
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES ›› 2020, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 695-701.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2020.06.004
• ORIGINAL ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Chun-li1( ), YANG Hui2,3, PAN Wen4, ZHANG Xin4, ZHU Xiao-ting4, ZHAO Jia-qing1,2,3,*(
), YANG Hui2,3, PAN Wen4, ZHANG Xin4, ZHU Xiao-ting4, ZHAO Jia-qing1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2020-08-07
Online:2020-12-30
Published:2021-01-12
Contact:
ZHAO Jia-qing
E-mail:forever_lily@126.com;nxmczhaojq@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
SHI Chun-li, YANG Hui, PAN Wen, ZHANG Xin, ZHU Xiao-ting, ZHAO Jia-qing. Proteomic analysis of human proteins in extracellular vesicles secreted by protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus[J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 695-701.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jsczz.cn/EN/10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2020.06.004
Fig. 1
Isolation and identification of EVs from culture supernatant of protoscoleces of E. granulosus A: Transmission electron microscopy image of EVs, which had a bilayer-membrane round-vesicle structure; B: The diameter of EVs, < 200 nm; C: The top 5 EV marker proteins with the highest number of unique peptides of the protein in EVs. FLNA: Filamin-A; 14-3-3: 14-3-3 protein; HSP90: Heat shock protein 90; HSPA8: Heat shock protein 70; PKM: Pyruvate kinase
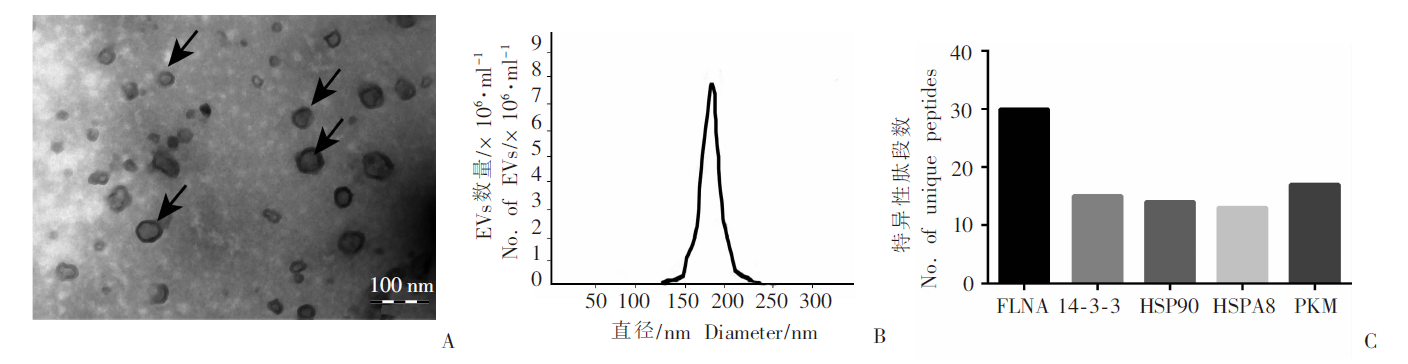
Table 1
Identified huamn proteins from EVs in culture supernatant of protoscoleces of E. granulosus
| 编号 No. | 登录号 Protein accession No. | 蛋白名称 Protein name | 基因名 Gene name | 肽段覆盖率/% Coverage rate/% | 相对分子质量 Mr | 特异性肽段数 Unique pep count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P35443 | 凝血酶敏感蛋白-4 Thrombospondin-4 | THBS4 | 16.6 | 105 870 | 9 |
| 2 | P13591 | 神经细胞黏附分子-1 Neural cell adhesion molecule-1 | NCAM1 | 19.0 | 94 573 | 14 |
| 3 | P00742 | 凝血因子 X Coagulation factor X | F10 | 12.1 | 54 731 | 6 |
| 4 | Q14515 | 半胱氨酸酸性蛋白-1 SPARC-like protein-1 | SPARCL1 | 6.6 | 75 207 | 5 |
| 5 | Q8NBJ4 | 高尔基膜蛋白-1 Golgi membrane protein-1 | GOLM1 | 8.5 | 45 333 | 5 |
| 6 | Q06828 | 纤维蛋白 Fibromodulin | FMOD | 17.3 | 43 178 | 5 |
| 7 | Q99983 | 骨调节蛋白 Osteomodulin | OMD | 3.6 | 49 492 | 2 |
| 8 | O60462 | 骨调节蛋白-2 Neuropilin-2 | NRP2 | 25.9 | 104 830 | 19 |
| 10 | Q7LGC8 | 碳水化合物磺基转移酶-3 Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 3 | CHST3 | 15.7 | 54 705 | 7 |
| 11 | P16070 | CD44抗原 CD44 antigen | CD44 | 2.7 | 81 537 | 2 |
| 12 | P23471 | 受体型酪氨酸蛋白磷酸酶 Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase zeta | PTPRZ1 | 3.9 | 254 580 | 8 |
| 13 | P13639 | 伸长因子-2 Elongation factor-2 | EEF2 | 10.7 | 95 337 | 8 |
| 14 | Q6YHK3 | CD109抗原 CD109 antigen | CD109 | 4.4 | 161 690 | 5 |
| 15 | Q9UBP4 | Dickkopf相关蛋白-3 Dickkopf-related protein-3 | DKK3 | 18.9 | 38 390 | 4 |
| 16 | Q92783 | 信号转导分子-1 Signal transducing adapter molecule-1 | STAM | 3.1 | 59 179 | 2 |
| 17 | P16112 | 聚集素核心蛋白 Aggrecan core protein | ACAN | 3.9 | 261 330 | 9 |
| 18 | O14786 | 神经肽-1 Neuropilin-1 | NRP1 | 18.4 | 103 130 | 12 |
| 19 | P23470 | 受体型酪氨酸蛋白磷酸酶γ Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase gamma | PTPRG | 6.2 | 162000 | 7 |
| 20 | P20908 | 胶原α-1(V)链 Collagen alpha-1(V) chain | COL5A1 | 8.3 | 183 560 | 12 |
| [1] | Wei YH, Hu Yuan, Cao JP. Advances in genetic polymorphism of Echinococcus granulosus[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2019,37(4):481-485. (in Chinese) |
| ( 魏玉环, 胡媛, 曹建平. 细粒棘球绦虫基因多态性的研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2019,37(4):481-485.) | |
| [2] |
Heidari Z, Sharbatkhori M, Mobedi I, et al. Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus granulosus in canines in North-Khorasan Province, Northeastern Iran, identified using morphology and genetic characterization of mitochondrial DNA[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2019,12(1):606.
pmid: 31881913 |
| [3] | Agudelo Higuita NI, Brunetti E, McCloskey C. Cystic echinococcosis[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2016,54(3):518-523. |
| [4] | Jenkins DJ, Romig T, Thompson RCA. Emergence/re-emergence of Echinococcus spp.: a global update[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2005,35(11/12):1205-1219. |
| [5] |
Hill AF. Extracellular vesicles and neurodegenerative diseases[J]. J Neurosci, 2019,39(47):9269-9273.
pmid: 31748282 |
| [6] | Shen H, Liu CY, Zhao YM. Research status and prospect of extracellular vesicles of parasites[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018,36(4):413-417. (in Chinese) |
| ( 沈辉, 刘春英, 赵玉敏. 寄生虫细胞外囊泡的研究现状及展望[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018,36(4):413-417.) | |
| [7] |
Akbar N, Azzimato V, Choudhury RP, et al. Extracellular vesicles in metabolic disease[J]. Diabetologia, 2019,62(12):2179-2187.
pmid: 31690986 |
| [8] | Siles-Lucas M, Sánchez-Ovejero C, González-Sánchez M, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes derived from fertile sheep hydatid cysts[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2017,236:22-33. |
| [9] | Monteiro KM, de Carvalho MO, Zaha A, et al. Proteomic analysis of the Echinococcus granulosus metacestode during infection of its intermediate host[J]. Proteomics, 2010,10(10):1985-1999. |
| [10] | Marcilla A, Trelis M, Cortés A, et al. Extracellular vesicles from parasitic helminths contain specific excretory/secretory proteins and are internalized in intestinal host cells[J]. PLoS One, 2012,7(9):e45974. |
| [11] | Hidalgo C, García MP, Stoore C, et al. Proteomics analysis of Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex stage[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2016,218:43-45. |
| [12] | Aziz A, Zhang WB, Li J, et al. Proteomic characterisation of Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst fluid from sheep, cattle and humans[J]. J Proteom, 2011,74(9):1560-1572. |
| [13] | Deolindo P, Evans-Osses I, Ramirez MI. Microvesicles and exosomes as vehicles between protozoan and host cell communication[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2013,41(1):252-257. |
| [14] | Fan XB, He X, Pan WQ. Advances in the study of exocrine bodies from parasites and their functions[J]. Chin Trop Med, 2017,17(12):1267-1272. (in Chinese) |
| ( 范晓斌, 何兴, 潘卫庆. 寄生虫来源的外泌体及其功能研究进展[J]. 中国热带医学, 2017,17(12):1267-1272.) | |
| [15] | Cheng WJ, Jiang H, Dong HF, et al. Progress of exocrine and other extracellular vesicles in the study of parasites and parasitic diseases[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2019,31(5):555-559. (in Chinese) |
| ( 程文君, 蒋洪, 董惠芬, 等. 外泌体及其他细胞外囊泡在寄生虫与寄生虫病研究中的进展[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2019,31(5):555-559.) | |
| [16] | Frotscher M. Dual role of Cajal-Retzius cells and reelin in cortical development[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 1997,290(2):315-322. |
| [17] |
Balaphas A, Meyer J, Sadoul K, et al. Platelets and platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in liver physiology and disease[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2019,3(7):855-866.
doi: 10.1002/hep4.1358 pmid: 31304449 |
| [18] |
Conigliaro P, Triggianese P, Ballanti E, et al. Complement, infection, and autoimmunity[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2019,31(5):532-541.
doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000633 pmid: 31192812 |
| [19] |
Marshall S, Kelly PH, Singh BK, et al. Extracellular release of virulence factor major surface protease via exosomes in Leishmania infantum promastigotes[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2018,11(1):355.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2937-y |
| [20] | Zhou X, Wang W, Cui F, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst fluid from patients: isolation, characterization and evaluation of immunomodulatory functions on T cells[J]. Int J Parasitol, 2019,49(13/14):1029-1037. |
| [1] | LU Junxia, XU Junying, ZHAO Bin, WANG Qianwen, LI Wenhua, GENG Yuqing, HOU Jun, WU Xiangwei, CHEN Xueling. Echinococcus granulosus infection induces macrophages to express CD73 and A2AR to suppress inflammatory response [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(5): 559-566. |
| [2] | WU Xiaoying, HU Yuan, CAO Jianping. Preparation of Echinococcus granulosus peptide embedded in chitosan quaternary ammonium salt nanoparticles [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 300-305. |
| [3] | LI Benfu, WANG Zhengqing, XU Qian, ZI Jinrong, YAN Xinliu, PENG Jia, LI Jianxiong, CAI Xuan, WU Fangwei, YANG Yaming. Sequence analysis of mitochondrial co1 and nd1 genes in Echinococcus granulosus in Yunnan Province [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(3): 306-311. |
| [4] | GUO Gang, REN Yuan, JIAO Hongjie, WU Juan, GUO Baoping, QI Wenjing, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao. Effect of intraperitoneal inoculation with Echinococcus microcysts on the infection and pathogenicity of E. multilocularis in mouse liver [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 156-162. |
| [5] | HAO Huinan, CHENG Yongkang, ZHANG Ru, HAN Lulu, SONG Yanyan, LONG Shaorong, LIU Ruodan, ZHANG Xi, WANG Zhongquan, CUI Jing. Immunoproteomic analysis on the soluble antigens of Trichinella spiralis newborn larvae [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(2): 176-182. |
| [6] | JIAO Hongjie, QI Wenjing, GUO Gang, BAO Jianling, WU Chuanchuan, SONG Chuanlong, LI Jun, ZHANG Wenbao, YAN Mei. Polarization effect of Echinococcus granulosus antigen B on the mouse macrophage RAW264.7 [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2023, 41(1): 23-28. |
| [7] | WU De-fang, FU Yong, REN Bin, ZHANG Yao-gang, XU Xiao-lei, PANG Ming-quan, FAN Hai-ning. Genetic diversity and differentiation time of human isolates of Echinococcus granulosus and E. multilocularis from Qinghai [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(5): 610-615. |
| [8] | QIAO Shi-yuan, ZHOU Xue, LIU Cheng-hao, JIANG Hui-jiao, BU Yuan-yuan, CHEN Xue-ling, WU Xiang-wei. Effect of albendazole-loaded vesicles on the vitality of protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(3): 324-329. |
| [9] | SUN Ye-ting, JIANG Nan, JIANG Yan-yan, LI Teng, JIANG Xiao-feng, CAO Jian-ping, SHEN Yu-juan. Study on the polarization of MDSC stimulated by Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex-derived exosomes in vitro [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2022, 40(2): 175-180. |
| [10] | HONG Yang, LIN Jiao-jiao. Research progress on proteomics in Schistosoma japonicum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(6): 725-730. |
| [11] | ZHOU Wen-zheng, SUN Jun-gang, ZHAO Xi-bin, CAO Li. Therapeutic effect of intensity modulated radiation therapy on secondary femur infection with Echinococcus granulosus in rats [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 443-448. |
| [12] | XU Feng-yan, YANG Yong, GAO Xin, LIU Xiao-lei, WANG Yang, LIU Ming-yuan, ZHANG Yuan-yuan, BAI Xue. Advances in research on parasite proteomics of extracellular vesicles [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(4): 526-532. |
| [13] | TIAN Meng-xiao, ZANG Xiao-yan, GUO Gang, QI Wen-jing, GUO Bao-ping, REN Yuan, LI Jun, ZHANG Wen-bao. Expression and activity assay of serine protease in Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 233-239. |
| [14] | SHI Shan-mei, CHEN Jun-hu. Research progress on the structure and function of RIFIN protein of Plasmodium falciparum [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2021, 39(2): 249-255. |
| [15] | FAN Jun-jie, HAN Xiu-min, Nur Fazleen Binti Idris, LI Kai, TAN Qing-qing, CAO Wen-qiao, LI Xiang, LIAO Peng, YE Bin. Bioinformatics characteristics and immunoreactivity of protein kinase A of Echinococcus granulosus [J]. CHINESE JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY AND PARASITIC DISEASES, 2020, 38(6): 682-687. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||