

中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 194-203.doi: 10.12140/j.issn.1000-7423.2022.02.010
收稿日期:2021-09-22
修回日期:2021-11-18
出版日期:2022-04-30
发布日期:2022-04-12
通讯作者:
董文鸽
作者简介:孙佳宁(1996-),女,硕士研究生,从事病原生物学研究。E-mail: 954343981@qq.com
基金资助:
SUN Jia-ning( ), CHEN Ting, DONG Wen-ge*(
), CHEN Ting, DONG Wen-ge*( )
)
Received:2021-09-22
Revised:2021-11-18
Online:2022-04-30
Published:2022-04-12
Contact:
DONG Wen-ge
Supported by:摘要:
目的 对缺齿甲胁虱线粒体基因组序列进行测定与分析,了解甲胁虱属线粒体基因组的结构特征和变异情况。 方法 在大理苍山世界地质公园捕获大绒鼠,全捕法采集大绒鼠体表吸虱,鉴定后选取缺齿甲胁虱用组织DNA提取试剂盒提取单只缺齿甲胁虱DNA。用通用引物扩增缺齿甲胁虱的rrnS和rrnL基因的短片段序列,测序后在短片段序列的保守区设计特异引物,PCR扩增包含rrnS和rrnL基因的全长或近乎全长的微环染色体,微环染色体组装成功后在其保守区设计一对微环染色体编码区特异性引物,PCR扩增出全部微环的编码区。扩增产物纯化后进行高通量测序法测序。利用Geneious、tRNAscan、CodonW、BLAST等生物信息学工具分析其线粒体基因结构特征与变异情况。 结果 共获得缺齿甲胁虱优质序列读数6 812 606 bp。组装后共找到节肢动物线粒体基因组常见基因24个,包括7个蛋白质编码基因(PCG)、15个tRNA基因和2个rRNA基因。缺齿甲胁虱线粒体基因组裂化为8个微环染色体(GenBank登录号:MW835203~MW835210),这些基因不均匀地分布在微环染色体上,每个微环染色体编码区包含1~4个基因,至少有1个PCG或rRNA基因。编码区的AT含量为61.0%。除cox2基因以TTG为起始密码子,其余PCG均以ATN为起始密码子,以典型的TAA和TAG为终止密码子。密码子AUU使用频率最高(RSCU:1.53)。15个tRNA基因的二级结构均为典型的三叶草结构,存在31处错配,主要为G-U错配。rrnS和M-L1(tag)-rrnL-V微环染色体获得了全部非编码区,存在2种串联重复序列模块,相似度达88.0%~90.0%,在编码区5′端上游的非编码区存在一处AT富集区(50 bp,64.0% A&T),在编码区3′端下游存在一处GC富集区(42 bp,85.7% G&C)。其余6个微环染色体仅获得部分非编码区,相似度达86.5%~88.5%。比较缺齿甲胁虱,克氏甲胁虱和红姬甲胁虱线粒体基因组发现:3种甲胁虱的线粒体基因组均裂化;E-cob-S1(tct)-S2(tga)、I-cox1、K-nad4和rrnS等4个微环的基因组成以及基因排序完全相同;缺齿甲胁虱的H-nad5-F-T微环,在其他2种甲胁虱没有发现;trnT移位频繁,分布在3种甲胁虱不同的微环上;缺齿甲胁虱trnS1(tct)二级结构为典型的三叶草结构,而其他2种甲胁虱trnS1(tct)缺少D臂。 结论 缺齿甲胁虱的24个基因不均匀地分布于8个微环染色体上,每个微环染色体上均含有1个编码区和1个非编码区。缺齿甲胁虱的24个基因虽AT含量较高,tRNA碱基错配次数较多,缺齿甲胁虱trnS1(tct)为典型的三叶草结构。甲胁虱属线粒体基因组的结构有差异,缺齿甲胁虱线粒体基因组结构的特殊性可能与线粒体基因组的裂化有关。
中图分类号:
孙佳宁, 陈婷, 董文鸽. 缺齿甲胁虱线粒体基因组测序与分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(2): 194-203.
SUN Jia-ning, CHEN Ting, DONG Wen-ge. Sequencing and analysis of the mitochondrial genome of Hoplopleura edentula[J]. Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases, 2022, 40(2): 194-203.
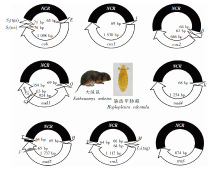
图1
大绒鼠体表缺齿甲胁虱裂化线粒体基因组 NCR:非编码区;S2(tga):丝氨酸转运RNA(反密码子UGA);S1(tct):丝氨酸转运RNA(反密码子UCU);cob:细胞色素b脱辅基酶;cox1:细胞色素C氧化酶亚基;nad1:NADH脱氢酶亚基1;rrnS:核糖体小亚基;rrnL:核糖体大亚基;E:谷氨酸转运RNA;I:异亮氨酸转运RNA;D:天冬氨酸转运RNA;G:甘氨酸转运RNA;Q:谷氨酰胺转运RNA;K:赖氨酸转运RNA;F:苯丙氨酸转运RNA;H:组氨酸转运RNA;V:缬氨酸转运RNA;M:蛋氨酸转运RNA;T:苏氨酸转运RNA;L1(tag):亮氨酸转运RNA(反密码子UAG)。
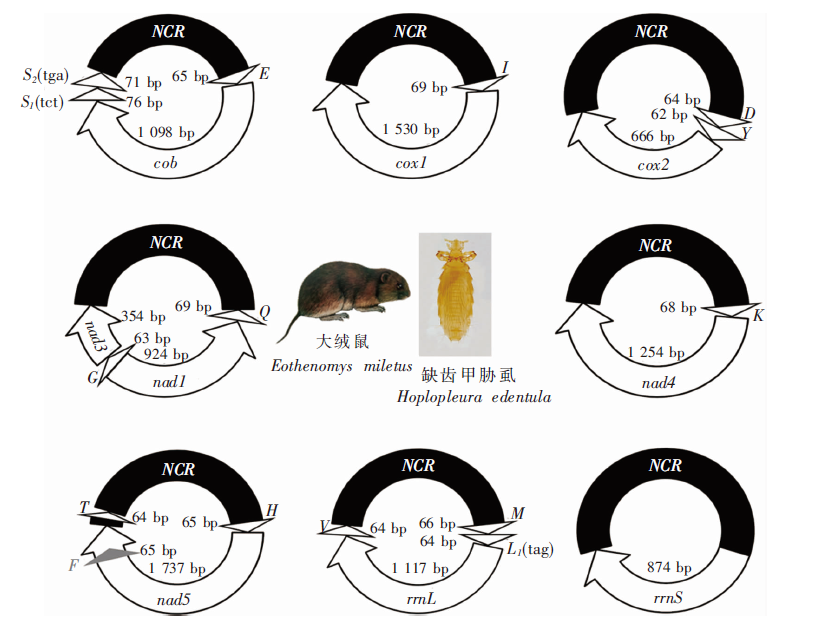
表1
大绒鼠体表缺齿甲胁虱微环染色体编码区大小
| 微环染色体 Minichromosome | 编码区大小/bp Size of coding region/bp | 序列读数/bp No. sequence read/bp |
|---|---|---|
| E-cob-S1(tct)-S2(tga) | 1 303 | 456 433 |
| I-cox1 | 1 599 | 206 917 |
| D-Y-cox2 | 791 | 822 133 |
| Q-nad1-G-nad3 | 1 446 | 712 883 |
| K-nad4 | 1 322 | 960 072 |
| H-nad5-F-T | 1 889 | 441 440 |
| M-L1(tag)-rrnL-V | 1 311 | 1 681 291 |
| rrnS | 874 | 1 290 852 |
| 合计Total | 10 535 | 6 572 021 |
表2
3种甲胁虱线粒体基因组结构的比较结果
| 特征 Feature | 缺齿甲胁虱 H. edentula | 克氏甲胁虱 H. kitti | 红姬甲胁虱 H. akanezumi |
|---|---|---|---|
| 微环染色体组成Composition of minichromosome | - | atp8-atp6-N | atp8-atp6-N |
| E-cob-S1(tct)-S2(tga) | E-cob-S1(tct)-S2(tga) | E-cob-S1(tct)-S2(tga) | |
| I-cox1 | I-cox1 | I-cox1 | |
| D-Y-cox2 | D-Y-cox2- 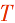 | D-Y-cox2 | |
| - | R-nad4L-P-cox3-A | R-nad4L-P-cox3-A- 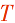 | |
| Q-nad1-G-nad3 | Q-nad1-G-nad3 | - | |
| - | nad2 | nad2 | |
| K-nad4 | K-nad4 | K-nad4 | |
H-nad5-F- 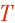 | - | - | |
| - | C-nad6-W-L2(taa) | C-nad6-W-L2(taa) | |
| M-L1(tag)-rrnL-V | M-L1(tag)-rrnL-V | 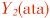 -rrnL-V -rrnL-V | |
| rrnS | rrnS | rrnS | |
| 微环染色 体数No. minichromosome | 8 | 11 | 11 |
| 基因数No. gene | 24 | 34 | 28 |
表3
大绒鼠体表缺齿甲胁虱线粒体基因组的核苷酸组成
| 基因序列 Gene sequence | 长度/bp Length/bp | 占比/% Proportion/% | AT偏倚值 AT-skew | GC偏倚值 GC-skew | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | T | G | C | A + T | ||||
| 编码区Coding region | 10 545 | 26.9 | 34.1 | 20.7 | 18.3 | 61.0 | -0.118 | 0.062 |
| 蛋白质编码基因 Protein-coding gene | 7 563 | 25.0 | 34.8 | 19.1 | 21.1 | 59.8 | -0.164 | -0.050 |
| 密码子第1位点 The 1st codon position | 2 521 | 28.2 | 28.4 | 25.6 | 17.8 | 56.6 | -0.004 | 0.180 |
| 密码子第2位点 The 2nd codon position | 2 521 | 16.9 | 43.5 | 18.0 | 21.6 | 60.4 | -0.440 | -0.091 |
| 密码子第3位点 The 3rd codon position | 2 521 | 26.8 | 35.7 | 19.5 | 18.0 | 62.5 | -0.426 | 0.040 |
| tRNAs | 995 | 31.5 | 32.8 | 19.6 | 16.1 | 64.3 | -0.020 | 0.098 |
| rrnL | 1 117 | 31.5 | 32.2 | 21.1 | 15.2 | 63.7 | -0.011 | 0.163 |
| rrnS | 874 | 31.2 | 31.5 | 19.2 | 18.1 | 62.7 | -0.005 | 0.029 |
表4
缺齿甲胁虱线粒体基因组蛋白质编码基因密码子使用情况
| 氨基酸 Amino acid | 密码子 Codon | 使用次数 No. use | 相对同义密码子使用频率 Relative synonymous codon usage | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 密码子 Codon | 使用次数 No. use | 相对同义密码子使用频率 Relative synonymous codon usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丙氨酸 Ala | GCU | 39 | 1.65 | 脯氨酸 Pro | CCU | 63 | 2.23 |
| GCC | 64 | 1.01 | CCC | 23 | 0.81 | ||
| GCA | 32 | 0.83 | CCA | 16 | 0.57 | ||
| GCG | 20 | 0.52 | CCG | 11 | 0.39 | ||
| 半胱氨酸 Cys | UGU | 21 | 1.08 | 谷氨酰胺 Gln | CAA | 15 | 0.77 |
| UGC | 18 | 0.92 | CAG | 24 | 1.23 | ||
| 天冬氨酸 Asp | GAU | 31 | 1.24 | 精氨酸 Arg | CGU | 6 | 0.27 |
| GAC | 19 | 0.76 | CGC | 10 | 0.45 | ||
| 谷氨酸 Glu | GAA | 41 | 1.32 | CGA | 10 | 0.45 | |
| GAG | 21 | 0.68 | CGG | 12 | 0.54 | ||
| 苯丙氨酸 Phe | UUU | 129 | 1.50 | AGA | 43 | 1.93 | |
| UUC | 43 | 0.50 | AGG | 53 | 2.37 | ||
| 甘氨酸 Gly | GGU | 24 | 0.57 | 丝氨酸 Ser | UCU | 77 | 2.23 |
| GGC | 25 | 0.60 | UCC | 40 | 1.16 | ||
| GGA | 50 | 1.20 | UCA | 40 | 1.16 | ||
| GGG | 68 | 1.63 | UCG | 12 | 0.35 | ||
| 组氨酸 His | CAU | 24 | 0.92 | AGU | 21 | 0.61 | |
| CAC | 28 | 1.08 | AGC | 17 | 0.49 | ||
| 异亮氨酸 Ile | AUU | 137 | 1.53 | 苏氨酸 Thr | ACU | 46 | 1.72 |
| AUC | 38 | 0.43 | ACC | 26 | 0.97 | ||
| AUA | 93 | 1.04 | ACA | 30 | 1.12 | ||
| 赖氨酸 Lys | AAA | 25 | 0.82 | ACG | 5 | 0.19 | |
| AAG | 36 | 1.18 | 缬氨酸 Val | GUU | 75 | 1.42 | |
| 亮氨酸 Leu | UUA | 124 | 1.97 | GUC | 32 | 0.60 | |
| UUG | 46 | 0.73 | GUA | 65 | 1.23 | ||
| CUU | 91 | 1.45 | GUG | 40 | 0.75 | ||
| CUC | 32 | 0.51 | 色氨酸 Trp | UGG | 32 | 1.00 | |
| CUA | 41 | 0.65 | UGA | 45 | 2.60 | ||
| CUG | 43 | 0.68 | 酪氨酸 Tyr | UAU | 46 | 1.12 | |
| 蛋氨酸 Met | AUG | 68 | 1.00 | UAC | 36 | 0.88 | |
| 天冬酰胺 Asn | AAU | 45 | 1.25 | 终止密码子* Stop codon* | UAA | 6 | 0.35 |
| AAC | 27 | 0.75 | UAG | 1 | 0.06 |
| [1] | Durden LA,, Musser GG. The sucking lice (Insecta, Anoplura) of the world: a taxonomic checklist with records of mammalian hosts and geographical distributions[J]. Bull Am Mus Nat Hist, 1994, 218: 1-90. |
| [2] | Chin TH. Taxonomy and fauna of sucking lice (Anoplura) in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1999: 44-45. (in Chinese) |
| (金大雄. 中国吸虱的分类与检索[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999: 44-45.) | |
| [3] | Luo ZX,, Chen W,, Gao W. Fauna sinica[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000: 449-451. (in Chinese) |
| (罗泽珣,, 陈卫,, 高武. 中国动物志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 449-451.) | |
| [4] | Zhu WL,, Jia T,, Lian X, et al. Seasonal variations of maximum metabolic rate in Eothenomys miletusin Hengduan mountains region[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2010, 30(5): 1133-1139. (in Chinese) |
| (朱万龙,, 贾婷,, 练硝, 等. 横断山脉大绒鼠最大代谢率的季节性差异[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(5): 1133-1139.) | |
| [5] | Guo M,, Dong XQ. Development situation of the plague foci Apodemus chevrieri and Eothenomys miletus in northwest Yunnan Province[J]. Chin J Control of Endem Dis, 2008, 23(1): 27-31. (in Chinese) |
| (郭牧,, 董兴齐. 滇西北齐氏姬鼠、大绒鼠鼠疫疫源地的发展概况[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2008, 23(1): 27-31.) | |
| [6] | Dong WG,, Guo XG,, Men XY, et al. Ectoparasites of Eothenomys miletus in the focus of plague in northwest Yunnan[J]. Sichuan J Zool, 2009, 28(5): 683-690. |
| [7] | Peng PY,, Guo XG,, Song WY, et al. Investigation of ectoparasites on body surface of Eothenomys miletus in some places of Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Agric Sci, 2015, 43(2): 75-79. (in Chinese) |
| (彭培英,, 郭宪国,, 宋文宇, 等. 贵州省部分地区大绒鼠体表寄生虫调查[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2015, 43(2): 75-79.) | |
| [8] | Zhang YZ,, Zhang HL,, Mi ZQ, et al. Monitoring of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Yunnan Province, China, 2005[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2008, 19(2): 148-150. (in Chinese) |
| (张云智,, 张海林,, 米竹青, 等. 2005年云南省肾综合征出血热监测研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2008, 19(2): 148-150.) | |
| [9] |
Boore JL. Animal mitochondrial genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 1999, 27(8): 1767-1780.
pmid: 10101183 |
| [10] |
Cameron SL. Insect mitochondrial genomics: implications for evolution and phylogeny[J]. Annu Rev Entomol, 2014, 59(1): 95-117.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-011613-162007 |
| [11] |
Jiang H,, Barker SC,, Shao R. Substantial variation in the extent of mitochondrial genome fragmentation among blood-sucking lice of mammals[J]. Genome Biol Evol, 2013, 5(7): 1298-1308.
doi: 10.1093/gbe/evt094 |
| [12] |
Song SD,, Barker SC,, Shao R. Variation in mitochondrial minichromosome composition between blood-sucking lice of the genus Haematopinus that infest horses and pigs[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2014, 7: 144.
doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-144 |
| [13] |
Shao R,, Kirkness EF,, Barker SC. The single mitochondrial chromosome typical of animals has evolved into 18 minichromosomes in the human body louse, Pediculus humanus[J]. Genome Res, 2009, 19(5): 904-912.
doi: 10.1101/gr.083188.108 |
| [14] |
Shao R,, Zhu XQ,, Barker SC, et al. Evolution of extensively fragmented mitochondrial genomes in the lice of humans[J]. Genome Biol Evol, 2012, 4(11): 1088-1101.
doi: 10.1093/gbe/evs088 |
| [15] |
Dong WG,, Song S,, Guo XG, et al. Fragmented mitochondrial genomes are present in both major clades of the blood-sucking lice(Suborder Anoplura): evidence from two Hoplopleura rodent lice (family Hoplopleuridae)[J]. BMC Genom, 2014, 15(1): 1-13.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1 |
| [16] |
Dong WG,, Song S,, Jin DC, et al. Fragmented mitochondrial genomes of the rat lice, Polyplax asiatica and Polyplax spinulosa: intra-genus variation in fragmentation pattern and a possible link between the extent of fragmentation and the length of life cycle[J]. BMC Genom, 2014, 15: 44.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-44 |
| [17] |
Shao R,, Li H,, Barker SC, et al. The mitochondrial genome of the guanaco louse, Microthoracius praelongiceps: insights into the ancestral mitochondrial karyotype of sucking lice (Anoplura, Insecta)[J]. Genome Biol Evol, 2017, 9(2): 431-445.
doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx007 |
| [18] |
Fu YT,, Dong Y,, Wang W, et al. Fragmented mitochondrial genomes evolved in opposite directions between closely related macaque louse Pedicinus obtusus and colobus louse Pedicinus badii[J]. Genomics, 2020, 112(6): 4924-4933.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.09.005 |
| [19] |
Herd KE,, Barker SC,, Shao R. The mitochondrial genome of the chimpanzee louse, Pediculus schaeffi: insights into the process of mitochondrial genome fragmentation in the blood-sucking lice of great apes[J]. BMC Genom, 2015, 16: 661.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1843-3 |
| [20] |
Kearse M,, Moir R,, Wilson A, et al. Geneious basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(12): 1647-1649.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199 |
| [21] |
Laslett D,, Canbäck B. ARWEN: a program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences[J]. Bioinformatics, 2008, 24(2): 172-175.
pmid: 18033792 |
| [22] |
Lowe TM,, Eddy SR. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 1997, 25(5): 955-964.
pmid: 9023104 |
| [23] |
Altschul SF,, Madden TL,, Schäffer AA, et al. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 1997, 25(17): 3389-3402.
doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389 pmid: 9254694 |
| [24] |
Gish W,, States DJ. Identification of protein coding regions by database similarity search[J]. Nat Genet, 1993, 3(3): 266-272.
pmid: 8485583 |
| [25] |
Puigbò P,, Bravo IG,, Garcia-Vallve S. CAIcal: a combined set of tools to assess codon usage adaptation[J]. Biol Direct, 2008, 3: 38.
doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-3-38 pmid: 18796141 |
| [26] |
Perna NT,, Kocher TD. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes[J]. J Mol Evol, 1995, 41(3): 353-358.
pmid: 7563121 |
| [27] |
Shao R,, Barker SC,, Li H, et al. Fragmented mitochondrial genomes in two suborders of parasitic lice of eutherian mammals (Anoplura and Rhynchophthirina, Insecta)[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 17389.
doi: 10.1038/srep17389 |
| [28] |
Song F,, Li H,, Liu GH, et al. Mitochondrial genome fragmentation unites the parasitic lice of eutherian mammals[J]. Syst Biol, 2019, 68(3): 430-440.
doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syy062 pmid: 30239978 |
| [29] |
Shi GH,, Cui ZX,, Hui M, et al. The complete mitochondrial genomes of Umalia orientalis and Lyreidus brevifrons: the phylogenetic position of the family Raninidae within Brachyuran crabs[J]. Mar Genom, 2015, 21: 53-61.
doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2015.02.002 |
| [30] | Chen XX,, Yuan ZW,, Yuan XW, et al. Advances in mitochondrial genome complete sequence structure of leafhopper[J]. Genom Appl Biol, 2020, 39(6): 2565-2577. (in Chinese) |
| (陈晓晓,, 袁周伟,, 苑晓伟, 等. 叶蝉线粒体基因组全序列结构研究进展[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2020, 39(6): 2565-2577.) | |
| [31] | Kolesnikov AA,, Gerasimov ES. Diversity of mitochondrial genome organization[J]. Biochemistry(Mosc), 2012, 77(13): 1424-1435. |
| [32] | Li JJ. Research on phylogeny and acoustic signal evolution of Ensifera based on complete mitochondrial genome[D]. Chang-chun:Northeast Normal University, 2018: 13-28. (in Chinese) |
| (李君健. 基于线粒体基因组的螽亚目昆虫系统发育与鸣声进化研究[D]. 长春:东北师范大学, 2018: 13-28.) | |
| [33] | Ou J. Complete mitochondrial genomes sequences of six stored grain beetles[D]. Xi’an:Shanxi Normal University, 2015: 15-57. (in Chinese) |
| (欧静. 六种储粮甲虫线粒体基因组测定及分析[D]. 西安:陕西师范大学, 2015: 15-57.) | |
| [34] | Zhou F. Complete mitochondrial genomes sequences of four locust and analyzed the phylogeny of Orthoptera[D]. Xi’an:Shanxi Normal University, 2015: 27-50. (in Chinese) |
| (周飞. 四种蝗虫线粒体基因组测定及直翅目系统发生分析[D]. 西安:陕西师范大学, 2015: 27-50.) | |
| [35] | Wu YM. Genome sequencing and transcriptome analysis of chemosensory genes of two meloids[D]. Guiyang:Guizhou University, 2018: 36-41. (in Chinese) |
| (吴渊明. 两种芫菁的全基因组测序和化学感受器转录组基因的鉴定与分析[D]. 贵阳:贵州大学, 2018: 36-41.) | |
| [36] | Xia LY,, Sun WW,, Cui M, et al. Sequencing and analysis of mitochondrial genome of Lasioderma serricorne[J]. Tob Sci Technol, 2020, 53(12): 1-8. (in Chinese) |
| (夏丽媛,, 孙为伟,, 崔淼, 等. 烟草甲线粒体基因组序列测定与分析[J]. 烟草科技, 2020, 53(12): 1-8.) | |
| [37] | Liu J,, Bian X. Characteristics of the Orthoptera mitogenome and its application[J]. J Guangxi Norm Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2021, 39(1): 17-28. (in Chinese) |
| 刘静,, 边迅. 直翅目昆虫线粒体基因组的特征及应用[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 39(1): 17-28.) | |
| [38] |
Yan D,, Tang Y,, Hu M, et al. The mitochondrial genome of Frankliniella intonsa: insights into the evolutionof mitochondrial genomes at lower taxonomic levels in Thysanoptera[J]. Genomics, 2014, 104(4): 306-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2014.08.003 |
| [39] | Chen S. Complete mitochondrial genomes sequences of six species of Spilomelinae[D]. Xi’an: Shanxi Normal University, 2017: 34-37. (in Chinese) |
| (陈汕. 六种斑野螟亚科昆虫全线粒体基因组的序列测定与分析[D]. 西安:陕西师范大学, 2017: 34-37.) | |
| [40] |
Varani G,, Mcclain WH. The G x U wobble base pair. A fundamental building block of RNA structure crucial to RNA function in diverse biological systems[J]. Embo Rep, 2000, 1(1): 18-23.
pmid: 11256617 |
| [41] | Wang XM. Structural characteristics of mitochondrial genome and preliminary phylogenetic analysis for Lepus hainanus[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2012: 3-4. (in Chinese) |
| (王晓明. 海南兔的线粒体基因组结构特征与系统演化初探[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2012: 3-4.) | |
| [42] |
Broughton RE,, Dowling TE. Length variation in mitochondrial DNA of the minnow Cyprinella spiloptera[J]. Genetics, 1994, 138(1): 179-190.
doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.1.179 pmid: 8001785 |
| [43] |
Ladoukakis ED,, Zouros E. Direct evidence for homologous recombination in mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) mitochondrial DNA[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2001, 18(7): 1168-1175.
pmid: 11420358 |
| [44] |
Okada K,, Yamazaki Y,, Yokobori S, et al. Repetitive sequences in the lamprey mitochondrial DNA control region and speciation of Lethenteron[J]. Gene, 2010, 465(1/2): 45-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2010.06.009 |
| [45] |
Ray DA,, Densmore LD. Repetitive sequences in the crocodilian mitochondrial control region: Poly-A sequences and heteroplasmic tandem repeats[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2003, 20(6): 1006-1013.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg117 |
| [46] |
Shi W,, Kong XY,, Wang ZM, et al. Pause-melting misalignment: a novel model for the birth and motif indel of tandem repeats in the mitochondrial genome[J]. BMC Genom, 2013, 14: 103.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-103 |
| [1] | 张苍林,周红宁,聂仁华,刘慧,王剑,李春富,杨亚明*. 云南省边境地区疟原虫18S rRNA基因种类鉴定与序列分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2016, 34(3): 7-220-226. |
| [2] | 袁忠英;沈玉娟;曹建平;刘晖;陈盛霞. 牛源隐孢子虫上海分离株的巢式PCR鉴定[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2009, 27(2): 9-139. |
| [3] | 罗建勋;殷宏;刘光远;关贵全;刘志杰;刘爱红;白启;吕文顺. 我国牛羊梨形虫病病原的收集与鉴定[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2006, 24(增刊): 10-s53. |
| [4] | 郑学礼;胡孝素;杨文天;章涛;敬保迁. 新疆皮肤利什曼病病原体SSUrRNA基因克隆与序列分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2000, 18(5): 2-262. |
| [5] | 李本文,刘多,姚开泰. 重组DNA技术在寄生虫学研究中的应用[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 1990, 8(3): 223-226. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||