
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 48-54.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2021.01.007
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Ji-hai1( ), CAO De-ping2, ZHAO Jun2, LIU Jun2, SHI Hu-xiang2, LIU Yan2,*(
), CAO De-ping2, ZHAO Jun2, LIU Jun2, SHI Hu-xiang2, LIU Yan2,*( )
)
Received:2020-07-27
Revised:2020-09-13
Online:2021-02-28
Published:2021-03-10
Contact:
LIU Yan
E-mail:zhujihai@126.com;543394169@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHU Ji-hai, CAO De-ping, ZHAO Jun, LIU Jun, SHI Hu-xiang, LIU Yan. Investigation of differentially expressed genes in liver tissues of patients with alveolar echinococcosis[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(1): 48-54.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2021.01.007
Table 2
Differentially expressed genes in GSE24376 gene chip between Echinococcus multilocularis-infected and healthy mice
| 差异表达基因 Differentially expressed genes | 倍数变化 Fold change | P值 P value | 注释 Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CHI3L3 | 6.53 | 5.57E-07 | 几丁质酶3-3 Chitinase 3-like 3 |
| CCL8 | 4.84 | 4.42E-06 | C-C基序趋化配体8 C-C motif chemokine ligand 8 |
| RETNLA | 4.82 | 2.85E-05 | 抵抗素-α Resistin like alpha |
| SLPI | 3.31 | 2.58E-04 | 分泌白细胞肽酶抑制剂 Secretory leukocyte peptidase inhibitor |
| CCL12 | 2.77 | 3.80E-04 | 趋化因子(C-C基序)配体12 Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 12 |
| CLEC4D | 2.04 | 6.35E-04 | c型凝集素域家族4成员D C-type lectin domain family 4 member D |
| EAR11 | 2.02 | 3.45E-04 | 嗜酸粒细胞相关,核糖核酸酶A家族,成员11 Eosinophil-associated, ribonuclease A family, member 11 |
| UBD | 1.93 | 6.82E-04 | 泛素D Ubiquitin D |
| CCL17 | 1.57 | 7.62E-04 | C-C基序趋化配体17 C-C motif chemokine ligand 17 |
| HSD3B4 | -4.66 | 1.46E-05 | 3-和甾体德尔塔-异构酶4 3 beta-and steroid delta-isomerase 4 |
| SULT5A1 | -3.55 | 2.34E-04 | 磺基转移酶家族5A,成员1 Sulfotransferase family 5A, member 1 |
| EGFR | -3.06 | 1.66E-04 | 表皮生长因子受体 Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| A1BG | -2.97 | 3.78E-04 | alpha-1-B糖蛋白 Alpha-1-B glycoprotein |
| CYP17A1 | -2.64 | 7.22E-05 | 细胞色素P450家族17亚家族A成员1 Cytochrome P450 family 17 subfamily A member 1 |
| AHSG | -2.27 | 1.14E-04 | α2-HS糖蛋白 Alpha 2-HS glycoprotein |
| SERPINA1D | -2.25 | 2.64E-04 | 丝氨酸(或半胱氨酸)肽酶抑制剂,分支A,成员1D Serine (or cysteine) peptidase inhibitor, clade A, member 1D |
| APOE | -2.23 | 1.88E-04 | 载脂蛋白e Apolipoprotein E |
| ALB1 | -1.80 | 6.16E-04 | 阿宾娜1 ALBINA 1 |
| NSG1 | -1.79 | 7.12E-04 | 神经元小泡转运相关1 Neuronal vesicle trafficking associated 1 |
| 2310005P05RIK | -1.62 | 6.78E-04 | 内切酶/外切酶/磷酸酶家族含域蛋白1 Endonuclease/exonuclease/phosphatase family domain containing 1 |
| FBP1 | -1.54 | 8.26E-04 | 果糖二磷酸酶1 Fructose-bisphosphatase 1 |
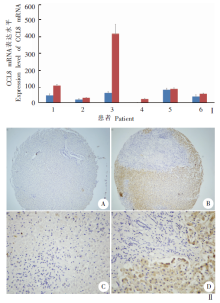
Fig. 2
Expression of CHI3L1 in liver tissue of patients with alveolar echinococcosis Ⅰ: Real-time PCR analysis of CHI3L1 gene expression; Ⅱ: Immunohistochemistry for CHI3L1 protein. Normal group; Infected group; A, C: Low expression of CHI3L1 protein in normal liver tissues (× 10, × 40); B, D: High expression of CHI3L1 protein in the liver lesions (× 10, × 40).
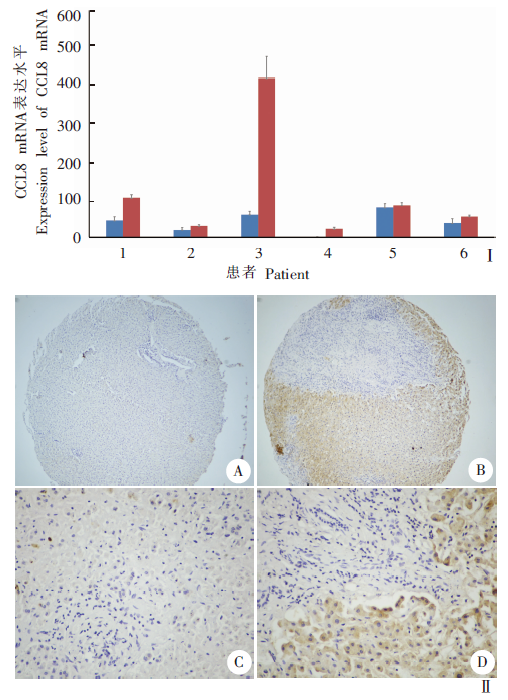
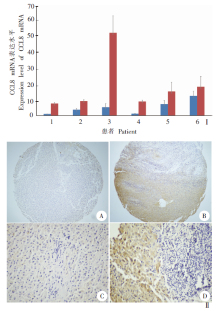
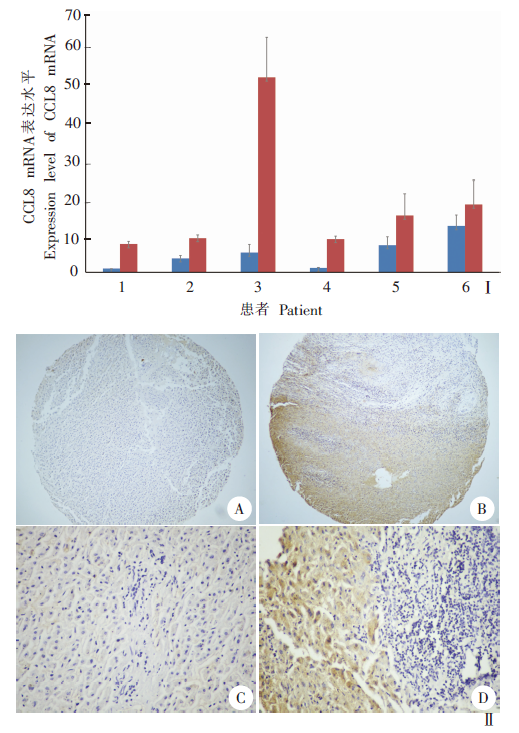
Fig. 3
Expression of CCL8 protein in human liver infected with Echinococcus multilocularis Ⅰ: Real-time PCR detection of CCL8 gene expression; Ⅱ: Immunohistochemistry detected the expression of CCL8 protein. Normal group; Infected group; A, C: Low expression of CCL8 protein in normal liver tissues (× 10, × 40); B, D: High expression of CCL8 protein in the liver lesions (× 10, × 40).
| [1] |
Cadavid Restrepo AM, Yang YR McManus DP, et al. The landscape epidemiology of echinococcoses[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2016,5:13.
doi: 10.1186/s40249-016-0109-x pmid: 26895758 |
| [2] |
Nunnari G, Pinzone MR, Gruttadauria S, et al. Hepatic echinococcosis: clinical and therapeutic aspects[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2012,18(13):1448-1458.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i13.1448 pmid: 22509076 |
| [3] | Xu XL, Wang ZX, Wang Z, et al. Treatment of complicated hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: our experience of 98 cases[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018,36(6):552-559. (in Chinese) |
| ( 许晓磊, 王志鑫, 王展, 等. 98例复杂性肝多房棘球蚴病外科治疗方案的比较分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018,36(6):552-559.) | |
| [4] |
Wen H, Vuitton L, Tuxun T, et al. Echinococcosis: advances in the 21st century[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2019,32(2):e00075-18.
doi: 10.1128/CMR.00075-18 pmid: 30760475 |
| [5] | Xie WJ, Lv GD, Li Y, et al. Gene expression profile analysis of the liver in BALB/C mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis by cDNA microarray[J]. Chin J Exp Surg, 2010,27(2):189-191. (in Chinese) |
| ( 谢文娟, 吕国栋, 李瑶, 等. 泡球蚴感染小鼠所致肝损伤基因表达谱的变化[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2010,27(2):189-191.) | |
| [6] | Wang L. Study on form mechanism of fibrosis capsule wall around Hepatichydaid[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2010. ( in Chinese) |
| ( 王蕾. 肝细粒棘球蚴周围纤维囊壁形成机制的初步探索[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2010.) | |
| [7] | Pan W, Zhang YM, Sun FF, et al. Changes of phenotype and phagocytosis of peritoneal macrophages in mice infected with the larval-stage of Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2016,34(4):315-318. (in Chinese) |
| ( 潘伟, 张玉梅, 孙芬芬, 等. 细粒棘球蚴感染小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞表型及吞噬功能的变化[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2016,34(4):315-318.) | |
| [8] | Liu HD, Wang HB, Fan HN, et al. Alveolar echinococcosis and immune evasion[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018,36(6):655-660. (in Chinese) |
| ( 刘寒冬, 王宏宾, 樊海宁, 等. 多房棘球蚴病的免疫逃避机制[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018,36(6):655-660.) | |
| [9] |
Schuster S, Hurrell B, Tacchini-Cottier F. Crosstalk between neutrophils and dendritic cells: a context-dependent process[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2013,94(4):671-675.
doi: 10.1189/jlb.1012540 pmid: 23250891 |
| [10] |
Cotterell SE, Engwerda CR, Kaye PM. Enhanced hematopoietic activity accompanies parasite expansion in the spleen and bone marrow of mice infected with Leishmania donovani[J]. Infect Immun, 2000,68(4):1840-1848.
doi: 10.1128/iai.68.4.1840-1848.2000 pmid: 10722572 |
| [11] | Liu J, Cen JJ, Lv ZY, et al. The chemokine CCL8 and its progress in disease research[J]. J Trop Med, 2015,15(9):1287-1291. (in Chinese) |
| ( 刘记, 岑俊杰, 吕志跃, 等. 趋化因子CCL8及其在疾病研究中的进展[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2015,15(9):1287-1291.) | |
| [12] |
Liu K, Jin M, Ye S, et al. CHI3L1 promotes proliferation and improves sensitivity to cetuximab in colon cancer cells by down-regulating p53[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2020,34(1):e23026.
doi: 10.1002/jcla.23026 pmid: 31536166 |
| [13] |
Libreros S, Iragavarapu-Charyulu V. YKL-40/CHI3L1 drives inflammation on the road of tumor progression[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2015,98(6):931-936.
doi: 10.1189/jlb.3VMR0415-142R pmid: 26310833 |
| [14] |
Fantino E, Gangell CL, Hartl D, et al. Airway, but not serum or urinary, levels of YKL-40 reflect inflammation in early cystic fibrosis lung disease[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2014,14:28.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-14-28 pmid: 24576297 |
| [15] |
Burman J, Raininko R, Blennow K, et al. YKL-40 is a CSF biomarker of intrathecal inflammation in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2016,292:52-57.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.01.013 pmid: 26943959 |
| [16] |
Tanaka Y, Matsumoto I, Inoue A, et al. Antigen-specific over-expression of human cartilage glycoprotein 39 on CD4+CD25+ forkhead box protein 3+ regulatory T cells in the generation of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase-induced arthritis [J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2014,177(2):419-427.
doi: 10.1111/cei.12349 |
| [1] | XUE Yushan, LIN Ping, CHENG Xunjia, FENG Meng. Damage caused by chronic infection of Toxoplasma gondii on the host central nervous system and its mechanism [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 527-531. |
| [2] | GUO Shuai, HE Biao, GAO Yuanli, FAN Yongling, ZHU Feng, DING Yan, LIU Taiping, XU Wenyue. Specie-specific analysis of plasmodia infecting rats and mice [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 539-545. |
| [3] | LIU Wenhu, HUANG Ming, LIANG Jin, LIU Jianxiong, WEN Zhaomeng, MA Shaobo. A case of ventricular cysticercosis complicated with hydrocephalus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 644-646. |
| [4] | ZHANG Li, MIAO Feng, SHEN Yanmei. A case of Capillaria hepatica infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 650-652. |
| [5] | CAO Deping, LI Jiajing, SONG Mengwei, MO Gang. Experimental observation on the changes of hepatic stellate cells stimulated in vitro with tissue protein of Echinococcus multilocularis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 440-445. |
| [6] | LI Xiaoli, LI Shaogang, WU Zhaoyong. Clinical characteristics of patients with intestinal Diphyllobothrium tapeworm infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 459-463. |
| [7] | ZHENG Yuhua, TIE Ping, BAI Yongfei, YAN Changfu, WANG Ting, WANG Jingying, TIAN Xiaodong, DAI Peifang. Investigation on visceral leishmaniasis in domestic dogs and sandfly density in epidemic area in Shanxi Province from 2021 to 2022 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 470-475. |
| [8] | LI Yuqiong, YU Youli, GAO Junrong, LIU Yunyun, LI Hongbing, NIU Xiaohao. Enterocytozoon bieneusi infection in dairy cows and its genotype identification in Yinchuan area of Ningxia Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 476-479. |
| [9] | WANG Feng, WU Fan, LI Linlin, HUANG Qingqing. Prevalence of parasitic infections in wild mice in Wuhu City, Anhui Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 516-519. |
| [10] | ZHU Canmin, PENG Weijian, WANG Dili, ZHOU Huajing, JIN Qiangjian, CHANG Chang. A case of acute primary amoebic meningoencephalitis [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(4): 524-526. |
| [11] | ZHANG Mizhen, HUANG Jilei, ZHU Huihui, ZHOU Changhai, ZHU Tingjun, QIAN Menbao, CHEN Yingdan, LI Shizhu. Epidemiological analysis of soil-transmitted nematode infections in China in 2020 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 331-335. |
| [12] | GUO Gang, REN Yuan, JIAO Hongjie, WU Juan, GUO Baoping, QI Wenjing, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao. Effect of intraperitoneal inoculation with Echinococcus microcysts on the infection and pathogenicity of E. multilocularis in mouse liver [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 156-162. |
| [13] | LI Chang, DU Xinyue, YAN Min, WANG Zhaojun. Research advances on the role and mechanism of neutrophil extracellular traps in parasitic infection [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 219-222. |
| [14] | ZHENG Dan, LIN Chenxin, CAI Wuwei, XIE Hangguo. Investigation of Anisakis spp. infection in marine fish in Fujian Province, 2019—2021 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 238-240. |
| [15] | ZHANG Fengyu, LIU Liu, ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Hao. Prevalence of trematode metacercariae in Pseudorasbora parva and species identification in Qiqihaer area [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 112-116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||