
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 337-343.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.03.009
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Li-ping( ), LV Chao, QIN Zhi-qiang, XU Jing, DENG Wang-ping(
), LV Chao, QIN Zhi-qiang, XU Jing, DENG Wang-ping( )
)
Received:2021-07-26
Revised:2021-12-13
Online:2022-06-30
Published:2022-07-06
Contact:
DENG Wang-ping
E-mail:wlpnlnl@163.com;dengwp@nipd.chinacdc.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Li-ping, LV Chao, QIN Zhi-qiang, XU Jing, DENG Wang-ping. Establishment and preliminary evaluation of a visualized detection technique for Schistosoma mansoni nucleic acid based on recombinase polymerase amplification[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 337-343.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.03.009
Fig. 1
Optimization of reaction condition for SmCox1-LFD-RPA A: Optimization of reaction temperature; B: Optimization of reaction time. 1-7: 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45 and 50 ℃; 8-14: 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 min. The result of adult S. mansoni DNA was shown on the left of each column; the result of sterile double distilled water was shown on the right of each column.
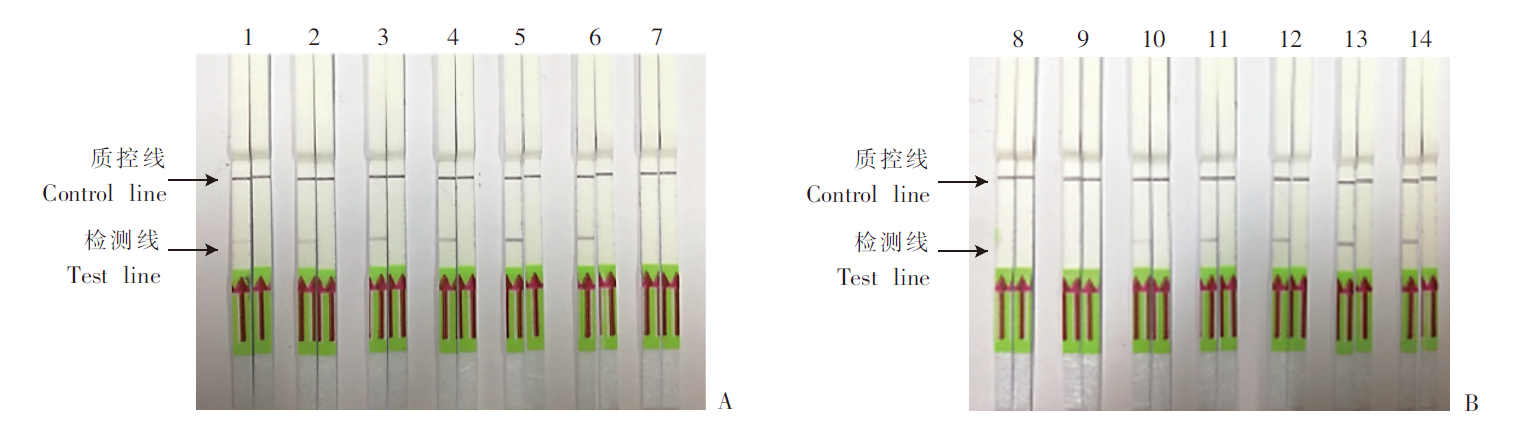
Fig. 2
Specificity evaluation of SmCox1-LFD-RPA 1-10: Genomic DNA of S. mansoni, S. japonica, S. haematobium, non-infected Oncomelania hupensis, infected Oncomelania hupensis, non-infected Biomphalaria glabrata, infected B. glabrata, Clonorchis sinensis, Fasciola gigantica and Paragonimus westermani; 11: Sterile double distilled water.
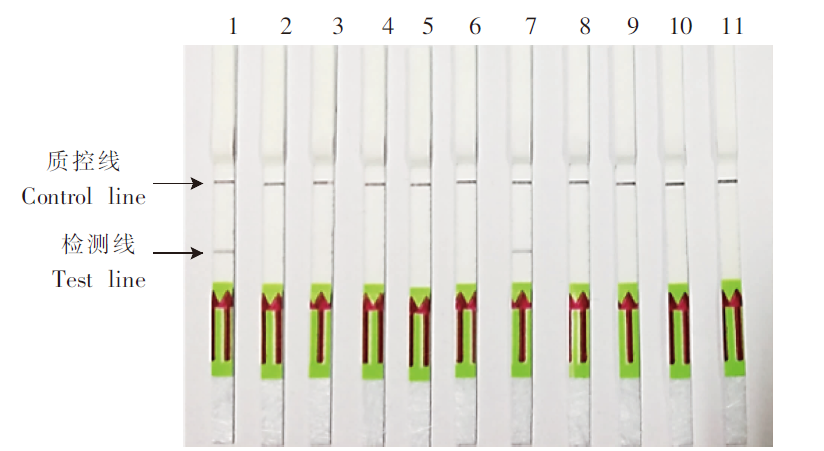
Fig. 3
Sensitivity evaluation of adult S. mansoni genomic DNA and recombinant SmCOX1 plasmids by SmCox1-LFD-RPA 1-8: 1 ng/μl, 100 pg/μl, 10 pg/μl, 1 pg/μl, 100 fg/μl, 10 fg/μl, 1 fg/μl, 0.1 fg/μl adult S. mansoni genomic DNA; 9, 17: Sterile double distilled water; 10-16: 105, 104, 103, 102, 101, 100, 10-1 copies/μl recombinant SmCox1 plasmids.
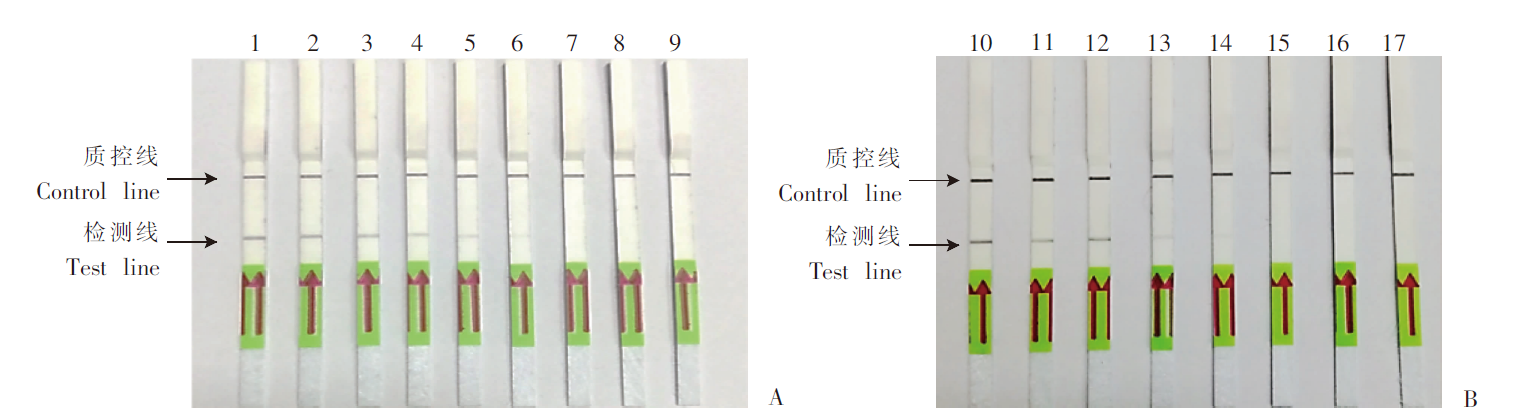
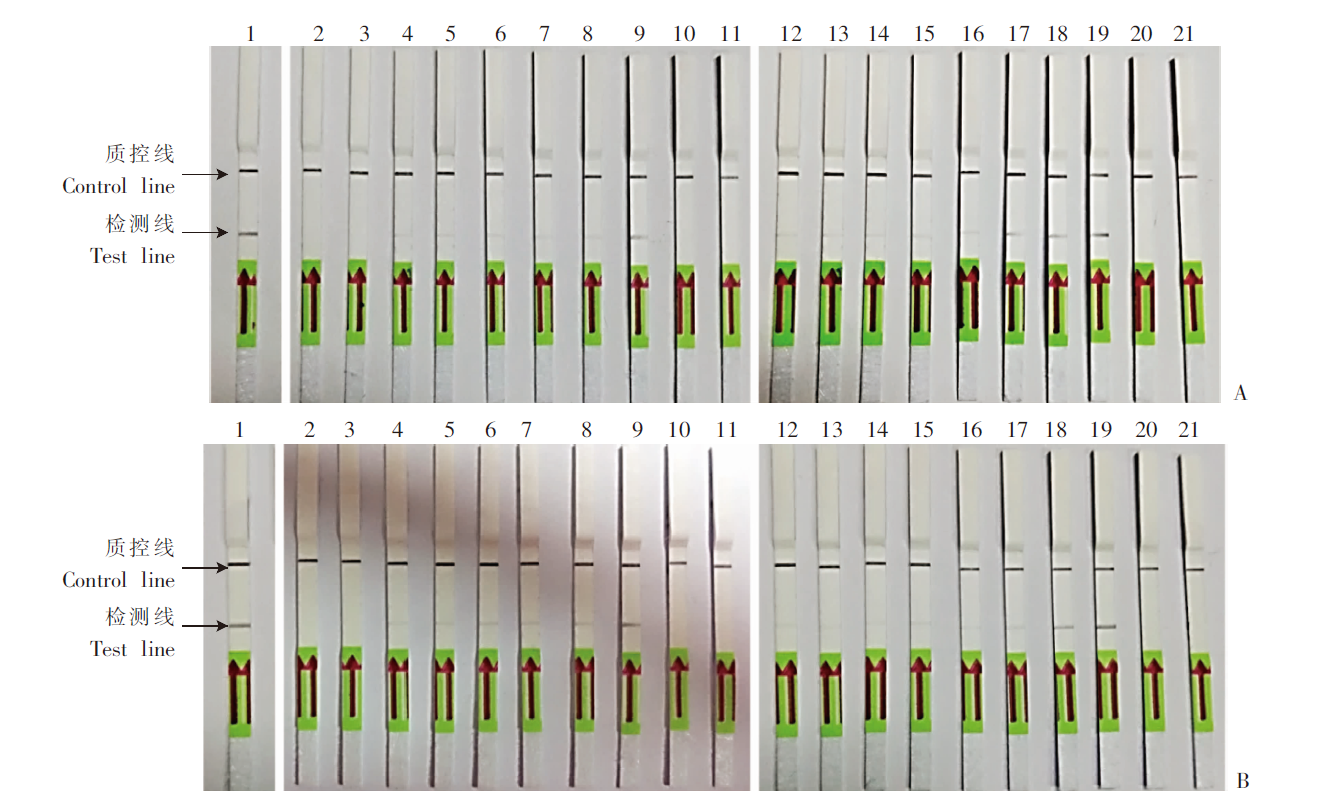
Fig. 4
Detection of S. mansoni cercariae-infected mouse fecal and blood samples by SmCox1-LFD-RPA A: Mixed fecal samples; B: Mixed blood samples. 1: Adult S. mansoni genomic DNA; 2-9: Mixed fecal/serum DNA of infected mice at the 1st to 8th week post infected with 40 S. mansoni cercariae; 10, 20: Mixed fecal/serum DNA of normal mice; 11, 21: Sterile double distilled water; 12-19: Mixed fecal/serum DNA of infected mice at the 1st to 8th week post infected with 80 S. mansoni cercariae.
| [1] |
Colley DG,, Bustinduy AL,, Secor WE, et al. Human schistosomiasis[J]. Lancet, 2014, 383(9936): 2253-2264.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61949-2 |
| [2] |
Ross AGP,, Bartley PB,, Sleigh AC, et al. Schistosomiasis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2002, 346(16): 1212-1220.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMra012396 |
| [3] |
Kalinda C,, Chimbari MJ,, Mukaratirwa S. Schistosomiasis in Zambia: a systematic review of past and present experiences[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2018, 7(1): 41.
doi: 10.1186/s40249-018-0424-5 |
| [4] | Fenwick A. Schistosomiasis: number of people treated worldwide in 2014[J]. Wkly Epidemiol Rec, 2016, 91(5): 53-60. |
| [5] | Zhang LJ,, Xu ZM,, Dang H, et al. Endemic status of schistosomiasis in People’s Republic of China in 2019[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2020, 32(6): 551-558. (in Chinese) |
| ( 张利娟,, 徐志敏,, 党辉, 等. 2019年全国血吸虫病疫情通报[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2020, 32(6): 551-558.) | |
| [6] | Wang YA,, Yang K,, Liang YS, et al. Studies on colonization risk and potential geographical distribution of Biomphalaria glabrata as an intermediate host of Schistosoma mansoni in China’s mainland[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2018, 30(3): 249-254, 259. (in Chinese) |
| ( 王宜安,, 杨坤,, 梁幼生, 等. 曼氏血吸虫中间宿主光滑双脐螺在中国大陆的定殖风险及潜在地理分布研究[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2018, 30(3): 249-254, 259.) | |
| [7] | Huang SY,, Zhang QM,, Li XH, et al. Distribution and schistosomiasis transmission risks of Biomphalaria straminea in inland China[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2014, 26(3): 235-237. (in Chinese) |
| ( 黄少玉,, 张启明,, 李晓恒, 等. 藁杆双脐螺在中国内陆的分布现状与传病风险[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2014, 26(3): 235-237.) | |
| [8] | Zou Y,, Wang L,, Li XL, et al. Clinical features of imported schistosomiasis mansoni in Beijing City: a report of 6 cases[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2017, 29(2): 150-154. (in Chinese) |
| ( 邹洋,, 王磊,, 李小丽, 等. 北京市6例输入性曼氏血吸虫病临床特点分析[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2017, 29(2): 150-154.) | |
| [9] | Zhang JF,, Wen LY,, Xu J, et al. Current status and transmission risks of oversea imported schistosomiasis in China[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2019, 31(1): 26-32. (in Chinese) |
| ( 张剑锋,, 闻礼永,, 许静, 等. 境外血吸虫病输入我国的现状及面临风险[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2019, 31(1): 26-32.) | |
| [10] | Silva-Moraes V,, Shollenberger LM,, Siqueira LMV, et al. Diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni infections: what are the choices in Brazilian low-endemic areas?[J]. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, 2019, 114: e180478. |
| [11] | Katz N,, Chaves A,, Pellegrino J. A simple device for quantitative stool thick-smear technique in schistosomiasis mansoni[J]. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo, 1972, 14(6): 397-400. |
| [12] |
Enk MJ,, Lima AC,, Drummond SC, et al. The effect of the number of stool samples on the observed prevalence and the infection intensity with Schistosoma mansoni among a population in an area of low transmission[J]. Acta Trop, 2008, 108(2/3): 222-228.
doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2008.09.016 |
| [13] |
Grenfell RFQ,, Martins W,, Enk M, et al. Schistosoma mansoni in a low-prevalence area in Brazil: the importance of additional methods for the diagnosis of hard-to-detect individual carriers by low-cost immunological assays[J]. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, 2013, 108(3): 328-334.
doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762013000300011 |
| [14] |
Grenfell RFQ,, Coelho PMZ,, Taboada D, et al. Newly established monoclonal antibody diagnostic assays for Schistosoma mansoni direct detection in areas of low endemicity[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e87777.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087777 |
| [15] |
Pontes LA,, Dias-Neto E,, Rabello A. Detection by polymerase chain reaction of Schistosoma mansoni DNA in human serum and feces[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2002, 66(2): 157-162.
pmid: 12135287 |
| [16] |
Hanelt B,, Adema CM,, Mansour MH, et al. Detection of Schistosoma mansoni in Biomphalaria using nested PCR[J]. J Parasitol, 1997, 83(3): 387-394.
pmid: 9194817 |
| [17] |
Espírito-Santo MCC,, Alvarado-Mora MV,, Pinto PLS, et al. Detection of Schistosoma mansoni infection by TaqMan®Real-Time PCR in a hamster model[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2014, 143: 83-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2014.05.013 pmid: 24858959 |
| [18] | Fuss A,, Mazigo HD,, Tappe D, et al. Comparison of sensitivity and specificity of three diagnostic tests to detect Schistosoma mansoni infections in school children in Mwanza region, Tanzania[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(8): e0202499. |
| [19] |
Piepenburg O,, Williams CH,, Stemple DL, et al. DNA detection using recombination proteins[J]. PLoS Biol, 2006, 4(7): e204.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040204 |
| [20] | Du YN,, Zhao X,, Fan XR, et al. Advances and applications of recombinase polymerase amplification[J]. Acta Agric Shanghai, 2018, 34(6): 117-122. (in Chinese) |
| ( 杜亚楠,, 赵笑,, 范小瑞. 重组酶聚合酶扩增技术的研究进展及其应用[J]. 上海农业学报, 2018, 34(6): 117-122.) | |
| [21] |
Kim J,, Easley CJ. Isothermal DNA amplification in bioanalysis: strategies and applications[J]. Bioanalysis, 2011, 3(2): 227-239.
doi: 10.4155/bio.10.172 |
| [22] | Gao WF,, Zhu P,, Huang HL. Recombinase polymerase amplification: a new DNA/RNA amplification strategy[J]. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol, 2016, 32(6): 627-634. (in Chinese) |
| ( 高威芳,, 朱鹏,, 黄海龙. 重组酶聚合酶扩增技术:一种新的核酸扩增策略[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2016, 32(6): 627-634.) | |
| [23] | Sun K. Establishment of nucleic acid visual detection based on LFD-RPA and its application[D]. Beijing: Academy of Military Sciences, 2017: 21-26. (in Chinese) |
| ( 孙魁. 基于LFD-RPA的核酸可视化检测技术的建立及应用[D]. 北京: 中国人民解放军军医学科学院, 2017: 21-26.) | |
| [24] | Deng WP,, Hong QH,, Xu B, et al. Development and preliminary evaluation of a rapid visualization detection method for circulating nucleic acids of Schistosoma japonicum based on RPA-LFD[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2020, 38(3): 286-292. (in Chinese) |
| ( 邓王平,, 洪清华,, 徐斌, 等. 基于RPA-LFD的日本血吸虫循环核酸快速可视化检测方法的建立及初步评价[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2020, 38(3): 286-292.) | |
| [25] |
Poulton K,, Webster B. Development of a lateral flow recombinase polymerase assay for the diagnosis of Schistosoma mansoni infections[J]. Anal Biochem, 2018, 546: 65-71.
doi: S0003-2697(18)30070-8 pmid: 29425749 |
| [26] |
Cheever AW,, Lenzi JA,, Lenzi HL, et al. Experimental models of Schistosoma mansoni infection[J]. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, 2002, 97(7): 917-940.
doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762002000700002 |
| [27] |
Wang YL,, Holmes E,, Nicholson JK, et al. Metabonomic investigations in mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni: an approach for biomarker identification[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2004, 101(34): 12676-12681.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404878101 |
| [28] |
Sandoval N,, Siles-Lucas M,, Lopez Aban J, et al. Schistosoma mansoni: a diagnostic approach to detect acute schistosomiasis infection in a murine model by PCR[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2006, 114(2): 84-88.
pmid: 16571353 |
| [29] |
Fernández-Soto P,, Gandasegui Arahuetes J,, Sánchez Hernández A, et al. A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for early detection of Schistosoma mansoni in stool samples: a diagnostic approach in a murine model[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2014, 8(9): e3126.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003126 |
| [30] | Zhao S,, Liu YH,, Ye YY, et al. Establishment of the gene detection method of Schistosoma mansoni based on the recombinase-aided isothermal amplification assay[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2020, 32(4): 335-339, 344. (in Chinese) |
| ( 赵松,, 刘燕红,, 叶钰滢, 等. 基于重组酶介导核酸等温扩增反应的曼氏血吸虫基因检测方法的建立[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2020, 32(4): 335-339, 344.) | |
| [31] |
Carneiro TR,, Peralta RHS,, Pinheiro MCC, et al. A conventional polymerase chain reaction-based method for the diagnosis of human schistosomiasis in stool samples from individuals in a low-endemicity area[J]. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, 2013, 108(8): 1037-1044.
doi: 10.1590/0074-0276130202 |
| [1] | ZHANG Yi-long, YE Run, LE Bin, CHEN Wen-zhu, PAN Wei-qing, ZHANG Dong-mei. A reverse transcriptase aid-enzymatic recombinase isothermal amplification-based method for detection of West Nile virus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 344-348. |
| [2] | JIANG Feng, CHEN Run, DU Ning-ning, ZHU Meng-yi, ZHONG Hao, CHEN Hui, XI Xu-xia, ZHAN Xiao-dong, LI Chao-pin. Investigation of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pet dogs and cats in Wuhu City [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(1): 124-126. |
| [3] | DENG Wang-ping, HONG Qing-hua, XU Bin, WANG Sheng-lin, WANG Li-ping, XU Jing, HU Wei, ZHOU Xiao-nong. Development and preliminary evaluation of a rapid visualization detection method for circulating nucleic acids of Schistosoma japonicum based on RPA-LFD [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 286-292. |
| [4] | WANG Sheng-lin, DENG Wang-ping, LI Yin-long, WANG Li-ping, ZHANG Li-juan, LV Shan, XU Jing. Establishment of recombinase polymerase amplification technique for rapid detection of Schistosoma japonicum nucleic acid [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 293-298. |
| [5] | ZHOU Hong-rang, MAO Guang-yao, WANG Xiao-ling, CHEN Mu-xin, YU Qing, WANG Ying, Ai Lin, XIAO Ning. Establishment and application of a multiplex recombinase-aided isothermal amplification technique for identifying Echinococcus granulosus and Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 310-316. |
| [6] | Wang-ping DENG, Bin XU, Qing-hua HONG, Sheng-lin WANG, Chao LV, Yin-long LI, Shi-ping SONG, Jun-hu CHEN, Jing XU, Shi-zhu LI, Wei HU, Xiao-nong ZHOU. Establishment of the detection method for Schistosoma japonicum by recombinase polymerase amplification combined with electrochemical DNA biosensor [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(2): 168-174. |
| [7] | Song ZHAO, Yan-hong LIU, Ting LI, Wei LI, Jian-feng ZHANG, Li-chuan GUO, Qing-jie YING, Hai-tao YANG, Kun YANG. Rapid detection of Schistosoma japonicum specific gene fragment by recombinase aided isothermal amplification combined with fluorescent probe [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(1): 23-27. |
| [8] | Ting FENG, Zhi-qiang QIN, Jing XU, Jie ZHOU, Yin-jun QIAN, Hong-qing ZHU, Shan LV, Chun-li CAO, Shi-zhu LI. Efficacy evaluation of a loop mediated isothermal amplification technique in detection of DNA of Schistosoma japonicum eggs in fecal samples [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2017, 35(3): 230-234. |
| [9] | XU Qian-ming1,2*, YUAN Heng-qing1, ZHAO Chang-cheng1, FANG Fen1, LIU Zhe1, NING Hong-rui1,2, SHI Da-li1, LI Yu1, WANG Hai-yang1. Establishment of LAMP Detection for Toxoplasma gondii Based on the 529 bp Repeat Sequence [J]. , 2016, 34(5): 12-444-450. |
| [10] | ZHANGHui;LIUXue-qing;HERong-zhi;JIATian-jun;ZHANGJin-shun*. Establishment of Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) for Detecting Pneumocystis carinii [J]. , 2010, 28(4): 18-307. |
| [11] | YANGQiu-lin*;ZHANGRu-sheng;WUHe-ping;ZHANGYu-kuai;WANGKe-geng. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification [J]. , 2008, 26(4): 14-306. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||