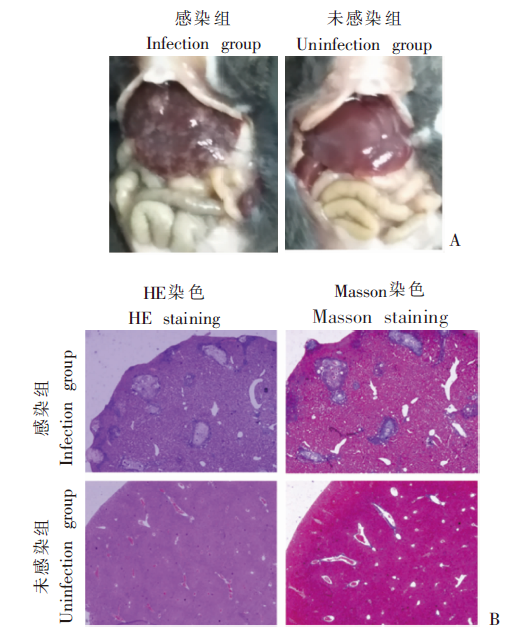
Table 2
Test results of elevated-plus maze test in mice with late-stage infection of S. japonicum
| 指标 Index | 感染组 Infection group | 未感染组 Uninfection group | 转基因组 Transgenic group |
|---|---|---|---|
| 开臂内运动路程/mm Locomotor distance in the open arms/mm | 206.31 ± 282.52ab | 47.43 ± 105.82 | 28.49 ± 73.41 |
| 闭臂内运动路程/mm Locomotor distance in the closed arms/mm | 2 304.63 ± 1704.01b | 3 959.01 ± 17117.29 | 1 512.28 ± 914.86 |
| 中央运动路程/mm Locomotor distance in the central zone/mm | 120.48 ± 112.95b | 80.51 ± 140.23 | 14.26 ± 24.78c |
| 开臂内运动路程百分比/% Percentage of locomotor distance in the open arms/% | 7.51 ± 9.90ab | 3.39 ± 10.02 | 1.36 ± 3.53 |
| 开臂进入次数/次 Number of entry in the open arms/times | 1.32 ± 1.51ab | 0.63 ± 1.01 | 0.12 ± 0.33c |
| 闭臂进入次数/次 Number of entry in the close arms/times | 3.44 ± 3.10ab | 1.60 ± 1.75 | 0.83 ± 1.04 |
| 中央进入次数/次 Number of entry in the central zone/times | 4.53 ± 4.21ab | 2.19 ± 2.57 | 0.95 ± 1.23c |
| 开臂进入次数百分比/% Percentage of number of entry in the open arms/% | 20.31 ± 20.71b | 16.05 ± 23.59 | 4.30 ± 12.45c |
| 开臂内停留时间/s Retention time in the open arms/s | 25.80 ± 35.99b | 15.60 ± 48.22 | 3.44 ± 7.86 |
| 闭臂内停留时间/s Retention time in the closed arms/s | 232.85 ± 88.82b | 262.27 ± 74.93 | 295.38 ± 9.88c |
| 中央停留时间/s Retention time in the central dwell time/s | 42.33 ± 71.66b | 23.12 ± 52.75 | 2.17 ± 3.45 |
| 开臂内停留时间百分比/% Percentage of retention time in the open arms/% | 8.57 ± 11.95b | 5.18 ± 16.02 | 1.14 ± 2.61 |
| [1] |
LoVerde PT. Schistosomiasis[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019, 1154: 45-70.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-18616-6_3 pmid: 31297759 |
| [2] |
Collins C,, Xu J,, Tang SL. Schistosomiasis control and the health system in P. R. China[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2012, 1: 8.
doi: 10.1186/2049-9957-1-8 |
| [3] | Zhang LJ,, Xu ZM,, Yang F, et al. Endemic status of schistosomiasis in People’s Republic of China in 2020[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2021, 33(3): 225-233. (in Chinese) |
| ( 张利娟,, 徐志敏,, 杨帆, 等. 2020年全国血吸虫病疫情通报[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2021, 33(3): 225-233.) | |
| [4] | Deng Y. The study on disease burden of advanced schistosomiasis and the quality of life of patients[D]. Beijing: Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2008: 6-16. (in Chinese) |
| ( 邓瑶. 晚期血吸虫病疾病负担与患者生命质量研究[D]. 北京: 中国疾病预防控制中心, 2008: 6-16.) | |
| [5] | Hua HY,, You H,, Zhang Y, et al. Evaluation of quality of life in advanced schistosomiasis patients in Jiangsu Province[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2010, 22(6): 562-566. (in Chinese) |
| ( 华海涌,, 尤华,, 张燕, 等. 江苏省晚期血吸虫病患者生命质量评估[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2010, 22(6): 562-566.) | |
| [6] | Jiang CG,, Chen SJ,, Li SM, et al. Study on economic and social burden caused by advanced schistosomiasis in Jurong City[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2010, 22(6): 616-618. (in Chinese) |
| ( 江成功,, 陈世军,, 李水明, 等. 句容市晚期血吸虫病经济及社会负担研究[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2010, 22(6): 616-618.) | |
| [7] | Li YT. Study on disease burden of advanced schistosomiasis Japonica in China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2019: 6-14. (in Chinese) |
| ( 李伊婷. 中国晚期血吸虫病疾病负担研究[D]. 北京: 中国疾病预防控制中心, 2019: 6-14.) | |
| [8] | Nie YX. Depression prevalence and quality of life of patients with advanced schistosomiasis[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2011, 23(5): 579-581. (in Chinese) |
| ( 聂永新. 晚期血吸虫病患者抑郁症发生率及生活质量调查[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2011, 23(5): 579-581.) | |
| [9] | Zhou RH,, Pan J,, Liu KF, et al. Quality of life and influencing factors in patients with advanced schistosomiasis complicated with depression[J]. J Nurs, 2014, 21(16): 65-68. (in Chinese) |
| ( 周瑞红,, 潘洁,, 刘科丰, 等. 晚期血吸虫病合并抑郁患者生活质量及影响因素研究[J]. 护理学报, 2014, 21(16): 65-68.) | |
| [10] | Pan J,, Zhou RH,, Liu KF, et al. Investigation on anxiety, depression and life quality of hospitalized patients with advanced schistosomiasis and related influencing factors[J]. J Trop Med, 2014, 14(8): 1082-1085, 1092. (in Chinese) |
| ( 潘洁,, 周瑞红,, 刘科丰, 等. 晚期血吸虫病住院患者焦虑抑郁与生活质量状况及影响因素研究[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2014, 14(8): 1082-1085, 1092.) | |
| [11] | Liu JY,, Yang DD. Effects of artesunate on the expression of type ⅰ, ⅲ, ⅳ collagen and TGF-β1 in liver tissue of mice with hepatic fibrosis[J]. Jilin J Tradit Chin Med, 2009, 29(5): 447-448. (in Chinese) |
| ( 刘金元,, 杨冬娣. 青蒿琥酯对肝纤维化小鼠肝组织中Ⅰ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ型胶原及TGF-β1表达的影响[J]. 吉林中医药, 2009, 29(5): 447-448.) | |
| [12] | Zhou YH,, Xu C,, Yang YY, et al. Effect of artesunate on expression of heat shock protein 47 in mice with liver fibrosis induced by Schistosoma japonicum[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2019, 37(2): 115-120, 126. (in Chinese) |
| ( 周永华,, 徐辰,, 杨莹莹, 等. 青蒿琥酯对日本血吸虫诱导的早期肝纤维化小鼠热休克蛋白47表达影响的研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2019, 37(2): 115-120, 126.) | |
| [13] | Xu X,, Fu JB,, Yao Z, et al. Therapeutical effect of dihydroartemisinin on bile duct ligation-induced liver fibrosis in rats and its mechanism[J]. J Nanjing Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2017, 33(4): 376-381. (in Chinese) |
| ( 许霞,, 付金柏,, 姚真, 等. 双氢青蒿素对胆管结扎致大鼠肝纤维化的治疗作用研究[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2017, 33(4): 376-381.) | |
| [14] | Kraeuter AK,, Guest PC,, Sarnyai Z. The open field test for measuring locomotor activity and anxiety-like behavior[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2019, 1916: 99-103. |
| [15] | Liu Y,, Yao RZ,, Shi HZ, et al. Detection of spontaneous movement, exploration behavior and anxiety in ICR mice and establishment of reference range of corresponding indicators[J]. J Heilongjiang Bayi Agric Univ, 2020, 32(1): 29-35. (in Chinese) |
| ( 刘洋,, 姚睿智,, 史宏昭, 等. ICR小鼠自发运动、探索行为和焦虑情绪的检测及其参考值的确立[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2020, 32(1): 29-35.) | |
| [16] | Seibenhener ML,, Wooten MC. Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice[J]. J Vis Exp, 2015(96): e52434. |
| [17] | Xin ZM,, Chen CJ. Study on anxiety-like behaviors of Zucker diabetic fatty model rats[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2019, 46(22): 4166-4169. (in Chinese) |
| ( 辛志明,, 陈超杰. Zucker糖尿病肥胖模型大鼠的焦虑样行为学研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2019, 46(22): 4166-4169.) | |
| [18] | Kraeuter AK,, Guest PC,, Sarnyai Z. The elevated plus maze test for measuring anxiety-like behavior in rodents[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2019, 1916: 69-74. |
| [19] | Tang XS,, Zhao S,, Xiong CR, et al. Therapeutic effect of arachidonic acid (ARA) on schistosomiasis japonicum in mice[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2021, 37(8): 722-727. (in Chinese) |
| ( 汤宪时,, 赵松,, 熊春蓉, 等. 花生四烯酸对小鼠日本血吸虫病治疗效果观察[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2021, 37(8): 722-727.) | |
| [20] |
Kuring JK,, Mathias JL,, Ward L. Prevalence of depression, anxiety and PTSD in people with dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Neuropsychol Rev, 2018, 28(4): 393-416.
doi: 10.1007/s11065-018-9396-2 pmid: 30536144 |
| [21] |
Leontjevas R,, van Hooren S,, Mulders A. The montgomery-asberg depression rating scale and the cornell scale for depression in dementia: a validation study with patients exhibiting early-onset dementia[J]. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry, 2009, 17(1): 56-64.
doi: 10.1097/JGP.0b013e31818b4111 pmid: 19092312 |
| [22] |
Bennett S,, Thomas AJ. Depression and dementia: cause, consequence or coincidence?[J]. Maturitas, 2014, 79(2): 184-190.
doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.05.009 pmid: 24931304 |
| [23] | Qu XS,, Shi H,, Cao XL, et al. Effects of adiponectin on the anxiety and memory impairment in triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease model mice[J]. Chin J Appl Physiol, 2017, 33(5): 405-409. (in Chinese) |
| ( 曲雪松,, 石辉,, 曹秀丽, 等. 脂联素改善阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠焦虑情绪及工作记忆[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志, 2017, 33(5): 405-409.) | |
| [24] | Bai Y. The neuroprotective effects and mechanism of adiponectin alleviates the anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease model mice[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Medical University, 2019: 15-22. (in Chinese) |
| ( 白羽. 脂联素改善三转基因阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠焦虑和抑郁样行为的神经保护作用及机制研究[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2019: 15-22.) |
| [1] | LAN Weiming, XU Hui, XU Yin, QIU Tingting, XIE Shuying, DENG Fenglin, HU Shaoliang, LIU Huan, GUO Jiagang, ZENG Xiaojun. Study on early warning of high risk environment of Schistosoma japonicum infection by quantitative real-time PCR [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 502-505. |
| [2] | LI Jie, WEN Yusong, LI Zhaojun. Effect of tourism development on schistosomiasis control in China [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 355-360. |
| [3] | CHEN Lin, ZHU Jifeng, QIU Jingfan, XU Zhipeng, ZHANG Donghui, CHEN Lu, HE Jian, LI Wei, YANG Kun, JI Minjun. Design and development of a virtual simulation project for schistosomiasis control based on the One Health concept [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 81-84. |
| [4] | CHEN Guo, ZHU Dan-dan, DUAN Yi-nong. Research progress of immune regulation protein B7 family on immune regulation during Schistosoma japonicum infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 774-779. |
| [5] | YAN Xiao-lan, WEN Li-yong, XIONG Yan-hong, ZHENG Bin, ZHANG Jian-feng, WANG Tian-ping, YU Li-ling, XU Guo-zhang, LIN Dan-dan, ZHOU Xiao-nong. Interpretation of Criteria for Detection of Antibody against Schistosoma japonicum—Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 798-800. |
| [6] | CHEN Bing, ZHANG Guo-li, ZHANG Gao-hong. Research progress on clinical trials of schistosomiasis vaccine candidates [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(4): 511-515. |
| [7] | GAO Yuan, ZHANG Xiao-cheng, HU Yuan, CAO Jian-ping. Study on the inhibitory effect of natural killer cells on liver fibrosis of schistosomiasis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 168-174. |
| [8] | GAO Yuan, HU Yuan, CAO Jian-ping. Research progress on the role of immune cells in liver fibrosis due to schistosomiasis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(1): 88-93. |
| [9] | LI Bo, ZHANG Cong, SHAN Xiao-wei, YI Jia, TU Zhen, HE Hui, TANG Li, ZHU Hong, LIU Jian-bing. Evaluation of the pathogen detection capacity in standardized schistosomiasis laboratories in Hubei Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(5): 572-576. |
| [10] | HU Fei, GAO Zhu-lu, YUAN Min, LI Zhao-jun, LI Yi-feng, LIU Yue-min, LI Jian-ying, XIE Shu-ying, WEN Yu-song, LIN Dan-dan. Changing trends of schistosome infection and liver fibrosis among residents in the Poyang Lake region [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(5): 629-636. |
| [11] | HUANG Ai-long, ZHANG Bei, SHEN Han-yu, CHEN Guo, LI Jing, ZHU Dan-dan, DUAN Yi-nong. Expression and function of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 in the liver of mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(5): 621-626. |
| [12] | WU Jia-li, LI Bo, LIU Si, TU Zu-wu, TANG Li, TU Zhen, ZHOU Xiao-rong, SUN Ling-cong, XIAO Ying, ZHU Hong. Assessment of transmission risk of human schistosomiasis japonica based on human population antibody level in Hubei Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(5): 578-584. |
| [13] | LIU Rong, ZHANG Jian-feng, YAN Xiao-lan, WEN Li-yong. Comparative study of SF-36 and EQ-5D-5L in evaluating quality of life for patients with advanced schistosomiasis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(5): 639-645. |
| [14] | HONG Zhong, WU Ling-ling, WANG Li-ping, XU Jing. Progress and challenges on global schistosomiasis control [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 514-519. |
| [15] | ZHU Hui-hui, ZHU Ting-jun, CHEN Ying-dan, DENG Zhuo-hui, XU Jing, ZHOU Chang-hai, QIAN Men-bao, QIN Zhi-qiang, HUANG Ji-lei, LV Chao, ZHANG Mi-zhen, LI Shi-zhu. The impact of COVID-19 epidemic on the control of important parasitic diseases [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(3): 365-369. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||