
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 204-210.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.02.011
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIE Hui-qun1( ), XU Yun1, GONG Zhi-hong1, HU Fei1, WAN Hui2, XU Chun-hua3, WU Jie4, LIU Jun-pu1, HONG Dao-jun2,*(
), XU Yun1, GONG Zhi-hong1, HU Fei1, WAN Hui2, XU Chun-hua3, WU Jie4, LIU Jun-pu1, HONG Dao-jun2,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-09
Revised:2021-08-06
Online:2022-04-30
Published:2022-04-06
Contact:
HONG Dao-jun
E-mail:huiqunxie@aliyun.com;hongdaojun@hotmail.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
XIE Hui-qun, XU Yun, GONG Zhi-hong, HU Fei, WAN Hui, XU Chun-hua, WU Jie, LIU Jun-pu, HONG Dao-jun. Clinical outcome and change of antibody level in cerebral sparganosis mansoni patients after treatment: a multicenter study[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 204-210.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.02.011
Table 1
Treatment of cerebral sparganosis mansoni in three centres
| 中心名称 Center | 病例数 No. case | 治疗例数 No. case | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 吡喹酮 Praziquantel | 外科 Surgey | ||
| 江西省寄生虫病防治研究所Jiangxi Provincial Institute of Parasitic Diseases | 52 - 6a | 52 - 6a | 0 |
| 南昌大学第一附属医院 First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University | 31 | 10 - 4a | 21 + 4a |
| 广东三九脑科医院 Guangdong 999 Brain Hospital | 4 + 6a | 0 | 4 + 6a |
| 合计Total | 87 | 62 - 10a | 35 |
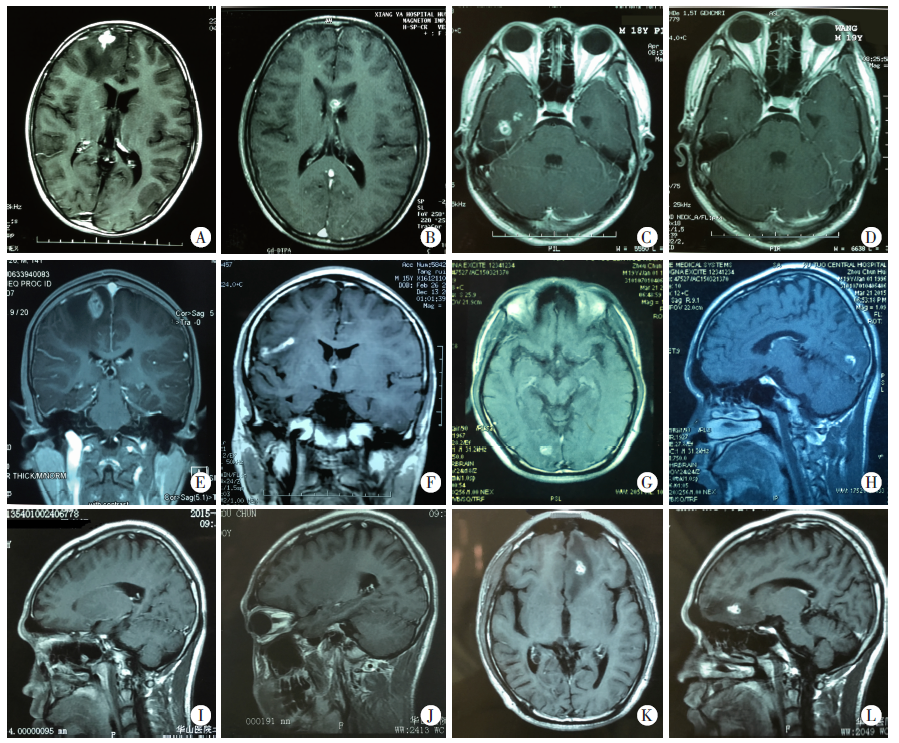
Fig. 1
Changes in images and antibodies of the patients with cerebral sparganosis mansoni with different treatment outcomes A-D: Patients with the good outcome: A: The enhancement lesions in the right frontal lobe, antibody titer 1 ∶ 3 200; B: After 1 treatment course, the enhancement lesions migrate to the corpus callosum, with an antibody titer of 1 ∶ 800; C: After 2 treatment courses, the enhancement lesions migrate to the right temporal lobe. Antibody titer 1 ∶ 1 600; D: After 12 months of treatment, the active enhancement lesions basically disappeared, antibody titer 1 ∶ 200. E-L: Patients with poor outcomes. E: Enhancement lesions on right parietal lobe, antibody titer 1 ∶ 1 600; F: After 12 months of treatment, the worms migrate to the right frontal lobe, antibody titer 1 ∶ 800. G, H: Enhancement lesions on right occipital lobe in the patients showing new lesions after treatment, antibody titer 1 ∶ 800; I: Active enhancement lesions resolved after 2 months of treatment, antibody titer 1 ∶ 800; J: No active enhancement lesions were seen after 6 months of treatment, antibody titer 1 ∶ 400; K, L: After 12 months of treatment, new active enhancement lesions found on the left frontal lobe, antibody titer 1 ∶ 800.
| [1] | Xu Y,, Wan H,, Hong DJ, et al. Cerebral clinical features and outcome of 123 patients with sparganosis[J]. Jiangxi Med J, 2017, 52(4): 286-289. (in Chinese) |
| (徐芸,, 万慧,, 洪道俊, 等. 123例曼氏裂头蚴病的临床特点及治疗观察[J]. 江西医药, 2017, 52(4): 286-289.) | |
| [2] | Yan XQ,, Li XL,, Sun ZQ, et al. Clinical features of 83 cases of cerebral sparganosis[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2021, 39(2): 240-245. (in Chinese) |
| (闫学强,, 李晓龙,, 孙祯卿, 等. 83例脑裂头蚴病患者临床资料分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2021, 39(2): 240-245.) | |
| [3] |
Kim JG,, Ahn CS,, Sohn WM, et al. Human sparganosis in Korea[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2018, 33(44): e273.
doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e273 |
| [4] |
Lo Presti A,, Aguirre DT, et al. Cerebral sparganosis: case report and review of the European cases[J]. Acta Neurochir (Wien), 2015, 157(8): 1339-1343.
doi: 10.1007/s00701-015-2466-9 pmid: 26085111 |
| [5] | Zeng QR,, He M,, Wang F, et al. Pathogen identification of 10 suspected cases of sparganosis mansoni[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2012, 30(3): 224-227, 232. (in Chinese) |
| (曾庆仁,, 贺美,, 王芳, 等. 10例疑似曼氏裂头蚴病的病原学诊断[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2012, 30(3): 224-227, 232.) | |
| [6] |
Meng YM,, Kuang ZW,, Liao L, et al. Case report: morphologic and genetic identification of cerebral sparganosis[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2019, 101(5): 1174-1176.
doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0468 |
| [7] |
Zhu YL,, Ye LQ,, Ding XS, et al. Cerebral sparganosis presenting with atypical postcontrast magnetic resonance imaging findings: a case report and literature review[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2019, 19(1): 748.
doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4396-2 |
| [8] |
Zhang P,, Zou Y,, Yu FX, et al. Follow-up study of high-dose praziquantel therapy for cerebral sparganosis[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2019, 13(1): e0007018.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007018 |
| [9] |
Hong DJ,, Xie HQ,, Wan H, et al. Efficacy comparison between long-term high-dose praziquantel and surgical therapy for cerebral sparganosis: a multicenter retrospective cohort study[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2018, 12(10): e0006918.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006918 |
| [10] |
Gonzenbach RR,, Kong Y,, Beck B, et al. High-dose praziquantel therapy for cerebral sparganosis[J]. J Neurol, 2013, 260(5): 1423-1425.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-013-6901-7 pmid: 23546305 |
| [11] | Xie HQ,, Long Y,, Xu Y, et al. Clinical features, radiological characteristics and pathological changes in 42 patients with cerebral sparganosis[J]. Chin J Neurol, 2015, 48(2): 108-113. (in Chinese) |
| (谢慧群,, 龙勇,, 徐芸, 等. 脑曼氏裂头蚴病患者42例的临床、 影像与病理特点分析[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2015, 48(2): 108-113.) | |
| [12] |
Hong DJ,, Xie HQ,, Zhu M, et al. Cerebral sparganosis in mainland Chinese patients[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2013, 20(11): 1514-1519.
doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2012.12.018 |
| [13] | Chen XH,, Shi GF. Clinical analysis of 6 cases with cerebral sparganosis mansoni[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2010, 28(5): 397-398. (in Chinese) |
| (陈先汉,, 施光峰. 脑曼氏裂头蚴病6例临床分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2010, 28(5): 397-398.) | |
| [14] | Ye SK,, Xu L,, Huang Q, et al. The epidemiology, clinical feature, radiology and outcome of 8 cases with cerebral sparganosis mansoni[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018, 36(2): 144-147. (in Chinese) |
| (叶善可,, 徐烈,, 黄琴, 等. 8例脑曼氏裂头蚴病的流行病学特点、 临床特征、 影像学表现与预后分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018, 36(2): 144-147.) | |
| [15] | Kim YB,, Hw ang SN,, Cho SY, et al. Cereberal spargnosis: two cases diagnosed by CT/MR and ELISA tests[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc, 1993, 22(6): 585-590. |
| [16] | Choi SH,, Kang SY,, Kong Y, et al. Antigenic protein fractions reacting with sera of sparganosis patients[J]. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi, 1988, 26(3): 163-167. |
| [17] | Hwang JM,, Hwang DS,, Kang C, et al. Subcutaneous sparganosis mimicking soft tissue tumor: a case report[J]. Int Med Case Rep J, 2019, 12: 47-50. |
| [18] | National Health and Family Planning Commission. Diagnosis of sparganosis WS 438-2013[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2013. (in Chinese) |
| 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 裂头蚴病的诊断 WS 438-2013[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013. | |
| [19] |
Wang P,, Su XY,, Mao Q, et al. The surgical removal of a live tapeworm with an interesting pathologic finding most likely representing the migration path: a case report of cerebral sparganosis[J]. Clinics (Sao Paulo), 2012, 67(7): 849-851.
doi: 10.6061/clinics/2012(07)24 |
| [20] |
Chu SG,, Lu XS,, Wang Y, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging features of pathologically proven cerebral sparganosis[J]. J Int Med Res, 2013, 41(3): 867-877.
doi: 10.1177/0300060513480925 |
| [21] |
Shirakawa K,, Yamasaki H,, Ito A, et al. Cerebral sparganosis: the wandering lesion[J]. Neurology, 2010, 74(2): 180.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181c91a15 pmid: 20065255 |
| [22] |
Torres JR,, Noya OO,, Noya BA, et al. Treatment of proliferative sparganosis with mebendazole and praziquantel[J]. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, 1981, 75(6): 846-847.
doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(81)90428-4 |
| [23] |
Deng L,, Xiong PJ,, Qian SK. Diagnosis and stereotactic aspiration treatment of cerebral sparganosis: summary of 11 cases[J]. J Neurosurg, 2011, 114(5): 1421-1425.
doi: 10.3171/2010.4.JNS1079 pmid: 20486898 |
| [24] |
Sohn WM,, Hong ST,, Chai JY, et al. Infectivity of the Sparganum treated by praziquantel, gamma-irradiation and mechanical cutting[J]. Korean J Parasitol, 1993, 31(2): 135-139.
pmid: 8343455 |
| [25] |
Chan JD,, Zarowiecki M,, Marchant JS. Ca2+ channels and praziquantel: a view from the free world[J]. Parasitol Int, 2013, 62(6): 619-628.
doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2012.12.001 |
| [26] |
Andrews P,, Thomas H,, Pohlke R, et al. Praziquantel[J]. Med Res Rev, 1983, 3(2): 147-200.
pmid: 6408323 |
| [27] |
Gonzenbach RR,, Kong Y,, Beck B, et al. High-dose praziquantel therapy for cerebral sparganosis[J]. J Neurol, 2013, 260(5): 1423-1425.
doi: 10.1007/s00415-013-6901-7 pmid: 23546305 |
| [28] |
Doenhoff MJ,, Cioli D,, Utzinger J. Praziquantel: mechanisms of action, resistance and new derivatives for schistosomiasis[J]. Curr Opin Infect Dis, 2008, 21(6): 659-667.
doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e328318978f pmid: 18978535 |
| [29] |
Kim DG,, Paek SH,, Chang KH, et al. Cerebral sparganosis: clinical manifestations, treatment, and outcome[J]. J Neurosurg, 1996, 85(6): 1066-1071.
pmid: 8929496 |
| [1] | RONG Zhi-li, SHI Ting-ting. A misdiagnosed case of brain sparganosis mansoni [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(6): 817-820. |
| [2] | OUYANG Bing, LI Ren-xi. One case of Diphyllobothrium latum infection caused by raw salmon [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 295-298. |
| [3] | HUANG Yan, YU Wen-jie, SHANG Jing-ye, HE Wei, ZHANG Guang-jia, WANG Qi, YANG Liu, LIAO Sha, LI Rui-rui, YAO Ren-xin, ZENG Ming-cai, ZHANG Fu-bing, LI Shu-cheng, LIU Yang, ZHONG Bo, WANG Qian. Efficacy of alternative and combined use of albendazole plus praziquantel in the treatment of echinococcosis for Tibetan herdsmen [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 171-177. |
| [4] | ZHAO Cheng-si, QIN Min, TAN Ming-juan, MIAO Ting-ting, SHAO Tian-ye, LIU Xin-jian, WANG Yong. Effect of praziquantel on impaired renal function in mice with acute infection of Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 200-209. |
| [5] | YAN Xue-qiang, LI Xiao-long, SUN Zhen-qing, WU Jie. Clinical features of 83 cases of cerebral sparganosis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 240-244. |
| [6] | WANG Wei, ZHAO Cheng-si, MIAO Ting-ting, ZHOU Chun-lei, ZHANG Cheng-cheng, QIN Min, SHAO Tian-ye, WANG Yong. Praziquantel inhibits splenic macrophage proliferation and inflammatory reaction in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 263-270. |
| [7] | ZHAO Jin-ying, LIU Peng, LI Yan-wei, WANG Shi-ping. Research progress on combined medications for schistosomiasis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(3): 370-377. |
| [8] | Aini ABUDUSALAMU, Ying-mei SHAO, Aji TUERGANAILI, Wen-bao ZHANG, Ren-yong LIN, Yan-yan HOU, Zhuang-zhi ZHANG, Hao WEN. Establishment and innovative practice of Integrative System of Prevention, Diagnosis and Management for echinococcosis in China [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2019, 37(4): 388-394. |
| [9] | Shan-ke YE, Lie XU, Qin HUANG, Yun LING. The epidemiology,clinical feature, radiology and outcome of 8 cases with cerebral sparganosis mansoni [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2018, 36(2): 144-147. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yu-mei1,2, WANG Yan-juan1 *, LIU Hua1, JIANG Yan-yan1, XU Yu-xin1,ZHENG Li1,3, HU Yuan1, SHEN Yu-juan1, CAO Jian-ping1. T Follicular Helper Cells and Related Molecules in Schistosoma japonicum Infected Mice after Praziquantel Treatment [J]. , 2016, 34(2): 2-99-104. |
| [11] | WEN Hao*, TUERGANAILI Aji, SHAO Ying-mei, LIN Ren-yong, LI Hai-tao, TUERHONGJIANG Tuxun, LV Guo-dong, ZHANG Wen-bao. Research Achievements and Challenges for Echinococcosis Control [J]. , 2015, 33(6): 13-466-471. |
| [12] | SONG Guo-ping,LI Jin-fu,CHEN Yan*,XU Jing. Effects of Omphalia lapidescens and Praziquantel on the Infectivity and Ultrastructure of Spirometra erinacei Plerocercoids [J]. , 2015, 33(1): 8-40-44. |
| [13] | LIU Xiang-qin1,2,TIAN Xi-feng1,ZHANG Jin2,XIN Xiao-fang2,ZHANG Ying2 *. Changes of IFN-γ, IL-4 and T Cells in Schistosoma japonicum- infected Mice after Praziquantel Treatment [J]. , 2014, 32(2): 5-106-109. |
| [14] | GUO Rui,MA Jin-shan,NU Er-Lan. Treatment of 42 Child Cases of Pulmonary Echinococcosis granulosus by Excision of Internal Cyst through Video-assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery [J]. , 2012, 30(4): 19-329-330. |
| [15] | XIAO Shu-Hua, XUE Jian. Study Progress on Mefloquine against Schistosomes and other Helminths [J]. , 2012, 30(2): 10-131-138,145. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||